Experts Nutritions
Diabetes in Dogs: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Care

Understanding Diabetes in Dogs

Diabetes in Dogs: mellitus is a serious but manageable condition that affects dogs, just as it does humans. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is essential for regulating blood sugar levels, and without it, sugar accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to various health complications.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
Types of Diabetes in Dogs

There are two primary types of diabetes in dogs:
- Type 1- Diabetes (Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus) –
- The most common type in dogs, caused by the immune system attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Dogs with this type require lifelong insulin injections.
- Type 2 – Diabetes (Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus) –
- Less common in dogs but occurs when the body produces insulin but does not use it efficiently.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes in Dogs

Early detection is crucial for managing diabetes in dogs. Common signs include:
- Excessive thirst and increased urination
- Unexplained weight loss despite a good appetite
- Increased hunger or loss of appetite
- Lethargy and weakness
- Cloudy eyes or cataracts
- Frequent infections, particularly urinary tract infections
- Sweet-smelling breath (a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis in severe cases)
Causes and Risk Factors

Several factors contribute to the development of diabetes in dogs, including:
- Genetics –
- Some breeds are more prone to diabetes, including Samoyeds, Poodles, Beagles, and Dachshunds.
- Obesity –
- Overweight dogs have an increased risk due to insulin resistance.
- Pancreatitis –
- Chronic inflammation of the pancreas can lead to insulin deficiency.
- Hormonal imbalances –
- Conditions like Cushing’s disease can interfere with insulin production.
- Certain medications –
- Long-term use of steroids can contribute to diabetes.
Most At-Risk Dog Breeds and Vet-Recommended Supplements

| Breed | Risk Level | Vet-Recommended Supplements |
|---|---|---|
| Samoyed | High | Omega-3 fatty acids,
|
| Poodle | High | L-carnitine,
|
| Beagle | High | Fiber supplements,
|
| Dachshund | High | Glucosamine,
|
| Golden Retriever | Moderate | Probiotics,
|
| Labrador Retriever | Moderate | Fiber,
|
| Miniature Schnauzer | High | Alpha-lipoic acid,
|
| Yorkshire Terrier | Moderate | Biotin,
|
Diagnosis of Canine Diabetes

A veterinarian will diagnose diabetes through a combination of:
- Blood tests –
- High blood glucose levels are a key indicator.
- Urinalysis –
- The presence of glucose and ketones in urine can confirm diabetes.
- Physical examination and medical history –
- Evaluating symptoms and risk factors.
Treatment and Management

While diabetes in dogs is not curable, it can be managed effectively with the right approach:
- Insulin Therapy –
- Most diabetic dogs require daily insulin injections.
- Dietary Changes –
- A high-fiber, low-fat diet helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise –
- Helps maintain a healthy weight and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring –
- Regular glucose checks help track progress.
- Routine Veterinary Visits –
- Regular check-ups ensure proper disease management.
Potential Complications of Untreated Diabetes

If left untreated, diabetes can lead to severe complications, including:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) –
- A life-threatening condition requiring emergency treatment.
- Cataracts and blindness –
- Many diabetic dogs develop vision loss over time.
- Neuropathy –
- Weakness in the limbs due to nerve damage.
- Organ failure –
- Chronic high blood sugar can damage the liver and kidneys.
Caring for a Diabetic Dog

Managing a diabetic dog requires commitment but can result in a good quality of life. Some key care tips include:
- Stick to a consistent routine for feeding and insulin injections.
- Avoid giving sugary treats or foods high in carbohydrates.
- Monitor your dog’s weight and adjust diet as needed.
- Ensure regular physical activity but avoid sudden changes in exercise levels.
- Be aware of signs of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), such as shaking, confusion, and weakness.
Recent advancements in canine diabetes

Closing Statement

Diabetes in dogs is a manageable condition with proper treatment, diet, and veterinary care. By staying informed and maintaining a structured care plan, pet owners can help their diabetic dogs live happy and healthy lives. If you notice any symptoms of diabetes in your dog, consult a veterinarian immediately for diagnosis and management.
For more expert dog health tips, visit DogsReader or follow us on social media!
FAQs About Diabetes in Dogs

Q1: Can diabetes in dogs be cured?
A: No, diabetes in dogs is a lifelong condition, but it can be managed effectively with proper treatment, diet, and insulin therapy.
Q2: What is the life expectancy of a diabetic dog?
A: With proper care, a diabetic dog can live a normal lifespan. Regular monitoring and veterinary check-ups are key to maintaining health.
Q3: Can I manage my dog’s diabetes with diet alone?
A: No, most diabetic dogs require insulin therapy in addition to a proper diet and exercise regimen.
Q4: How often should a diabetic dog receive insulin injections?
A: Typically, dogs need insulin injections twice daily, but your vet will determine the best schedule for your pet.
Q5: What should I do if I miss my dog’s insulin dose?
A: If you miss a dose, consult your veterinarian for guidance. Never double the next dose to compensate.
Q6: Are certain dog breeds more prone to diabetes?
A: Yes, breeds such as Poodles, Beagles, Samoyeds, and Dachshunds have a higher risk of developing diabetes.
Q7: Can a diabetic dog still have treats?
A: Yes, but only healthy, vet-approved treats that do not spike blood sugar levels.
Q8: How can I tell if my dog’s blood sugar is too low?
A: Signs of low blood sugar include shaking, confusion, weakness, and seizures. If you notice these signs, provide a small amount of honey or sugar water and contact your vet immediately.
Experts Nutritions
Top Dog Training Trends: The Ultimate Guide for Every Breed and Life Stages

Introduction: The Future of Dog Training

Top Dog Training Trends: Dog training is evolving faster than ever, with new techniques emerging that cater to different breeds and life stages. In 2025, training is not just about teaching commands but enhancing mental agility, physical health, and overall well-being. This guide breaks down the latest trends by breed size and type, ensuring every dog owner has the right tools for effective training. From puppies to seniors, this is your go-to resource for modern dog training.
Training Steps for All Dog Life Stages

Puppy Training (8 Weeks – 6 Months)
- House Training & Crate Training – Use a consistent schedule for potty breaks.
- Basic Commands – Teach ‘sit,’ ‘stay,’ and ‘come‘ using positive reinforcement.
- Leash Training – Introduce a harness and practice loose-leash walking.
- Socialization – Expose puppies to different people, environments, and sounds.
- Bite Inhibition – Teach controlled play by redirecting biting behavior.
Adult Dog Training (6 Months – 7 Years)

- Advanced Obedience – Reinforce commands with distractions.
- Agility Training – Engage dogs in obstacle courses to improve fitness.
- Impulse Control – Use ‘wait’ and ‘leave it’ commands to manage energy levels.
- Off-Leash Reliability – Practice recall training in a secure environment.
- Behavioral Corrections – Address issues like jumping, excessive barking, or chewing.
Senior Dog Training (7+ Years)

- Gentle Exercises – Short walks and swimming maintain joint health.
- Mental Stimulation – Puzzle toys and new tricks keep cognitive function sharp.
- Reinforced Basic Commands – Maintain training consistency for safety.
- Pain Awareness – Modify training if arthritis or stiffness is present.
- Slow-Paced Training Sessions – Adjust sessions to accommodate reduced energy levels.
Small Dog Breeds Training (Chihuahua, Pomeranian, Dachshund, Maltese.)

