MEDIUM BREEDS
American Water Spaniel Colors Chocolate In Crcols:

American Water Spaniel Colors: Focus on Chocolate
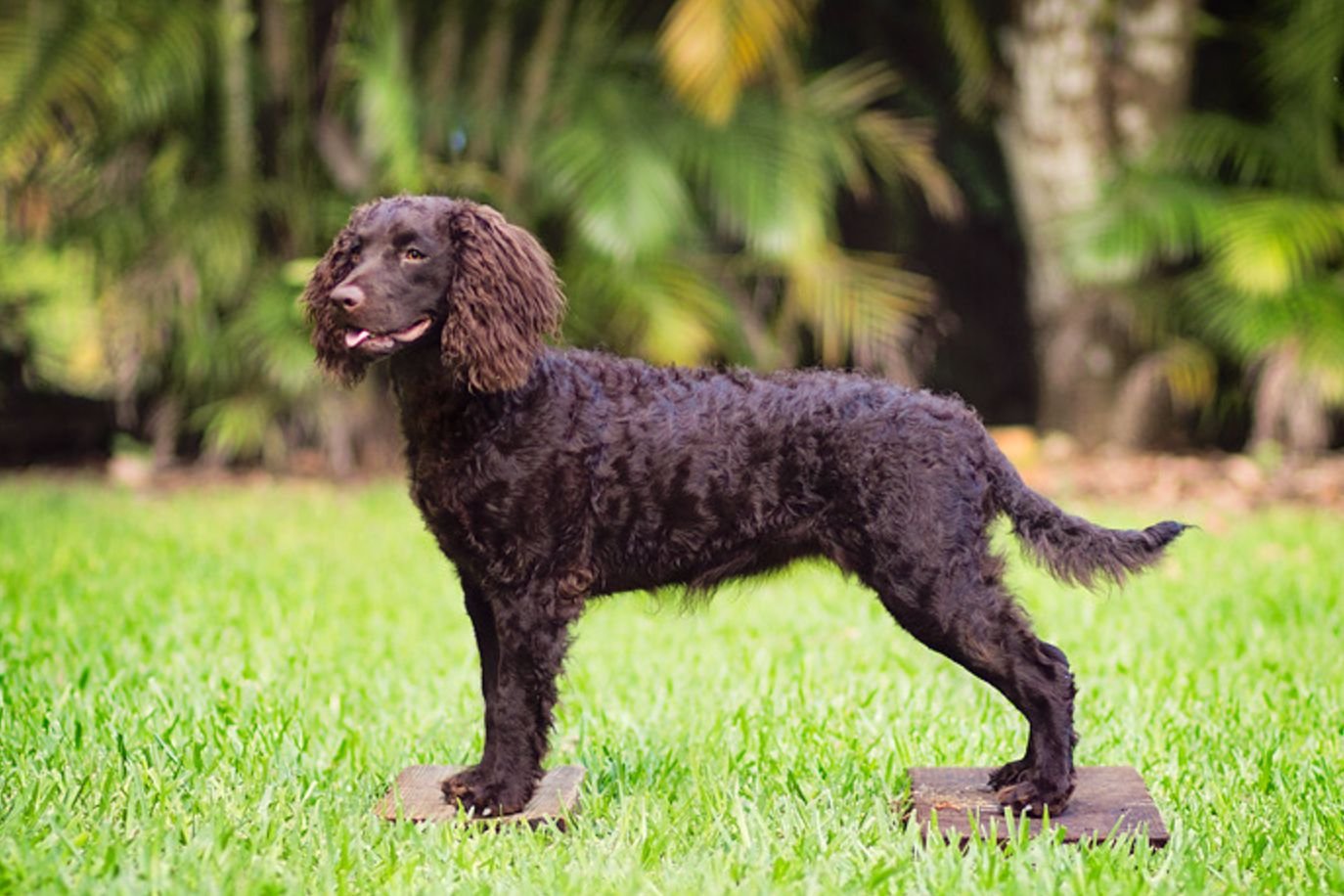

american water spaniel colors chocolate in crcols The American Water Spaniel (AWS)is a medium-sized, versatile hunting dog known for its intelligence, energy, and adaptability. One of the most distinctive aspects of this breed is its rich coat colors, with chocolate being the most iconic and desirable among enthusiasts.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
https://www.youtube.com/@Dogsreaders
Overview of Chocolate Coat in American Water Spaniels

1. Description of the Chocolate Color
The chocolate color in American Water Spaniels ranges from a deep, rich brown to lighter shades such as liver or a sun-kissed cocoa hue. This color is solid throughout the coat, providing a uniform and striking appearance. The coat’s curliness adds depth to the chocolate shade, giving the dog an almost textured, velvety look.
2. Genetics of the Chocolate Coat
The chocolate coloration in AWS is the result of a recessive gene in the B-locus (specifically, the bb genotype). Both parent dogs must carry the recessive gene to produce chocolate-colored offspring. This gene suppresses black pigmentation, resulting in the brown tones characteristic of the chocolate coat.
Genetics of the Chocolate Coat Table

| Gene Locus | Gene/Allele | Function | Expression in Chocolate Coat |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-Locus | b (Recessive) | Controls the production of eumelanin (black or brown pigment). | The bb genotype suppresses black pigment, producing brown (chocolate) tones. |
| E-Locus | E (Dominant) | Allows the expression of eumelanin-based pigmentation. | E allows the chocolate coloration to appear; ee would produce yellow/red coats instead. |
| K-Locus | Ky (Recessive) | Allows the expression of agouti patterns or B-Locus-controlled pigments. | Ky permits the b gene to influence the coat color, resulting in chocolate. |
| A-Locus | a (Recessive) | Controls patterns such as solid or sable. | Chocolate American Water Spaniels are typically solid-colored due to the recessive a allele. |
| Dilution Gene | D (Dominant) | Influences the intensity of pigmentation. | The D gene ensures full chocolate intensity; dd dilution can lighten chocolate to a silvery or fawn-like color. |
Explanation:

- B-Locus: This is the primary determinant for chocolate coloration. The presence of two recessive alleles (bb) results in a brown or chocolate coat.
- E-Locus: A dominant E allele is necessary for eumelanin (black or brown pigments) to be expressed. Without it (ee), the dog would have a yellow or red coat, regardless of the B-Locus.

- K-Locus: Determines whether the coat expresses solid eumelanin (black or brown) or agouti patterns. For chocolate coats, Ky is necessary to reveal the influence of the bb genotype.
- A-Locus: Regulates the distribution of pigmentation patterns, like solid or saddle markings. Solid chocolate coats are common due to the recessive a allele.
- Dilution Gene: Chocolate intensity can be altered if the dog carries the dd dilution, resulting in a lighter shade, sometimes referred to as “silver chocolate.”