Time Limits & Training Focus:
- Puppies (8-16 weeks): 5–10 minutes per session, 3-4 times a day.
- Adults (1-7 years): 10–15 minutes per session, 2-3 times a day.
- Seniors (8+ years): 5–10 minutes per session, focusing on mental stimulation.
Trending Training Methods:
- Tiny Trick Training – Teaching fun tricks like spinning and paw shakes boosts confidence.
- Balance & Core Strength Exercises – Helps prevent injury in delicate breeds.
- Adaptive Smart Toy Training – AI-powered interactive toys reinforce learning.
- Positive Socialization Training – Helps small breeds overcome fearfulness.
Essential Diet Table:
| Nutrient | Small Dogs (Daily) |
|---|---|
| Water | ½ – 1 cup |
| Protein | 25-30% of diet |
| Carbohydrates | 40-50% of diet |
| Healthy Fats | 10-15% of diet |
| Vitamins & Supplements | Omega-3, glucosamine,
|
Medium Dog Breeds Training (Border Collie, Cocker Spaniel, Beagle, Bulldog.)

Time Limits & Training Focus:
- Puppies: 10–15 minutes per session, 3 times a day.
- Adults: 15–20 minutes per session, 2 times a day.
- Seniors: 10–15 minutes per session, focusing on gentle movement and scent work.
Trending Training Methods:
- Precision Recall Training – Uses AI tracking collars for off-leash safety.
- Agility & Focus Courses – Enhances coordination and impulse control.
- Scent-Based Mental Stimulation – Tapping into natural tracking instincts.
- Clicker Training 2.0 – A refined version using VR cues for faster responses.
Essential Diet Table:
| Nutrient | Medium Dogs (Daily) |
| Water | 1 – 2 cups |
| Protein | 22-27% of diet |
| Carbohydrates | 35-45% of diet |
| Healthy Fats | 10-12% of diet |
| Vitamins & Supplements | Chondroitin, antioxidants,
|
Large Dog Breeds Training (Labrador, Golden Retriever, German Shepherd, Doberman, etc.)

Time Limits & Training Focus:
- Puppies: 15–20 minutes per session, 2-3 times a day.
- Adults: 20–30 minutes per session, 2 times a day.
- Seniors: 10–20 minutes per session, focusing on mobility and cognitive function.
Trending Training Methods:
- Strength & Endurance Training – Using resistance bands for muscle health.
- Canine Cognitive Tasks – Teaching problem-solving for mental sharpness.
- Advanced Obedience & Guard Training – Combining voice and hand signals.
- Emotional Support & Therapy Dog Prep – Developing calmness and empathy.
Essential Diet Table:
| Nutrient | Large/Giant Dogs (Daily) |
| Water | 2 – 4 cups |
| Protein | 20-25% of diet |
| Carbohydrates | 30-40% of diet |
| Healthy Fats | 8-10% of diet |
| Vitamins & Supplements | Glucosamine, chondroitin,
|
Giant Dog Breeds Training (Great Dane, Mastiff, Saint Bernard, Newfoundland, etc.)

Time Limits & Training Focus:
- Puppies: 10–15 minutes per session, 2 times a day.
- Adults: 15–25 minutes per session, 1-2 times a day.
- Seniors: 10–15 minutes per session, focusing on joint-friendly activities.
Trending Training Methods:
- Low-Impact Strength Training – Prevents joint strain while maintaining muscle.
- Confidence Building – Overcoming fear in large but gentle breeds.
- Hydrotherapy Training – Improves endurance and reduces injury risk.
- Slow-Paced Agility – Modified agility courses for body control.
Essential Diet Table:
| Nutrient | Working/Hound Dogs (Daily) |
| Water | 2 – 3 cups |
| Protein | 26-32% of diet |
| Carbohydrates | 30-35% of diet |
| Healthy Fats | 12-15% of diet |
| Vitamins & Supplements | Omega-3, glucosamine,
|
Working Dog Breeds Training (Husky, Malinois, Rottweiler, Boxer, etc.)

Time Limits & Training Focus:
- Puppies: 15–20 minutes per session, 3 times a day.
- Adults: 30–40 minutes per session, 2 times a day.
- Seniors: 20–30 minutes per session, focusing on controlled movement.
Trending Training Methods:
- Tactical Obedience – Military-grade training for control and reliability.
- Energy Regulation Workouts – Managing hyperactivity through structured play.
- Advanced Tracking & Detection – Strengthening problem-solving skills.
- Cross-Sport Training – Combining agility, obedience, and endurance activities.
Essential Diet Table:
| Nutrient | Large/Giant Dogs (Daily) |
| Water | 2 – 4 cups |
| Protein | 20-25% of diet |
| Carbohydrates | 30-40% of diet |
| Healthy Fats | 8-10% of diet |
| Vitamins & Supplements | Glucosamine, chondroitin, probiotics |
Hound Dog Breeds Training (Beagle, Bloodhound, Greyhound, Afghan Hound, etc.)

Time Limits & Training Focus:
- Puppies: 10–15 minutes per session, 3 times a day.
- Adults: 15–25 minutes per session, 2 times a day.
- Seniors: 10–15 minutes per session, focusing on mental stimulation.
Trending Training Methods:
- Trail & Urban Tracking – Developing scent work in various environments.
- Long-Distance Recall Training – Enhancing recall reliability over long distances.
-
Cardio Endurance Runs – Structured running plans for stamina.
-
Scented Puzzle Training – Using scented toys to reinforce problem-solving.
Essential Diet Table:
| Nutrient | Large/Giant Dogs (Daily) |
| Water | 2 – 4 cups |
| Protein | 20-25% of diet |
| Carbohydrates | 30-40% of diet |
| Healthy Fats | 8-10% of diet |
| Vitamins & Supplements | Glucosamine, chondroitin, probiotics |
Terrier Dog Breeds Training (Jack Russell, Bull Terrier, Airedale, Scottish Terrier, etc.)

Time Limits & Training Focus:
- Puppies: 5–10 minutes per session, 3-4 times a day.
-
Adults: 15 minutes per session, 2-3 times a day.
-
Seniors: 10 minutes per session, focusing on softer activities.
Trending Training Methods:
- Structured Digging Areas – Providing controlled outlets for natural digging instincts.
-
Quick Reflex Agility – Enhancing fast movements and reactions.
-
Tug-of-War Regulation – Teaching bite inhibition and control.
-
Puzzle & Reward Training – Increasing focus through interactive problem-solving.
Essential Diet Table:
| Nutrient | Working/Hound Dogs (Daily) |
| Water | 2 – 3 cups |
| Protein | 26-32% of diet |
| Carbohydrates | 30-35% of diet |
| Healthy Fats | 12-15% of diet |
| Vitamins & Supplements | Omega-3, glucosamine,
|
Closing Statement: Elevate Your Dog’s Training
Training in 2025 is not just about commands—it’s about enhancing your dog’s life through modern, breed-specific methods. Whether you have a tiny Chihuahua or a massive Great Dane, these trends will boost intelligence, obedience, and overall happiness. Start incorporating these techniques today and watch your dog thrive like never before!
🚀 Stay updated with DogsReader for more expert training guides and the latest canine trends! 🐶
Top Dog Training Trends: The Ultimate Guide – Detailed FAQs
1. What are the key dog training trends
Modern training focuses on:
Breed-specific techniques (Agility for Border Collies, scent work for Beagles)
Tech integration (AI collars, VR clicker training, smart toys)
Mental stimulation (Puzzle games, cognitive tasks)
Lifestyle adaptation (Senior-friendly exercises, puppy socialization)
2. How long should training sessions be for puppies vs. adult dogs?
| Life Stage | Session Length | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Puppies (8 wks-6 mos) | 5-15 mins | 3-4x daily |
| Adults (6 mos-7 yrs) | 15-30 mins | 2x daily |
| Seniors (7+ yrs) | 5-15 mins | 1-2x daily |
Pro Tip: Keep sessions short to avoid frustration!
3. What’s the best way to train small breeds like Chihuahuas?
- Tiny Trick Training: Teach spins, paw shakes.
- Socialization: Prevent “small dog syndrome” with positive exposure.
- Core Exercises: Use balance pads to avoid injuries.
- Smart Toys: Interactive games reinforce commands.
Avoid: Overloading with complex tasks—small breeds have shorter attention spans.
4. How do I train a high–energy breed (e.g., Border Collie, Labrador)?
- Agility Courses (Weaves, jumps, tunnels)
- Precision Recall (Use GPS collars for off-leash safety)
- Scent Work (Hide treats or use tracking games)
- Advanced Obedience (Combine voice + hand signals)
Warning: Undertrained herding/working breeds may develop destructive habits.
5. What’s unique about training giant breeds (e.g., Mastiffs, Great Danes)?
- Strength Training: Resistance bands build muscle safely.
- Hydrotherapy: Low-impact swimming for joint health.
- Cognitive Challenges (Puzzle feeders, “find it” games)
- Early Leash Manners (Prevent pulling while they’re still manageable).
Diet Note: Giant breeds need glucosamine for joint support.
6. Can senior dogs learn new tricks?
✅ Yes! Focus on:
- Low-impact tricks (High-five, gentle spins)
- Puzzle toys (Slows cognitive decline)
- Reinforced basics (Ensures safety as mobility declines)
- Adjust for Pain: Use soft flooring and shorter sessions.
7. What tech tools are revolutionizing dog training?
- AI Collars (Track location & monitor behavior)
- VR Clickers (Visual + sound cues for faster learning)
- Interactive Smart Toys (Dispense treats for correct responses)
- Agility Apps (Design custom courses at home)
8. How does diet affect training success?
| Breed Size | Key Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Small | High protein (25-30%), omega-3s |
| Medium | Moderate protein (22-27%), antioxidants |
| Large/Giant | Joint supplements (glucosamine), lean proteins |
Tip: Feed 1-2 hours before training for optimal energy.
9. What are common training mistakes to avoid?
Inconsistency (Mixed commands confuse dogs)
Punishment-based methods (Increases anxiety)
Skipping socialization (Leads to fear/aggression)
Overtraining (Causes burnout—watch for fatigue signs)
10. Where can I find professional trainers using these trends?
- Certified trainers (Look for CCPDT or IAABC members)
- Breed-specific clubs (AKC affiliates for agility/herding)
- Online courses (Fenzi Dog Sports Academy, Udemy)
- Local vet recommendations (For behavior issues)
Experts Nutritions
Dog Diseases Around the World: Causes, Prevention & Solutions

Introduction

Dog Diseases Around the World: Dogs, like humans, are susceptible to various diseases, which can vary based on geographic location, climate, and prevalent pathogens. This article explores the most common diseases in puppies, adult, and senior dogs by country, their causes, prevention methods, common misconceptions, and why these illnesses are widespread among dogs.
Major Reasons for Dog Diseases
Several factors contribute to the prevalence of diseases in dogs worldwide. These include:
- Climate and Environmental Conditions:
- Regions with warm, humid climates foster mosquito populations, leading to diseases such as heartworm. Cold regions see higher cases of arthritis due to joint stress.
- Stray Dog Population:
- Countries with high numbers of stray dogs, such as India, experience frequent outbreaks of rabies and distemper due to lack of vaccination.
- Tick and Flea Infestation:
- Lyme disease is prevalent in regions with a high tick population, like the United States and Canada.
- Waterborne Contaminants:
- Leptospirosis thrives in areas with stagnant water, affecting dogs that drink from puddles or contaminated water sources.
- Urbanization and Socialization:
- High-density dog populations in cities contribute to the rapid spread of kennel cough and canine influenza.
- Poor Nutrition and Genetics:
- Some diseases, such as hypothyroidism and arthritis, are influenced by genetic predisposition and diet quality.
- Lack of Vaccination and Preventive Care:
- Many dog owners neglect regular veterinary check-ups, leading to higher disease susceptibility.
Major Diseases in Dogs by Country
United States
Canine Parvovirus (Parvo)
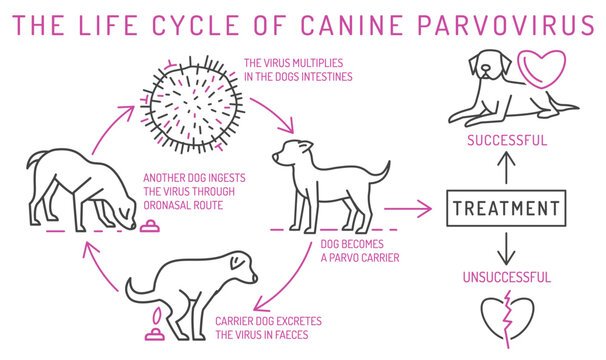
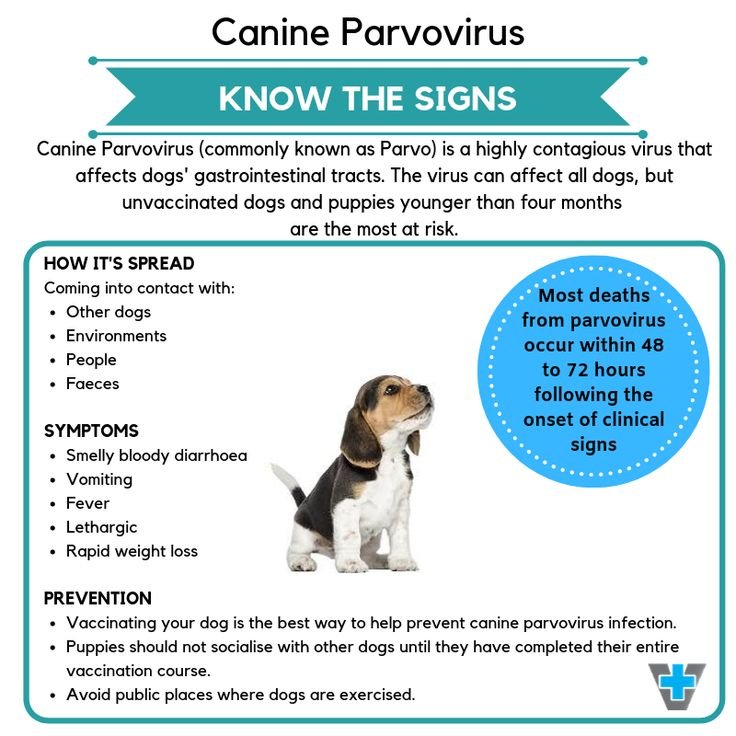
-
- Cause: Highly contagious viral infection.
- Prevention: Vaccination, sanitation, and isolation of infected dogs.
- Assumptions: Some believe only puppies get Parvo, but adult dogs can also be affected.
- Why common? Due to high dog population density and frequent interactions.
Lyme Disease

-
- Cause: Bacterial infection transmitted by ticks.
- Prevention: Tick control, regular veterinary check-ups, and vaccination.
- Assumptions: Many think city dogs are not at risk, but urban green spaces harbor ticks.
- Why common? High deer population contributes to tick prevalence.
United Kingdom
Leptospirosis

-
- Cause: Bacteria found in contaminated water.
- Prevention: Annual vaccinations, avoiding stagnant water sources.
- Assumptions: Misconception that only farm dogs are at risk.
- Why common? Rainy climate increases exposure to infected water.
Kennel Cough