This table reflects how multiple genes interact to create and refine the chocolate coat coloration in American Water Spaniels. If you’d like, I can expand on this further or add references to specific studies.
Physical Characteristics of Chocolate-Coated AWS

The chocolate coat is often complemented by features like:
- Eye Color: Eyes typically range from hazel to brown, harmonizing with the coat.
- Nose and Paw Pads: These areas are often a liver or brown color, reflecting the chocolate gene’s influence.
Physical Characteristics of Chocolate-Coated American Water Spaniels (AWS)
| Characteristic | Description | Details Specific to Chocolate-Coated AWS |
|---|---|---|
| Coat Type | Dense, double-layered, water-resistant, ranging from wavy to tightly curled. | The chocolate coat enhances the visual texture, with curls or waves appearing more prominent in rich brown tones. |
| Coat Color | Solid shades of chocolate, liver, or brown. | Chocolate AWS coats range from dark, rich brown to lighter, sun-kissed shades; uniformity is preferred, though small white markings on the chest or toes may appear. |
| Size (Height) | Males: 15–18 inches; Females: 15–17 inches | The compact size supports agility in hunting environments and makes the breed suitable for both work and companionship. |
| Weight | Males: 30–45 pounds; Females: 25–40 pounds | Weight varies depending on activity levels and diet; proper weight management is critical for maintaining coat health and mobility. |
| Eye Color | Typically hazel or dark brown. | Chocolate-coated AWS often have hazel or lighter brown eyes, complementing their coat color. |
| Nose & Paw Pads | Liver or dark brown pigmentation. | Consistent with the chocolate coat’s genetic makeup (bb genotype), matching pigmentation is observed on the nose and paw pads. |
| Ears | Long, floppy, and heavily feathered. | Chocolate AWS coats can exhibit a slight curl or wave in ear feathering, adding to their striking appearance. |
| Tail | Moderately long, feathered, carried level with the body or slightly curved. | The chocolate coat on the tail is often sleek, with feathering slightly lighter in color due to exposure to sunlight. |
| Musculature | Compact, well-proportioned, and athletic. | Chocolate AWS possess muscular hindquarters and strong shoulders, essential for swimming and hunting in challenging terrains. |
| Feet | Webbed, with strong pads adapted for swimming and retrieving. | The dark pads of chocolate-coated AWS resist abrasions, aiding in their agility across water and rugged surfaces. |
Notes on Grooming and Maintenance
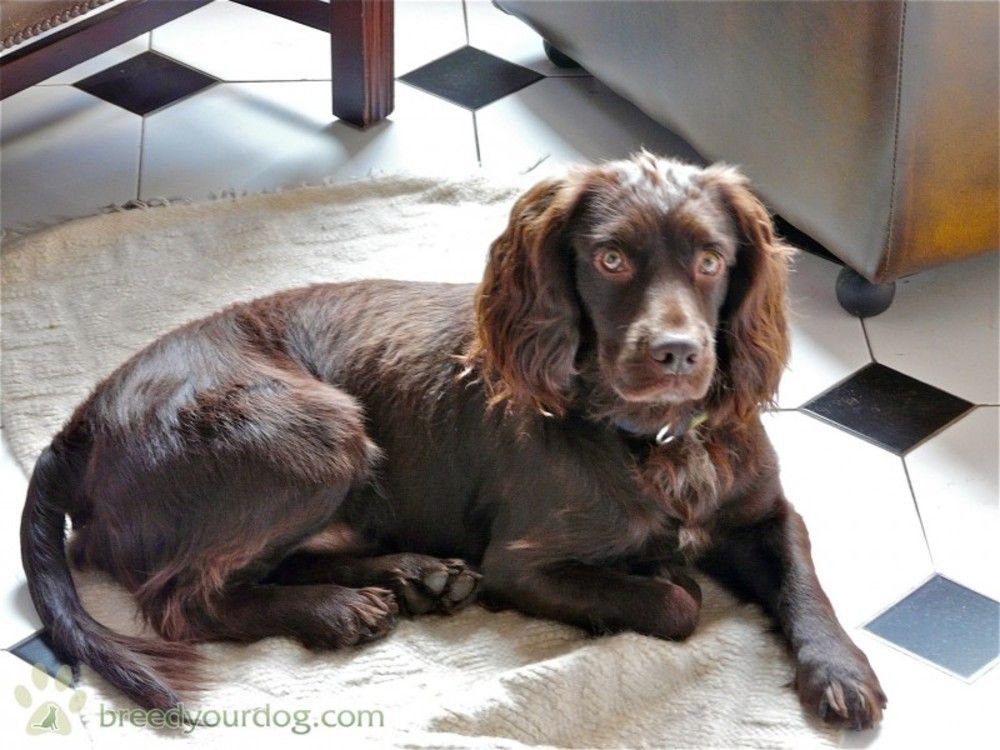

- Coat Care: Regular brushing is essential to prevent matting, especially in the curly or wavy coats typical of the breed.
- Sun Protection: The chocolate coat is prone to sun bleaching, particularly in outdoor working dogs. Limiting exposure and providing shade can help maintain the richness of the coat color.
- Diet Impact: Nutrition rich in omega fatty acids promotes coat health and shine.
Care and Maintenance of the Chocolate Coat
1. Coat Type
American Water Spaniel Colors Chocolate In Crcols: American Water Spaniels have a dense, water-resistant double coat, which can range from wavy to tightly curled. The chocolate color makes them particularly susceptible to visible wear and tear, such as fading or staining.
2. Grooming Tips

- Regular Brushing: Use a slicker brush or comb weekly to prevent matting and remove debris.
- Protection from Sunlight: Excessive exposure to sunlight can cause the chocolate coat to fade. Protect your AWS during peak hours with shade or dog-safe sunscreen.
- Nutritional Support: High-quality omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids promote a shiny and healthy coat.
Common Diseases in Chocolate-Coated American Water Spaniels: Table with Precautions and Assumptions
| Disease | Description | Precautions | Assumptions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hip Dysplasia | A genetic condition where the hip joint develops improperly, leading to arthritis and mobility issues. | – Genetic testing before breeding. – Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint stress. – Provide joint supplements (e.g., glucosamine). – Avoid high-impact exercise. | Assumes proper breeding practices can reduce incidence. Assumes that early intervention improves quality of life. |
| Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA) | A hereditary condition causing gradual vision loss and eventual blindness due to retinal degeneration. | – Conduct regular eye exams. – Perform genetic screening on breeding dogs. – Provide adaptive training for vision-impaired dogs. | Assumes affected dogs adapt well to vision loss if caught early. Assumes regular veterinary care prevents secondary complications like injuries. |
| Bloat (Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus) | A life-threatening condition where the stomach fills with gas and twists, cutting off blood supply. | – Feed smaller, frequent meals. – Avoid exercise immediately after meals. – Consider preventive gastropexy surgery for at-risk dogs. | Assumes early intervention and awareness of symptoms (e.g., restlessness, bloating) can save lives. Assumes balanced feeding reduces risk. |
| Hypothyroidism | A hormonal imbalance caused by underactive thyroid glands, leading to lethargy, weight gain, and coat thinning. | – Routine blood tests to monitor thyroid function. – Provide lifelong hormone replacement therapy (levothyroxine). – Include omega-3 and vitamin-rich diets. | Assumes early diagnosis through regular checkups prevents complications. Assumes consistent medication adherence ensures normal energy levels and metabolism. |
| Ear Infections | Common in AWS due to their floppy ears, which trap moisture and debris, especially in water-loving dogs. | – Regularly clean ears with vet-approved solutions. – Keep ears dry after swimming. – Monitor for signs like odor, redness, or discharge. | Assumes attentive owners can reduce incidence of ear infections. Assumes preventive care (cleaning and drying) minimizes recurrence. |
| Allergies | Sensitivities to environmental factors (pollen, dust) or dietary components causing skin irritation, itching, and digestive problems. | – Feed hypoallergenic diets if food allergies are suspected. – Regular grooming to remove allergens from the coat. – Consult vets for allergy-specific medications. | Assumes early identification of triggers reduces the severity of allergic reactions. Assumes hypoallergenic care improves overall coat and skin health. |
Details and Preventive Measures

- Routine Health Screening: Conduct genetic tests and physical exams for common hereditary conditions before breeding.
- Balanced Diet and Weight Management: Feed high-quality dog food with omega-3 and glucosamine to support coat, skin, and joint health.
- Exercise: Provide appropriate levels of physical activity to maintain mobility and prevent obesity, especially for conditions like hip dysplasia.
- Veterinary Checkups: Schedule regular vet visits for vaccinations, blood tests, and eye or ear exams to catch issues early.
- Owner Awareness: Educate pet owners about symptoms of diseases like bloat or hypothyroidism and how to address them immediately.
For more information:
Common Diseases in Chocolate-Coated American Water Spaniels (AWS): Descriptions and Solutions
American Water Spaniel Colors Chocolate In Crcols are beautiful and versatile dogs, but like all breeds, they are susceptible to certain health issues. The coat color itself does not cause health problems, but genetic factors linked to breed traits may contribute. Below are common diseases observed in AWS, with descriptions and solutions.
1. Hip Dysplasia
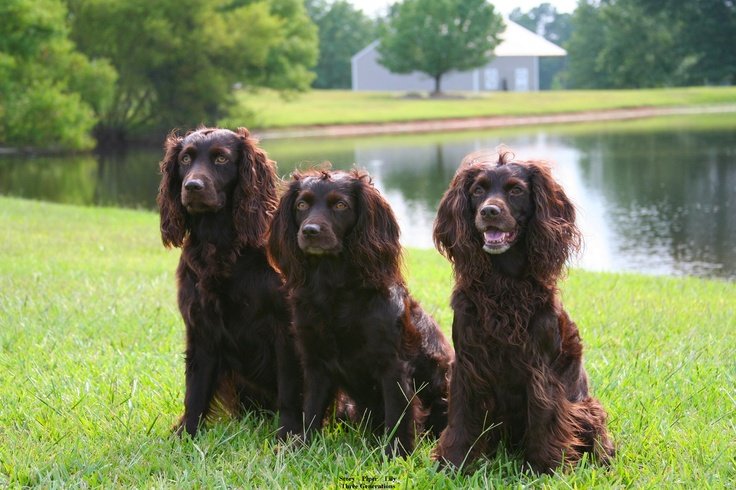

Description:
A hereditary condition where the hip joint doesn’t fit properly into the hip socket, leading to pain, arthritis, and reduced mobility. It is more prevalent in medium-sized active breeds like AWS.
Solutions:
-
- Genetic screening for breeding stock to reduce transmission of the condition.
- Weight management to reduce stress on joints.
- Physical therapy or anti-inflammatory medications for affected dogs.
- In severe cases, surgical correction.
Resources:
2. Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA)
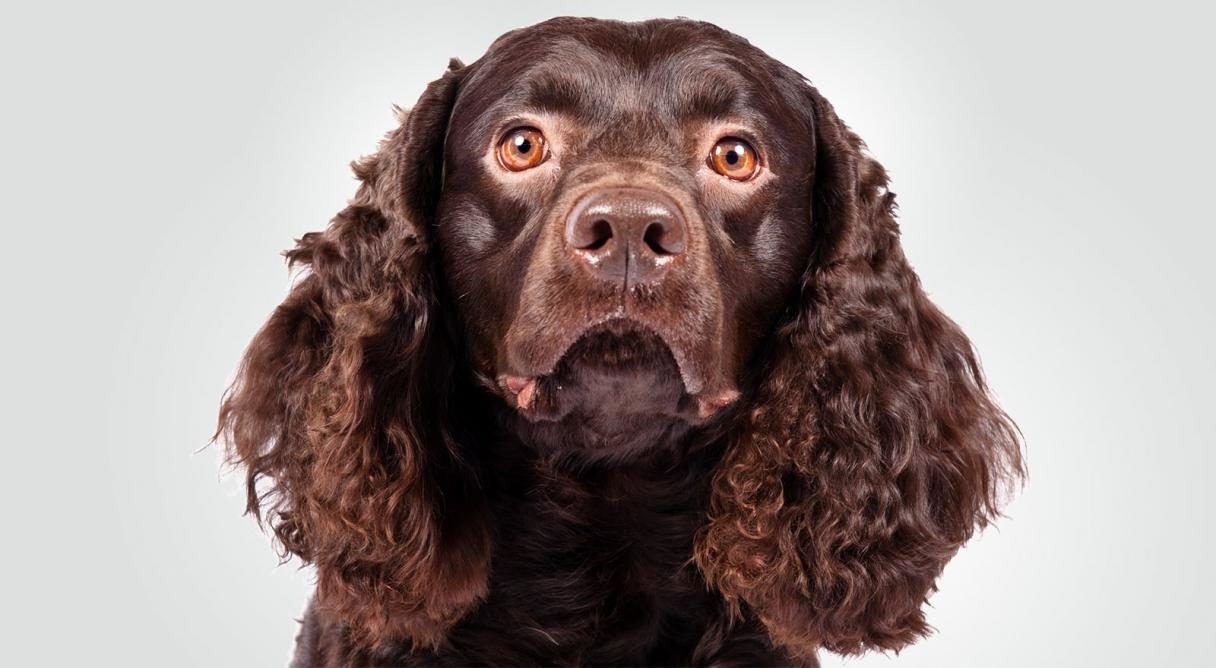

Description:
A group of genetic disorders leading to the degeneration of the retina, causing vision loss and eventually blindness. PRA is common in spaniel breeds, including AWS.
Solutions:
-
- Routine eye exams with veterinary ophthalmologists for early detection.
- Genetic testing for responsible breeding.
- Supportive care such as adapting the home environment for blind dogs.
Resources:
3. Hypothyroidism

- Description: A condition where the thyroid gland under-produces hormones, causing lethargy, weight gain, hair thinning, and skin problems. It may affect coat quality, including the chocolate coat’s luster.
- Solutions:
- Routine blood tests to monitor thyroid levels.
- Lifelong hormone replacement therapy (levothyroxine).
- High-quality diets with supplements for skin and coat health.
4. Bloat (Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus)

- Description: A life-threatening condition where the stomach fills with gas and twists, cutting off blood flow. Active breeds like AWS are at higher risk, especially after eating large meals or exercising immediately after eating.
- Solutions:
- Feed smaller, more frequent meals instead of one large meal.
- Avoid vigorous activity immediately before or after meals.
- Preventive gastropexy surgery in at-risk dogs.
Resources:
5. Ear Infections

- Description: Chocolate AWS with floppy ears are prone to ear infections due to moisture and debris getting trapped in the ear canal. This is exacerbated by their love for water activities.
- Solutions:
- Regular ear cleaning with vet-approved solutions.
- Thoroughly drying ears after swimming or baths.
- Monitoring for signs like head shaking or foul odor.
Resources:
Recommended Preventive Measures

- Genetic testing for hereditary conditions before breeding.
- Regular checkups with veterinarians, including orthopedic and ophthalmic exams.
- A balanced diet with omega fatty acids to support coat and skin health.
- Consistent exercise to maintain weight and prevent joint stress.
Useful URLs for Further Reading
- American Kennel Club (AKC) – American Water Spaniel
- Canine Health Foundation
- Orthopedic Foundation for Animals
Popularity of Chocolate in AWS