-
- Cause: Viral and bacterial infection spread in dog communities.
- Prevention: Vaccination and avoiding exposure to infected dogs.
- Assumptions: Some believe it only affects dogs in kennels.
- Why common? High population of socialized pets and dog daycare centers.
Australia
Heatstroke
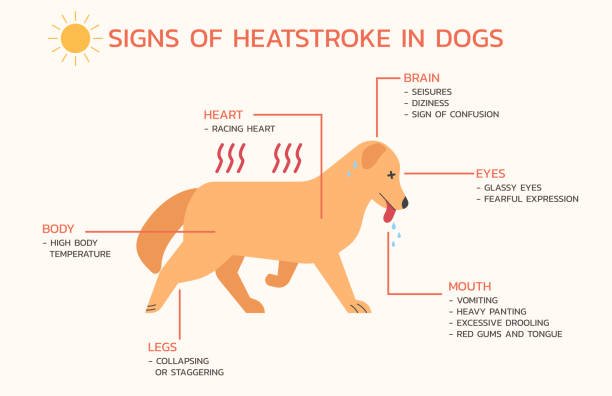

-
- Cause: High temperatures and humidity.
- Prevention: Hydration, avoiding excessive exercise in heat.
- Assumptions: Thick-coated dogs are the only ones at risk.
- Why common? Hot climate and lack of awareness about overheating in dogs.
Heartworm Disease

-
- Cause: Mosquito-borne parasite.
- Prevention: Monthly preventive medication.
- Assumptions: Dogs who stay indoors are safe.
- Why common? Warm climate with high mosquito activity.
India
Rabies
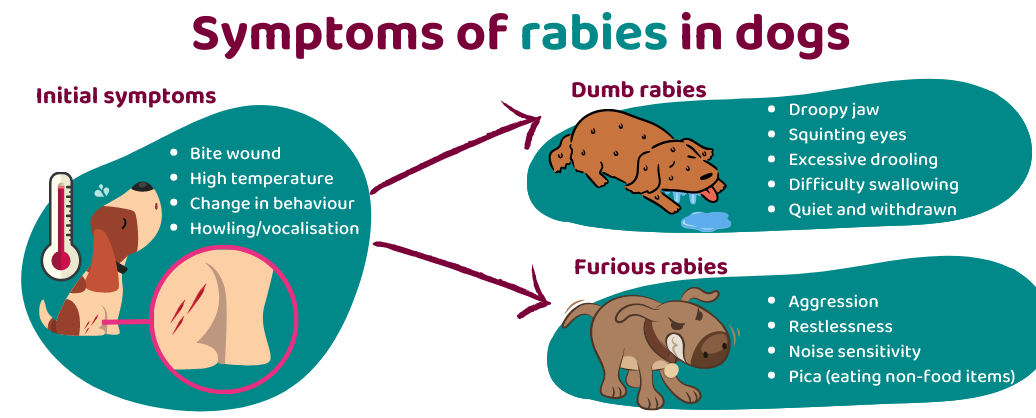
-
- Cause: Virus transmitted through bites of infected animals.
- Prevention: Vaccination and controlling stray dog populations.
- Assumptions: Only stray dogs get rabies.
- Why common? Large stray dog population and insufficient vaccination coverage.
Distemper

-
- Cause: Viral infection.
- Prevention: Vaccination and avoiding exposure to infected dogs.
- Assumptions: Many believe home dogs cannot get distemper.
- Why common? High density of stray and unvaccinated dogs.
Canada
Hypothyroidism