Chocolate is the preferred color among American Water Spaniel enthusiasts and breeders. This preference stems from its historical prominence as a hallmark of the breed, as well as its aesthetic appeal. The American Water Spaniel Club (AWSC) recognizes chocolate, liver, and brown as standard colors in the breed’s official guidelines.
Five Reasons for the Popularity of the Chocolate Color in American Water Spaniels
Historical Significance
The chocolate color has deep roots in the breed’s history and standard. The American Water Spaniel was bred in the midwestern United States, and the chocolate coat quickly became synonymous with the breed’s identity. Early breeders favored this color for its aesthetic appeal and because it reflected the hunting dog’s rugged, versatile nature. The coat color was historically linked with adaptability to the field, forest, and water, cementing its iconic status.
Camouflage for Hunting
Chocolate-coated AWS dogs blend seamlessly into their natural environments, such as wetlands, forests, and fields. This natural camouflage is advantageous for hunters, as the dog remains inconspicuous while retrieving game or flushing birds. The practicality of the chocolate coat contributes significantly to its popularity among hunting enthusiasts.
Aesthetic Appeal
The rich, warm tones of chocolate-colored coats give these dogs a visually striking yet earthy appearance. The unique texture of their wavy or curly fur enhances the depth of the color, making the chocolate AWS particularly photogenic and appealing to both hunters and non-hunting pet owners. Their chocolate coloration often matches darker eye and nose pigments, giving a harmonious and pleasing look.
Breed Standard Recognition
The American Kennel Club (AKC) and the United Kennel Club (UKC) recognize chocolate as a standard color for the breed. This official acknowledgment ensures that chocolate-colored AWS dogs are often highlighted in show rings and breeding programs. Such recognition increases demand for chocolate-coated dogs among both professional breeders and pet owners.
Durability of the Coat
Chocolate coats in AWS are admired for their ability to hide dirt and stains, especially in field or water work. Unlike lighter-colored coats, which show wear more visibly, the chocolate coat retains its aesthetic and practical appeal even after rigorous activity. Owners find this both functional and low-maintenance, contributing to the enduring popularity of the color.
Supporting Resources
If you’d like a deeper dive into the genetics or care for chocolate coats, let me know!
Health Considerations for Chocolate AWS
Common Concerns
While coat color does not directly impact health, genetic factors associated with the breed may affect chocolate AWS. These include:
- Hip Dysplasia:Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce risks.
- Ear Infections: The dense, curly coat can trap moisture, making ear cleaning essential.
- Skin Sensitivity: Chocolate coats can sometimes display skin irritation more visibly, requiring careful attention.
Recommended Resources
- Books:
- The Complete Dog Breed Book by DK Publishing
- Hunting Dogs: The American Water Spaniel by Evan S. Krohn
- Web Resources:
FAQs
Q: Can chocolate American Water Spaniels have white markings?
A: While the breed standard prefers solid coats, small white markings on the chest or toes are permissible.
Q: How do I prevent sun bleaching on my chocolate AWS?
A: Limit sun exposure during peak hours and use dog-safe sunscreen for prolonged outdoor activities.
Q: Is the chocolate color linked to specific health issues?
A: No direct link exists between the chocolate coat and health, but regular care and genetic screening ensure overall well-being.
Latest Research on the American Water Spaniel (AWS)
Recent studies and ongoing research have focused on both the genetics and health concerns of American Water Spaniels, particularly with regard to their coat color and breed-specific health issues.
1. Genetic Research on Alopecia
Alopecia (hair loss) has been identified as a notable condition in American Water Spaniels, particularly manifesting between 6 months and 1 year of age. Research led by Drs. Brian Husbands, Sheila Torres, and Steven Friedenberg is investigating the genetic basis of this condition. Their aim is to identify the mutation responsible for alopecia to develop diagnostic tests that can help reduce its occurrence in future generations of the breed.
2. Coat Color and Genetic Diversity
The chocolate coat color, prominent in AWS, has sparked interest in genetic studies due to its popularity and implications for breeding practices. Studies reveal that selective breeding for coat colors like chocolate can inadvertently reduce genetic diversity, potentially exacerbating the prevalence of certain hereditary conditions such as hip dysplasia and eye issues. Responsible breeding practices emphasize maintaining genetic diversity alongside desired traits.
3. Common Health Risks: Chondrodystrophy (CDDY)
CDDY, linked to intervertebral disc disease (IVDD), is a recognized genetic risk in AWS. Testing through panels such as Wisdom Panel™ enables breeders and owners to identify dogs that carry or express this condition, facilitating preventative care and informed breeding decisions.
4. Diet and Exercise for Health
Research into the dietary and exercise needs of AWS highlights the importance of high-protein diets and consistent physical activity. Meeting these requirements not only supports their active nature but also mitigates risks of obesity and joint issues.
5. Improved Health Screening Tools
Advances in DNA testing have expanded the ability to screen for over 200 genetic conditions, including those affecting AWS. These tools help breeders ensure the health of their lines and offer pet owners insights into their dog’s potential health needs.
References
- Wisdom Panel – AWS Genetic Health Overview
- American Water Spaniel Club – Health and Genetics
- Animal Genetics Research
These efforts underline the importance of responsible breeding and early detection to safeguard the well-being and longevity of American Water Spaniels. For more details or participation in ongoing research, you can visit the AWS Club Health Section.
MEDIUM BREEDS
Dog Canine Mental Fatigue: The Hidden Cause of Behavioral Issues

Understand The Topic

Dog Canine Mental Fatigue: Many dog owners believe that a tired dog is a well-behaved dog. While physical exercise is crucial, mental stimulation plays an equally important role in a dog’s overall well-being. Canine mental fatigue is a hidden issue that often leads to behavioral problems, anxiety, and even long-term health risks. Understanding and addressing this issue can significantly improve your dog’s quality of life.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
What Is Canine Mental Fatigue?

Mental fatigue in dogs occurs when their brains are overworked, either from excessive stimulation or a lack of proper cognitive engagement. Just like humans, dogs need a balance between mental activity and rest. When this balance is disturbed, they can become stressed, irritable, and even depressed.
Signs of Mental Fatigue in Dogs
- Increased irritability or aggression
- Lack of interest in playtime or training
- Difficulty focusing or following commands
- Frequent yawning, licking, or stress signals
- Excessive sleeping or sudden hyperactivity
- Avoidance of interaction with owners or other pets
Causes of Mental Fatigue in Dogs