-
- Cause: Immune system attacking thyroid gland.
- Prevention: Regular check-ups and balanced diet.
- Assumptions: Only old dogs are affected.
- Why common? Genetic predisposition in certain breeds.
Arthritis
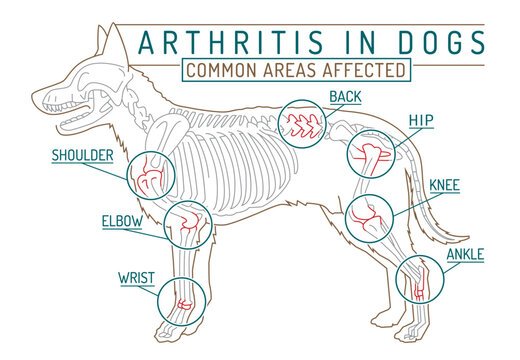
-
- Cause: Joint inflammation due to aging or injury.
- Prevention: Weight management and joint supplements.
- Assumptions: Only large breeds develop arthritis.
- Why common? Cold climate exacerbates joint pain.
Legal Arrangements for Dog Health Problems by Country
| Country | Legal Regulations & Arrangements |
|---|---|
| United States | Mandatory rabies vaccination, animal welfare acts, breed-specific laws |
| United Kingdom | Compulsory microchipping, Dangerous Dogs Act, strict breeding regulations |
| Australia | Strict quarantine laws, mandatory vaccinations, animal cruelty laws |
| India | Animal Birth Control (ABC) program, stray dog sterilization laws, rabies eradication campaigns |
| Canada | Provincial animal welfare laws, required vaccinations, and dog licensing |
Vaccinations by Country and Age Group
| Country | Puppies (Under 1 Year) | Adult Dogs (1-7 Years) | Senior Dogs (7+ Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Rabies, Parvo, Distemper, Hepatitis, Bordetella | Rabies booster, Leptospirosis, Lyme, Bordetella | Rabies booster, Leptospirosis, Flu shot |
| United Kingdom | Leptospirosis, Kennel Cough, Parvo, Distemper | Leptospirosis booster, Rabies, Kennel Cough | Rabies booster, Leptospirosis, Flu shot |
| Australia | Parvo, Distemper, Hepatitis, Rabies (imported dogs) | Rabies booster, Leptospirosis, Parainfluenza | Rabies booster, Leptospirosis, Flu shot |
| India | Rabies, Parvo, Distemper, Leptospirosis | Rabies booster, Distemper booster, Leptospirosis | Rabies booster, Distemper, Leptospirosis |
| Canada | Rabies, Parvo, Distemper, Lyme, Bordetella | Rabies booster, Leptospirosis, Lyme, Bordetella | Rabies booster, Leptospirosis, Flu shot |
Recommended Supplements for Dogs by Age Group
| Supplement Name | Benefits | Puppies (Under 1 Year) | Adult Dogs (1-7 Years) | Senior Dogs (7+ Years) |
| Glucosamine & Chondroitin | Joint support & arthritis prevention | No | Occasionally | Yes |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Skin, coat health, and anti-inflammatory | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Probiotics | Gut health & digestion | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Multivitamins | General health maintenance | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| CBD Oil or Hemp Oil
|
Pain relief & anxiety reduction | No | Occasionally | Yes |
Closing Statement
Understanding the major diseases that affect dogs in different countries helps pet owners take preventive measures. By ensuring proper vaccinations, using preventive treatments, and providing necessary supplements, dog owners can significantly improve their pet’s health and longevity. Always consult a veterinarian for personalized care and treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the most common diseases in dogs worldwide?
The most common diseases in dogs globally include rabies, parvovirus, distemper, kennel cough, leptospirosis, Lyme disease, and heartworm. The prevalence of these diseases varies by country due to climate, stray dog populations, and veterinary care standards.
Q2: How often should I vaccinate my dog?
Puppies should receive core vaccinations starting at 6-8 weeks, with booster shots given at intervals recommended by veterinarians. Adult dogs need booster shots annually or every three years, depending on the vaccine. Senior dogs may require additional vaccinations for flu and leptospirosis.
Q3: Are certain breeds more prone to specific diseases?
Yes, some breeds are genetically predisposed to certain conditions. For example:
-
Large breeds ( German Shepherds) are prone to hip dysplasia.
-
Small breeds (Chihuahuas) may suffer from dental diseases.
-
Labrador Retrievers are more likely to develop obesity and arthritis.
Q4: How can I protect my dog from tick-borne diseases like Lyme disease?
Regular tick prevention using medications, collars, and spot-on treatments can reduce the risk of Lyme disease. Checking your dog for ticks after outdoor activities and maintaining a clean environment also help prevent tick infestations.
Q5: What is the best way to prevent heartworm disease in dogs?
Heartworm prevention involves monthly medications (oral or topical) and annual heartworm testing. Mosquito control in and around your home can also reduce the risk.
Q6: What are the symptoms of rabies in dogs?
Rabies symptoms include excessive drooling, aggression, difficulty swallowing, paralysis, and sudden behavioral changes. It is a fatal disease, so vaccination is crucial.
Q7: Can dogs get colds or flu like humans?
Yes, dogs can contract canine influenza (dog flu) and kennel cough, both of which cause coughing, sneezing, and fever. Vaccinations and limiting contact with infected dogs help prevent these illnesses.
Q8: How do I know if my senior dog has arthritis?
Symptoms of arthritis in dogs include stiffness, limping, difficulty standing up, reluctance to jump, and behavioral changes due to pain. Joint supplements like glucosamine and omega-3 fatty acids can help manage symptoms.
Q9: Are natural supplements effective for preventing dog diseases?
Some natural supplements, such as probiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, and glucosamine, support overall health and can prevent conditions like arthritis and digestive issues. However, they should be used alongside veterinary care, not as replacements for medical treatments.
Q10: What should I do if my dog shows symptoms of a serious disease?
If your dog exhibits symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, difficulty breathing, or persistent coughing, seek immediate veterinary attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can save your pet’s life.
Experts Nutritions
Dog Grooming: Keeping, Dog Clean & Healthy
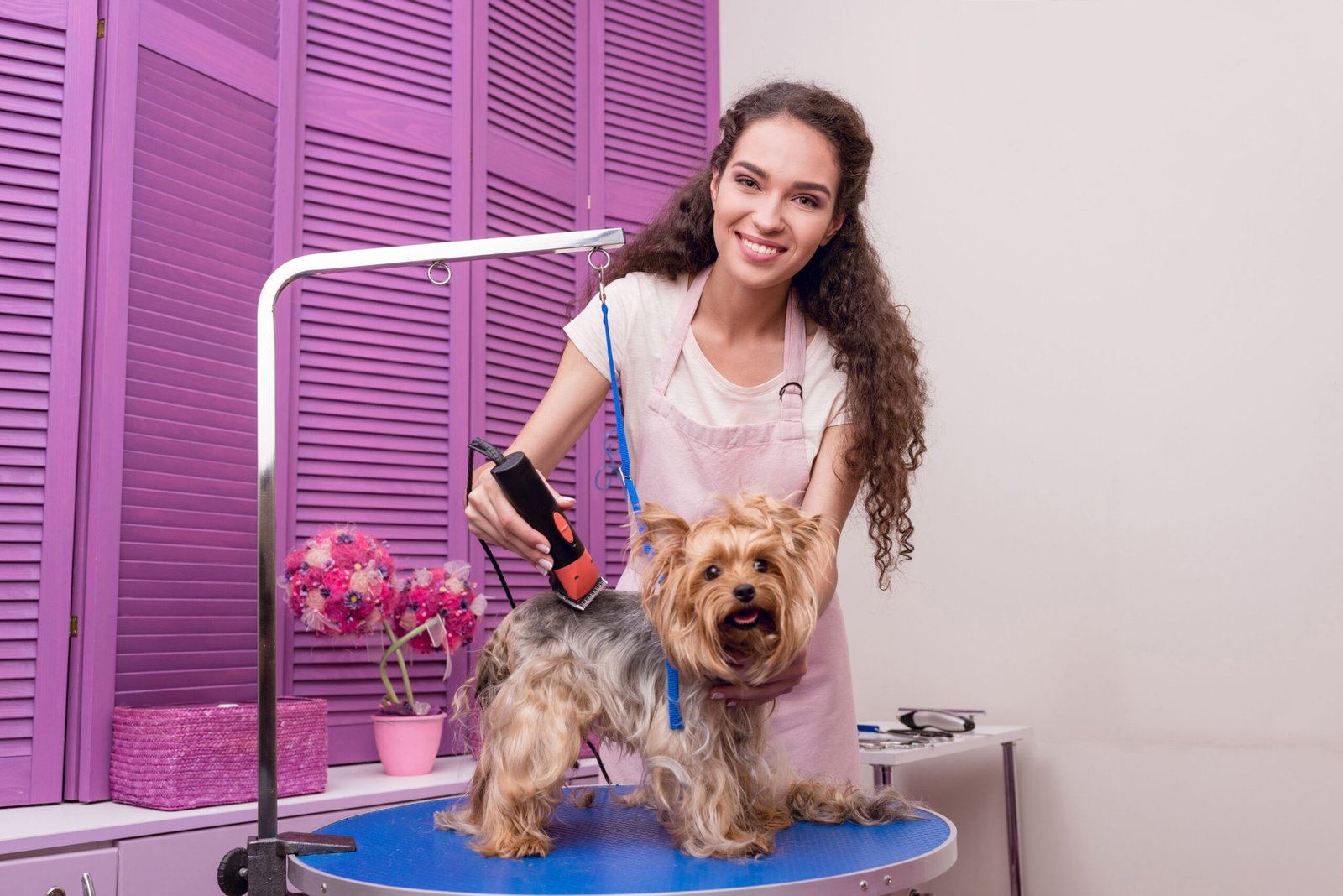

Introduction

Dog grooming is an essential part of responsible pet ownership. Regular grooming not only keeps your dog looking neat but also contributes to their overall health and well-being. From brushing to bathing and nail trimming, each aspect of grooming plays a vital role in your dog’s comfort and hygiene.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
Why Grooming is Important for Dogs

Regular grooming helps in:
- Maintaining a healthy coat and skin
- Preventing matting and tangling
- Reducing shedding and allergens
- Detecting early signs of infections, parasites, or skin conditions
- Strengthening the bond between the dog and owner
Grooming also improves a dog’s mood, as a clean and well-maintained coat can prevent discomfort and irritation.
Most Important Age Phases for Puppy Grooming