1. Overtraining Without Breaks
- Training is essential, but excessive or repetitive training sessions without breaks can exhaust a dog mentally. Their brain needs downtime to process and retain information.
2. Lack of Mental Stimulation
- Many dogs do not receive enough cognitive engagement, leading to boredom and frustration. Simple physical exercise is not enough; dogs need mental challenges to stay sharp.
3. Sensory Overload
- Loud noises, crowded environments, and excessive human interaction can cause stress. Certain dog breeds are more sensitive to sensory overload and require quiet spaces for relaxation.
4. Too Many Commands in One Session
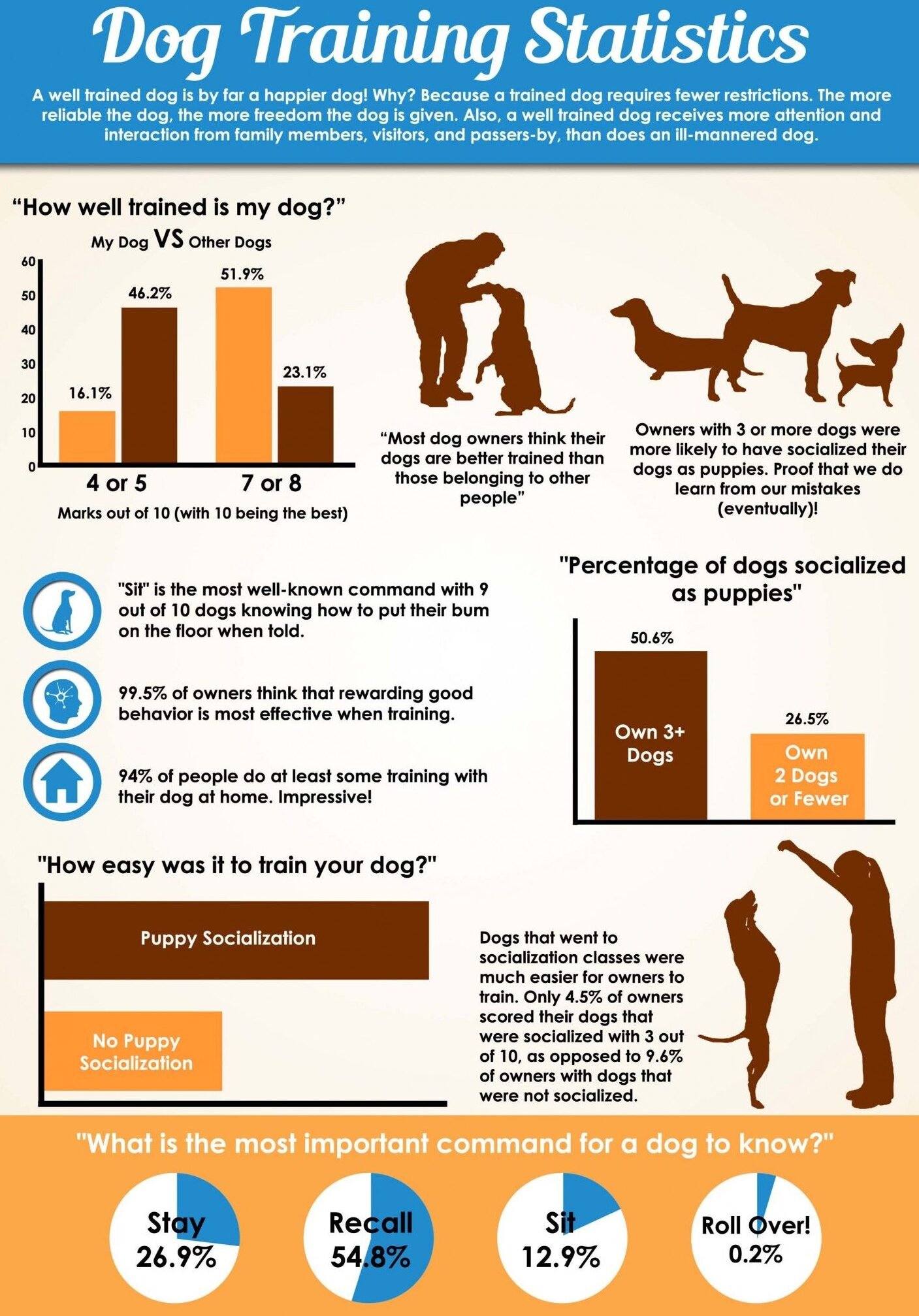
- Constantly introducing new tricks without giving a dog time to master previous ones can overwhelm them, leading to frustration and mental exhaustion.
5. Lack of Proper Sleep Schedule

- Dogs require 12-14 hours of sleep per day (puppies and older dogs may need even more). Irregular sleep patterns or disturbances can contribute to mental fatigue.
How to Prevent and Reduce Canine Mental Fatigue

1. Implement a Balanced Routine
- Mix physical exercise, mental stimulation, and rest periods to ensure your dog is not overworked or bored.
2. Provide Puzzle Toys and Interactive Games
- Invest in treat-dispensing puzzles, snuffle mats, and interactive toys that encourage problem-solving skills. These activities keep your dog engaged and mentally sharp.
3. Allow Free Exploration
- Taking a dog on a walk is not just about exercise—it’s an opportunity for them to use their senses. Allow them to sniff and explore their surroundings to engage their minds.
4. Keep Training Sessions Short and Reward-Based
- Limit training to 5–10 minutes per session and use positive reinforcement. Overloading a dog with new tricks can lead to frustration and fatigue.
5. Create a Quiet Resting Space
- Ensure your dog has a designated, quiet area in the home where they can relax and recover from stimulation.
6. Monitor and Adjust Their Social Interactions
- Not all dogs enjoy the same level of social interaction. Some may need more playtime, while others require calm and solitude to recharge. Pay attention to your dog’s individual needs.
7. Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule
- Make sure your dog has a consistent bedtime routine and a comfortable sleeping environment to promote deep, restorative sleep.
Closing Statement

Mental fatigue is an often-overlooked issue that affects a dog’s behavior, mood, and overall health. Recognizing the signs and making simple adjustments can prevent stress-related problems and improve your dog’s happiness. By balancing mental and physical stimulation, you’ll have a healthier, more engaged, and well-behaved companion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do I know if my dog is mentally tired or just sleepy?
- Mental fatigue often includes signs like irritability, lack of focus, or disinterest in activities. If your dog is simply sleepy, they will rest and recover quickly.
2. Can mental fatigue lead to serious health problems in dogs?
- Yes. Chronic stress from mental exhaustion can lead to anxiety disorders, weakened immunity, and even digestive issues.
3. How often should I give my dog mental exercises?
- Daily mental stimulation is important but should be balanced with rest. Short, engaging activities a few times a day work best.
4. What are the best mental exercises for dogs?
- Puzzle toys, interactive games, scent work, hide-and-seek, and short training sessions are great ways to keep your dog mentally sharp.
5. Can over-socialization cause mental fatigue in dogs?
- Yes, some dogs become mentally drained from too much interaction with people or other animals. Always monitor your dog’s behavior to adjust their social time accordingly.
MEDIUM BREEDS
Hepatitis in Dogs: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention

Understand The Topic
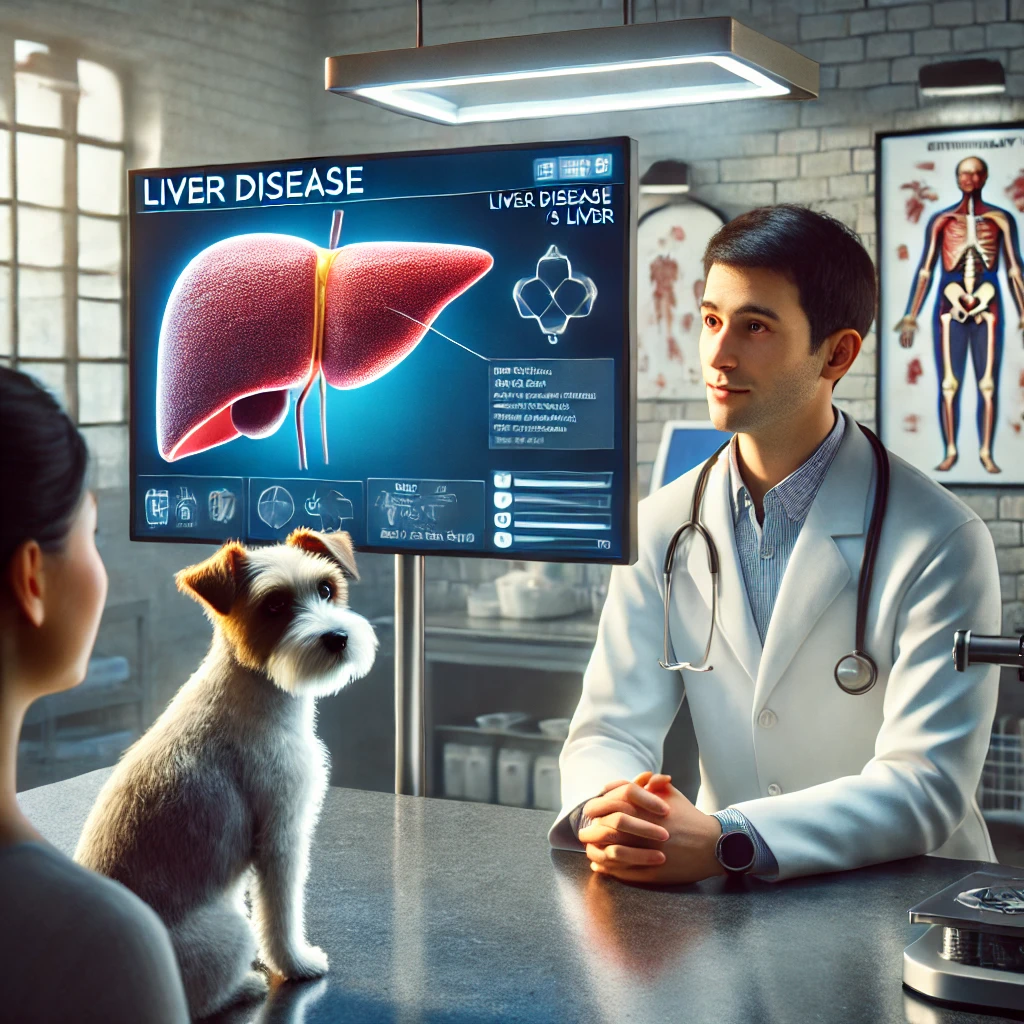

Hepatitis in dogs is a serious condition that affects the liver, leading to inflammation and potential organ damage. It can be caused by infections, toxins, or immune system disorders. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help dog owners protect their pets from this life-threatening disease.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
What is Hepatitis in Dogs?
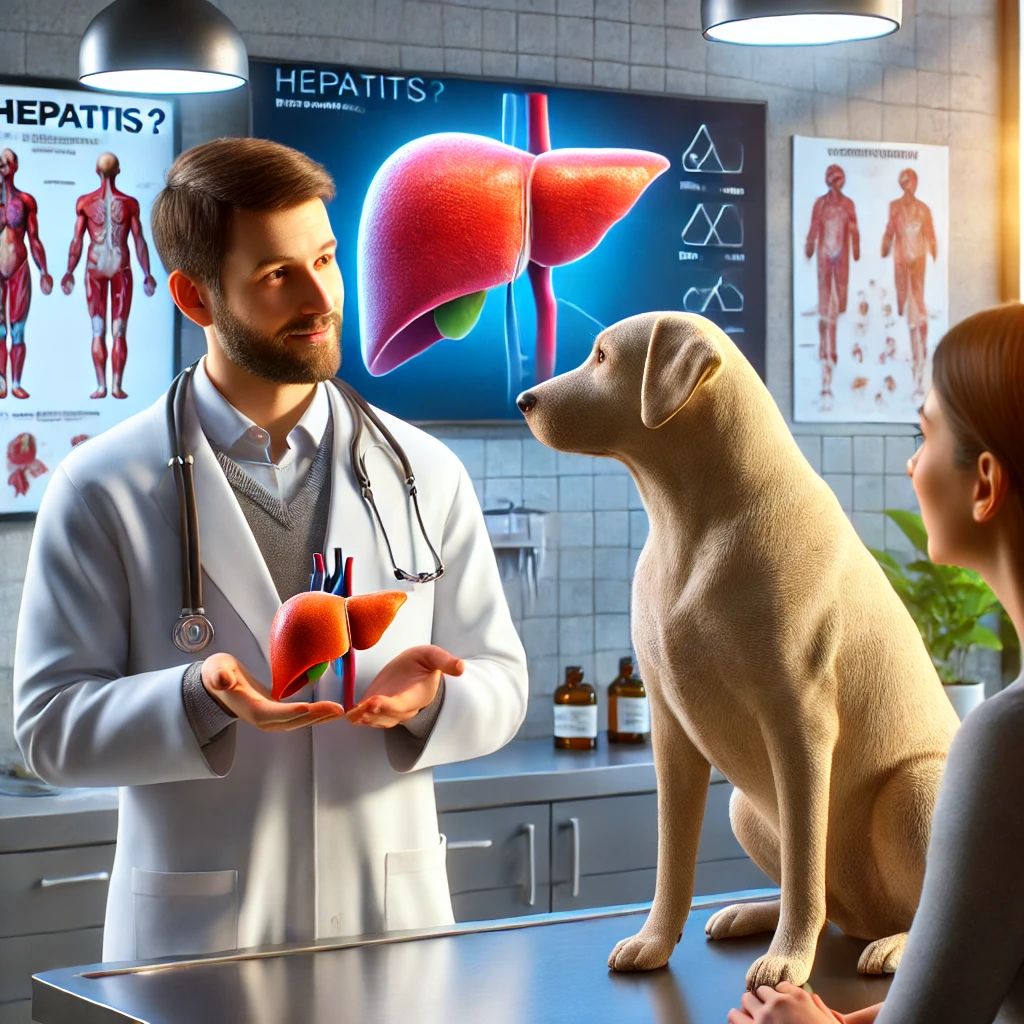

Hepatitis in dogs refers to liver inflammation caused by infectious agents, toxic substances, or immune-related conditions. The most common types include:
- Infectious Canine Hepatitis (ICH):
- Caused by Canine Adenovirus Type 1 (CAV-1), this highly contagious viral infection primarily affects young dogs.
- Chronic Hepatitis:
- A long-term condition that results from infections, autoimmune disorders, or prolonged exposure to toxins.
- Toxic Hepatitis:
- Caused by ingesting harmful substances like chemicals, medications, or poisonous plants.
Causes of Hepatitis in Dogs
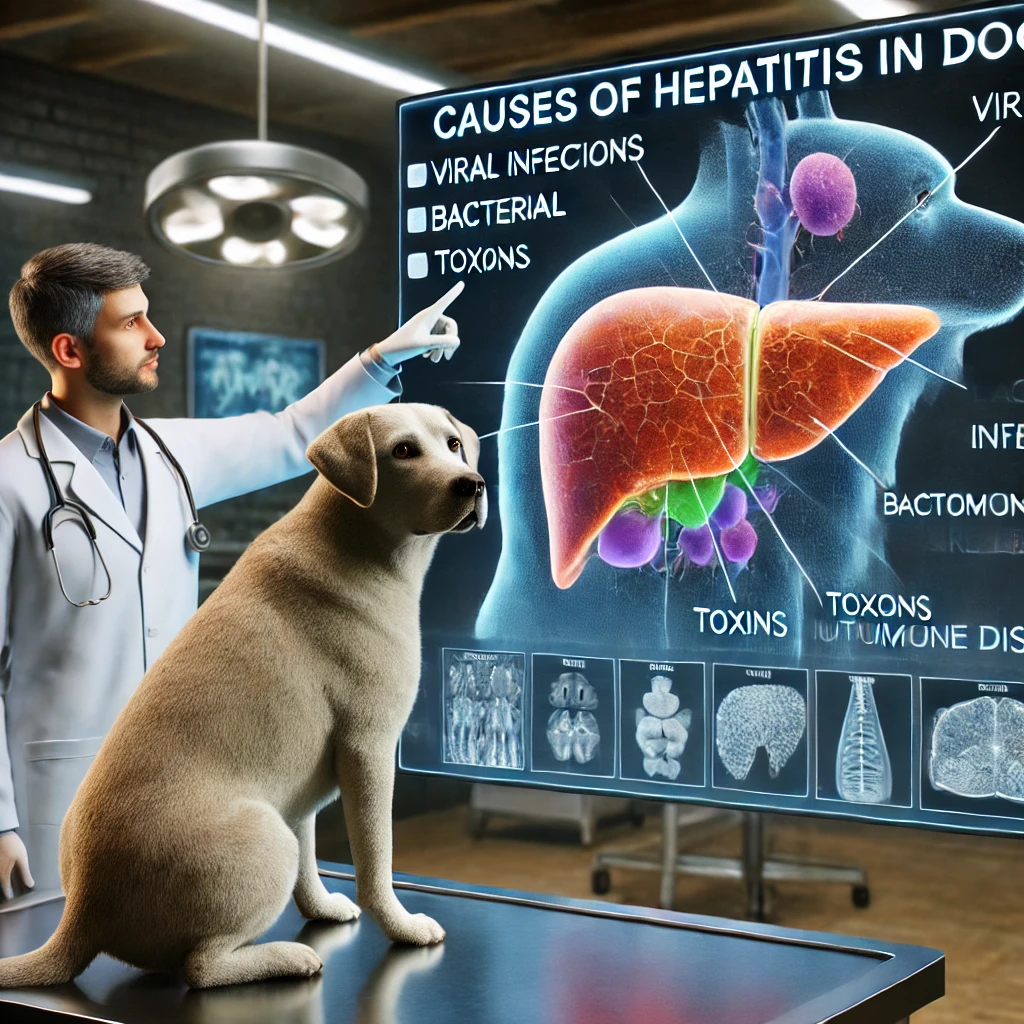
Hepatitis in dogs can develop due to several factors, including:
- Viral infections – CAV-1 is the primary cause of infectious canine hepatitis.
- Bacterial infections – Certain bacterial infections can lead to liver inflammation.
- Toxins – Exposure to harmful substances such as pesticides, contaminated food, or certain medications can trigger toxic hepatitis.
- Autoimmune disorders – The immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells, causing chronic hepatitis.
- Genetic predisposition – Some breeds, such as Doberman Pinschers and Cocker Spaniels, are more prone to chronic hepatitis.
Hepatitis Causes by Dog Size and Most Affected Breeds

Certain dog sizes and breeds are more susceptible to hepatitis due to genetic predisposition, metabolic factors, or environmental exposure.
| Dog Size | Common Causes of Hepatitis
|
Most Affected Breeds and Why
|
|---|---|---|
| Small Breeds | Genetic liver issues, toxin sensitivity | Yorkshire Terrier, Maltese – Prone to liver shunts and congenital hepatic disorders |
| Medium Breeds | Autoimmune disorders, infections | Cocker Spaniel, Beagle – Higher risk of chronic hepatitis due to immune response issues |
| Large Breeds | Metabolic liver issues, chronic infections | Doberman Pinscher, Golden Retriever – Prone to chronic hepatitis and liver fibrosis |
| Giant Breeds | Dietary-related liver strain, toxin exposure | Great Dane, Labrador Retriever – Susceptible to toxin-induced hepatitis due to larger food intake |
Knowing these risks can help dog owners take preventive measures based on their dog’s size and breed.
Most Affected Countries and Their Efforts to Overcome Hepatitis in Dogs

Hepatitis in dogs is a global concern, but certain countries have reported higher infection rates due to climate, stray dog populations, and vaccination policies. Below are some of the most affected countries and how they are combating hepatitis:
| Country | Infection
Rate (%)
|
Measures Taken to Overcome Hepatitis
|
| USA | 8-10% | Increased vaccination programs, widespread use of liver supplements, strict pet health regulations |
| India | 12-15% | Focus on rabies and CAV-1 vaccinations, stray dog population control, environmental hygiene improvements |
| Brazil | 10-12% | Government-led vaccination drives, improved veterinary care access, awareness campaigns |
| UK | 6-8% | Regular veterinary screenings, high pet owner awareness, government-funded disease tracking |
| China | 9-11% | Encouraging pet vaccination programs, stricter pet import regulations, better food safety laws |
These countries have successfully managed hepatitis outbreaks through a combination of vaccinations, medications, liver supplements, and environmental control efforts.
Symptoms of Hepatitis in Dogs
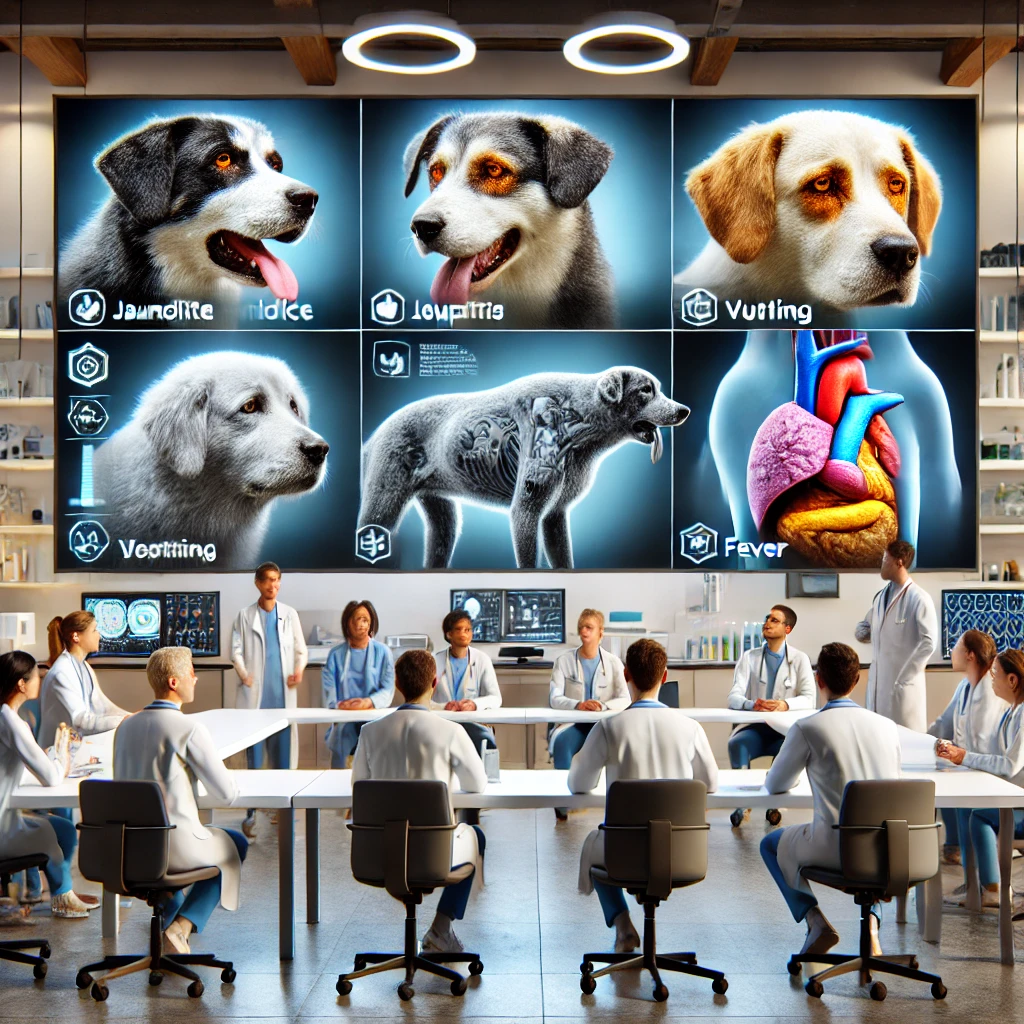