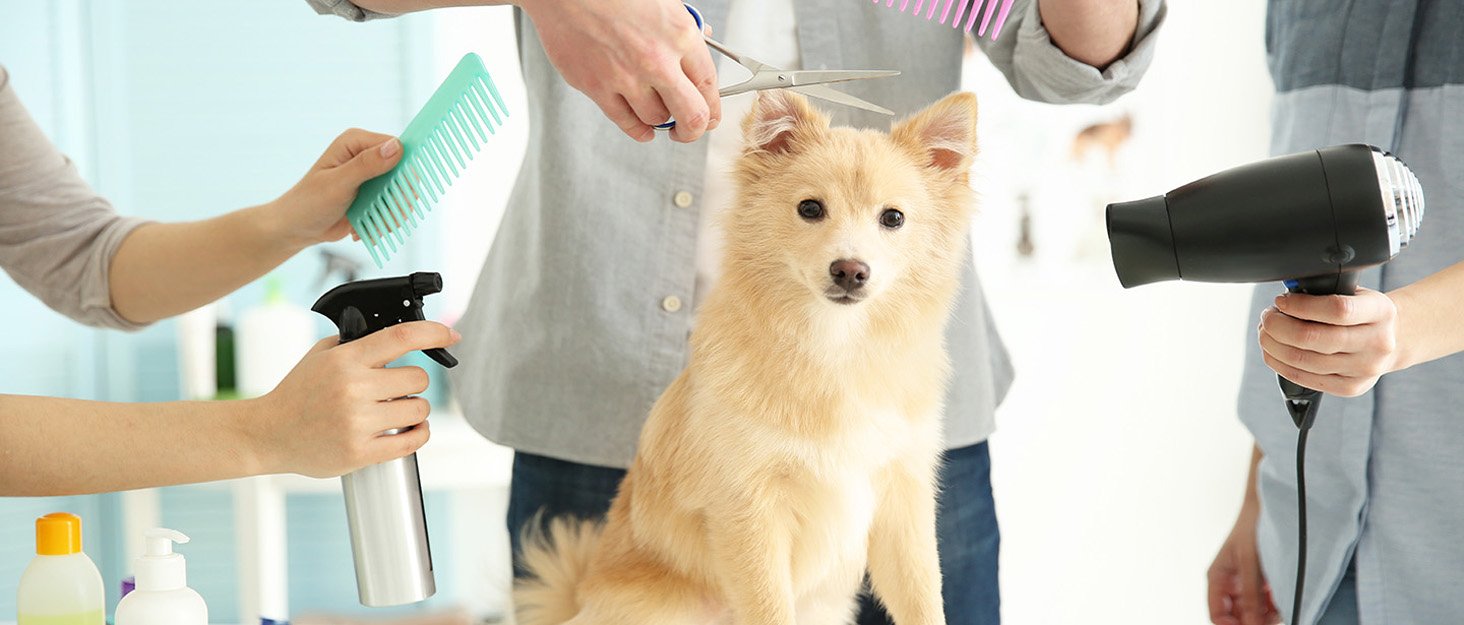
Grooming should start early to help puppies get comfortable with the process. Key age phases include:
3-4 Weeks Old:
- Start handling the puppy gently to get them used to touch.
- Introduce a soft brush to familiarize them with brushing.
6-8 Weeks Old:
- First bath using a mild puppy shampoo.
- Introduce nail trimming and ear cleaning in a gentle manner.
10-12 Weeks Old:
- First professional grooming session (for breeds needing frequent trims).
- Continue regular brushing and bathing routines.
- Begin using a toothbrush and dog-friendly toothpaste.
4-6 Months Old:
- Establish a regular grooming schedule, including coat brushing, bathing, and nail trimming.
- Accustom the puppy to clippers or trimming tools if necessary.
6+ Months Old:
- Full grooming routine should be in place.
- Regular visits to a professional groomer (if needed) to maintain coat health.
- Continue reinforcing positive grooming experiences.
Starting grooming early and maintaining consistency helps ensure a stress-free experience for both the puppy and the owner.
Most core and additional puppy vaccinations (such as DHPP, Rabies, and Leptospirosis) are not available for purchase on Amazon or other general online stores due to strict regulations. These vaccines must be administered by a licensed veterinarian because:
General Puppy Vaccination Schedule

| Age | Vaccine |
|---|---|
| 6-8 Weeks |
|
| 10-12 Weeks |
|
| 12-16 Weeks |
|
| 14-16 Weeks |
|
| 6 Months |
|
| 12-16 Months |
|
Essential Vaccinations by Country

| Country | Core Vaccines | Additional Vaccines |
| USA | DHPP, Rabies |
|
| UK | DHPP, Rabies |
|
| Canada | DHPP, Rabies |
|
| Australia | C3 (Distemper, Hepatitis, Parvovirus), Rabies |
|
| India | DHPP, Rabies |
|
| Germany | DHPP, Rabies |
|
| France | DHPP, Rabies |
|
Core vaccines protect against the most severe diseases, while additional vaccines are recommended based on location, lifestyle, and risk factors.
Essential Supplements for Puppies

Proper nutrition is vital for a puppy’s development, especially during grooming stages. Here is a list of essential liquid supplements based on age and gender.
Supplements by Grooming Age

| Age | Essential Liquid Supplements |
| 3-4 Weeks | Puppy milk replacer,
|
| 6-8 Weeks | DHA for brain development,
|
| 10-12 Weeks | Omega-3 fatty acids,
|
| 4-6 Months | Joint support (glucosamine),
|
| 6+ Months | Multivitamins, skin & coat enhancers |
Supplements for Male Puppies

| Purpose | Recommended Supplements |
| Muscle Development | Protein supplements,
|
| Joint & Bone Health | Calcium,
|
| Immune System Boost | Probiotics, colostrum |
| Energy & Stamina | Omega-3,
|
| Coat & Skin Health | Fish oil, biotin |
Supplements for Female Puppies
| Purpose | Recommended Supplements |
| Bone & Joint Strength | Calcium,
|
| Hormonal Balance | Omega-3,flaxseed oil |
| Skin & Coat Health | Fish oil, biotin |
| Digestive Support | Probiotics, digestive enzymes |
| Immune Boost | Colostrum, multivitamins |
Providing the right supplements ensures proper growth and overall well-being, making grooming easier and maintaining a healthy coat and skin.
Essential Grooming Products for Puppies
| Category | Recommended Products |
| Shampoo | Mild puppy shampoo,
|
| Brush | Soft bristle brush,
|
| Nail Clippers | Small guillotine or scissor-style clippers |
| Ear Cleaner | Dog-friendly liquid ear cleaner |
| Toothbrush & Paste | Puppy toothbrush, enzymatic dog toothpaste |
| Wipes | Hypoallergenic grooming wipes for quick clean-ups |
| Towel & Dryer | Absorbent towel,
|
| Flea & Tick Prevention | Puppy-safe flea & tick spray or shampoo |
| Detangling Spray | Leave-in coat conditioner for long-haired breeds |
| Paw Balm | Moisturizing balm for dry paw pads |
Using the right grooming products ensures a safe and enjoyable experience for both the puppy and the owner.
15 Grooming Secrets from Show Dog Experts
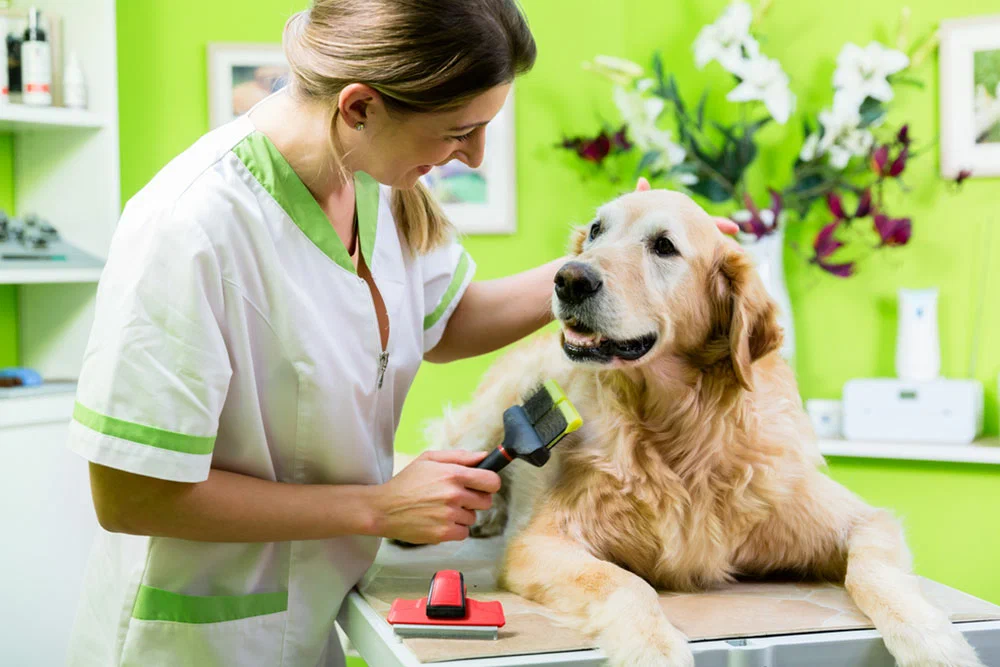

- Brush your dog daily to maintain a shiny, tangle-free coat.
- Use a high-quality shampoo suited for your dog’s coat type.
-
Condition the coat after shampooing to keep it soft and manageable.
-
Trim hair around the paws to prevent dirt buildup.
-
Use a leave-in spray to keep the coat hydrated.
-
Regularly clean your dog’s ears to prevent infections.
-
Trim nails carefully to avoid cutting the quick.
-
Use dog-specific wipes for quick touch-ups.
-
Apply paw balm to prevent cracking and dryness.
-
Keep teeth clean with dog-friendly toothpaste.
-
Brush in the direction of hair growth to avoid breakage.
-
Use a cool air dryer instead of a hot dryer to avoid skin damage.
-
Invest in high-quality grooming tools for the best results.
-
Practice positive reinforcement to make grooming a pleasant experience.
-
Maintain a consistent grooming routine for the best coat health.
Essential Dog Grooming Practices
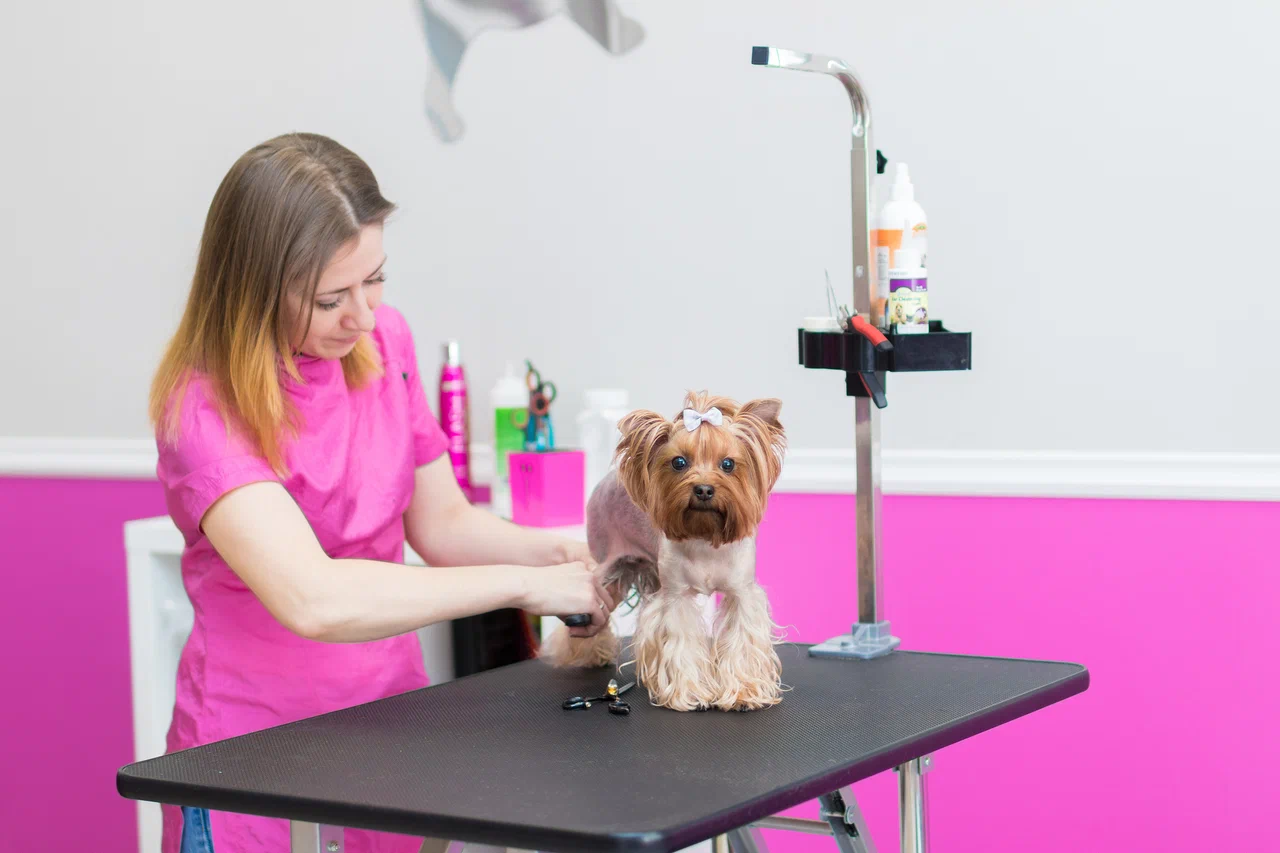

1. Brushing the Coat
Brushing is crucial for removing dirt, loose hair, and preventing tangles. The frequency and type of brush depend on the dog’s breed and coat type:
- Short-haired dogs ( Beagle, Boxer): Once a week using a bristle brush.
- Medium-haired dogs ( Golden Retriever, Border Collie): A few times a week with a slicker brush.
- Long-haired dogs ( Shih Tzu, Afghan Hound): Daily brushing with a pin brush and comb to prevent matting.
2. Bathing Your Dog
Bathing helps remove dirt, odor, and excess oils. However, excessive bathing can dry out a dog’s skin. The recommended frequency varies:
- Every 4-6 weeks for most dogs
- More frequent baths for dogs with skin conditions or allergies
Use a dog-specific shampoo to avoid skin irritation. Ensure you rinse thoroughly to prevent residue buildup.
3. Nail Trimming
Overgrown nails can cause discomfort and posture issues. Trimming should be done every 3-4 weeks using:
- Guillotine-style clippers for small to medium dogs
- Scissor-style clippers for large breeds
- Grinders for smooth and precise trimming
Avoid cutting too close to the quick (pink area inside the nail), as it can cause bleeding.
4. Ear Cleaning
Ear infections are common in dogs, especially those with floppy ears (e.g., Cocker Spaniel, Basset Hound). Clean the ears every 2-4 weeks using a vet-recommended ear cleaner and a cotton ball. Avoid inserting cotton swabs into the ear canal.
5. Dental Care
Good oral hygiene prevents gum disease and bad breath. Brush your dog’s teeth 2-3 times per week using dog-friendly toothpaste. Dental chews and professional cleanings also help maintain oral health.
6. Eye Cleaning
Some breeds ( Pugs, Bulldogs) are prone to tear staining. Wipe around the eyes daily using a soft, damp cloth or vet-approved eye wipes to prevent buildup.
Professional vs. At-Home Grooming

Some grooming tasks can be done at home, while others require professional assistance.
Professional grooming is recommended for:
- Breeds with complex coat types ( Poodles, Shih Tzus)
- Dogs that dislike being groomed
- Specific haircuts and styling needs
At-home grooming is suitable for regular maintenance and bonding time with your pet.
Dog Grooming Based on Coat Type
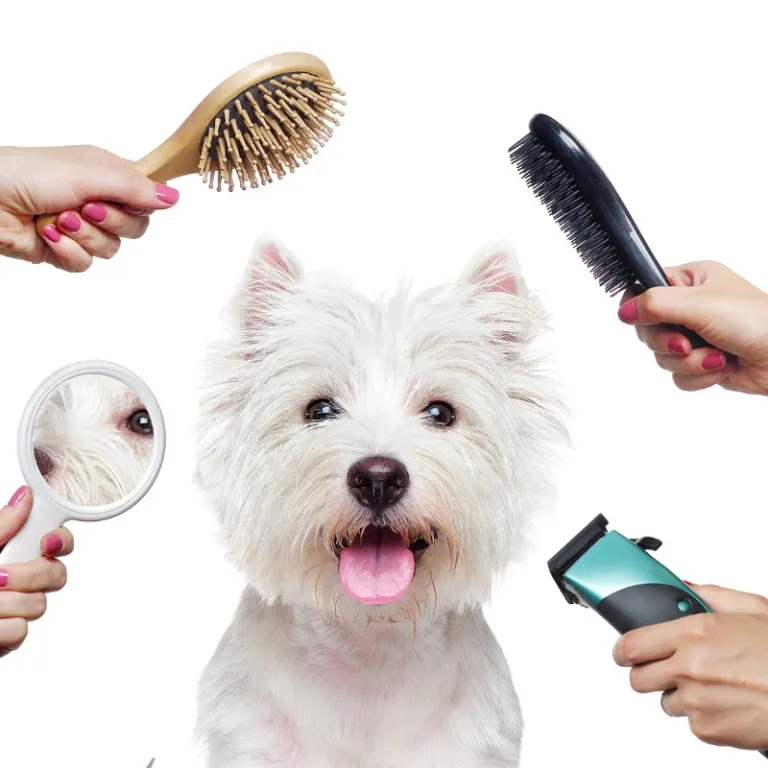

Different coat types require unique care:
1. Short-Coated Dogs
- Minimal grooming required
- Weekly brushing with a soft bristle brush
- Occasional baths
2. Double-Coated Dogs
- Heavy shedding (Siberian Husky, German Shepherd)
- Use a de-shedding tool during shedding season
- Do not shave double-coated breeds, as it affects insulation
3. Curly or Wavy-Coated Dogs
- Regular brushing to prevent matting (e.g., Poodles, Bichon Frise)
- Professional grooming every 4-6 weeks
4. Wire-Coated Dogs
- Hand-stripping may be necessary for breeds like Terriers
- Brushing weekly with a slicker brush
5. Long-Coated Dogs
- Daily brushing to prevent tangles
- Frequent trimming and baths
Common Grooming Mistakes to Avoid
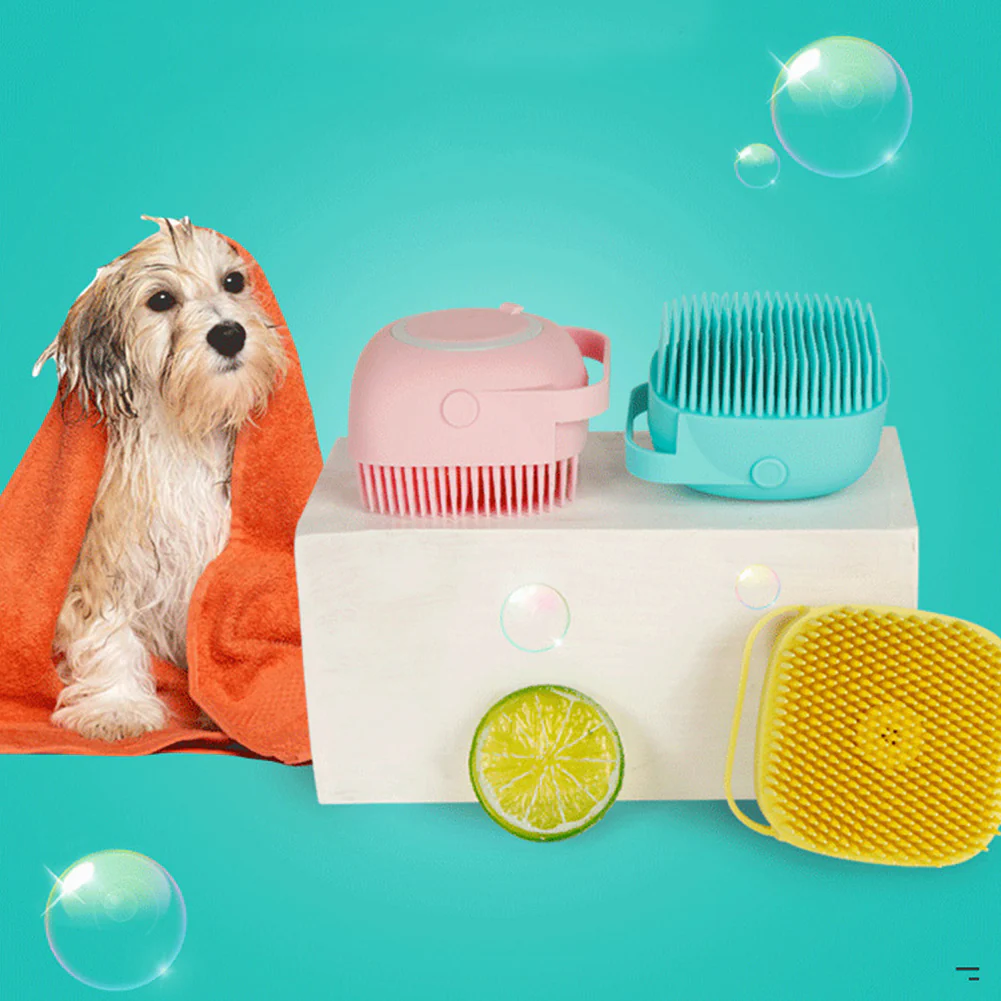

- Using human shampoo: It can disrupt a dog’s skin pH and cause irritation.
- Skipping ear checks: Leads to unnoticed infections.
- Not drying properly after a bath: Can cause fungal infections.
- Cutting nails too short: Risk of bleeding and pain.
- Over-bathing: Can lead to dry skin.
Closing Statement
Dog grooming is not just about aesthetics—it’s essential for your pet’s health and comfort. Establishing a consistent grooming routine will keep your dog happy, clean, and healthy. Whether you choose professional services or at-home care, maintaining your dog’s hygiene ensures a long and comfortable life.
For more expert dog care tips, visit DogsReader today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How often should I groom my dog?
It depends on the breed. Long-haired dogs need grooming every few days, while short-haired dogs may only need weekly brushing.
2. Can I use human shampoo on my dog?
No, human shampoos can be too harsh and disrupt your dog’s skin pH. Always use a dog-specific shampoo.
3. How do I prevent my dog’s coat from matting?
Regular brushing and using detangling sprays help prevent mats, especially in long-haired breeds.
4. When should I start grooming my puppy?
Begin handling and brushing at 3-4 weeks old, with full grooming routines starting by 10-12 weeks.
5. What if my dog is afraid of grooming?
Introduce grooming gradually, use positive reinforcement, and take breaks to make the experience pleasant.
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months agoMerle Chihuahua: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months agoMaltese: A Beloved Companion
-

 Large Breeds4 months ago
Large Breeds4 months agoSamoyeds Hypoallergenic: Closer Look at the Breed
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months agoMerle Pomeranian: A Adorable Companion
-

 Large Breeds4 months ago
Large Breeds4 months agoStandard Poodle Weight: Country Wise
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months agoYorkshire Terrier: a Big Personality
-

 MEDIUM BREEDS4 months ago
MEDIUM BREEDS4 months agoAmerican Water Spaniel Colors Chocolate In Crcols:
-

 Terrier Breeds3 months ago
Terrier Breeds3 months agoDog Breeds: by Country & Category