The symptoms of hepatitis vary based on its severity and underlying cause. Common signs include:
- Fever and lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Yellowing of the skin, gums, and eyes (jaundice)
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Increased thirst and urination
- Seizures in severe cases
- Cloudy or bluish eyes (specific to ICH)
- Early detection and prompt veterinary care can significantly improve a dog’s chances of recovery.
Diagnosis of Hepatitis in Dogs
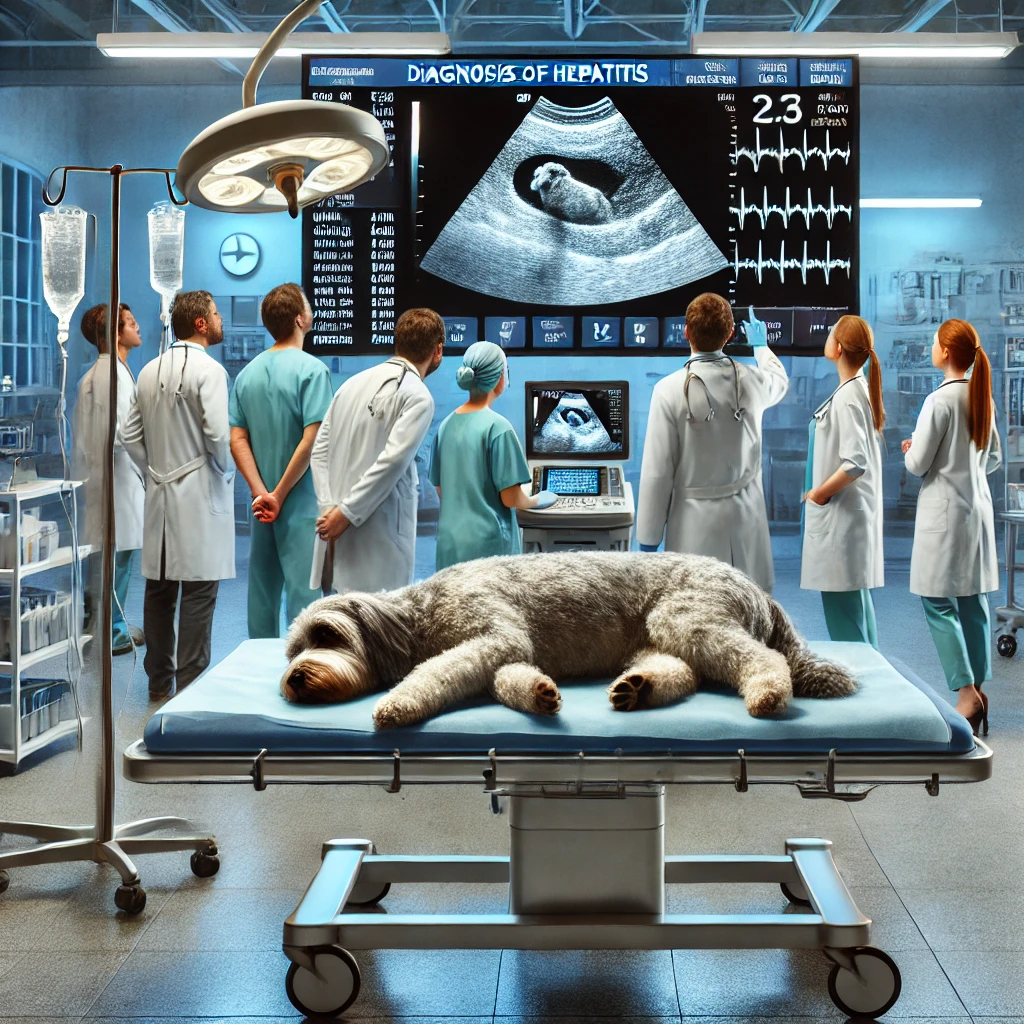

A veterinarian will conduct a thorough examination and recommend diagnostic tests, such as:
- Blood tests – To check liver enzyme levels and overall health.
- Urinalysis – To assess kidney and liver function.
- Ultrasound or X-rays – To examine liver size and detect abnormalities.
- Liver biopsy – To determine the underlying cause of hepatitis.
Treatment Options for Hepatitis in Dogs

Treatment depends on the type and severity of hepatitis:
- Supportive care – Intravenous fluids, anti-nausea medications, and pain relief.
- Antiviral or antibiotic medications – If an infection is present.
- Liver supplements – To support liver function and repair damage.
- Dietary changes – Low-fat, high-protein diets help reduce liver strain.
- Hospitalization – In severe cases, dogs may require intensive care.
Relevant Liver Supplements for Different Dog Sizes

| Dog Size |
Recommended Supplements
|
| Small Breeds | Milk Thistle,
|
| Medium Breeds | S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM-e),
|
| Large Breeds | Denamarin,
|
| Giant Breeds | URSOLYX or. Ursodiol
|
Timely medical intervention increases the chances of recovery and prevents further liver damage.
Prevention of Hepatitis in Dogs

Preventive measures can help reduce the risk of hepatitis:
Vaccination – The CAV-1 vaccine effectively prevents infectious canine hepatitis.
Regular veterinary check-ups – Early detection of liver issues can improve outcomes.
Avoid toxins – Keep household chemicals, medications, and toxic foods out of reach.
Proper hygiene – Prevent bacterial infections by maintaining cleanliness.
Breed-specific screening – If your dog is genetically predisposed, regular monitoring is essential.
Closing Statement

For more expert insights on dog health, training, and care, visit DogsReader today!
Canine Hepatitis: Detailed FAQs

Hepatitis in dogs is a serious condition involving liver inflammation that can range from mild to life-threatening. Below is a comprehensive FAQ guide covering infectious canine hepatitis (ICH), toxic hepatitis, and other liver-related disorders in dogs.
1. What is Canine Hepatitis?
Definition:
An inflammatory liver condition categorized into two main types:
Infectious Canine Hepatitis (ICH) – Caused by canine adenovirus-1 (CAV-1)
Toxic/Non-Infectious Hepatitis – Liver damage from toxins, medications, or metabolic diseases
Key Fact:
ICH is not contagious to humans but spreads rapidly among unvaccinated dogs.
2. What Causes Hepatitis in Dogs?
A. Infectious Causes
Canine Adenovirus-1 (CAV-1) – Spread via urine, feces, or saliva of infected dogs
Leptospirosis (Bacterial infection from contaminated water)
B. Non-Infectious Causes
Toxins (Xylitol, pesticides, moldy food, certain medications)
Autoimmune disease
Chronic conditions (Diabetes, Cushing’s disease)
Trauma or cancer
3. What Are the Symptoms of Hepatitis in Dogs?
| Early Signs |
Advanced Symptoms
|
|---|---|
Loss of appetite |
Jaundice (yellow gums/eyes) |
Lethargy |
Abdominal swelling |
Mild fever |
Blood in vomit/stool |
Increased thirst |
Seizures or coma (severe cases) |
Note: Some dogs show no symptoms until liver damage is severe.
4. How is Hepatitis Diagnosed?
Blood tests (High liver enzymes, bilirubin)
Ultrasound/X-rays – Check liver size & abnormalities
Biopsy – Confirms inflammation or cancer
PCR test – Detects CAV-1 virus
5. How is Canine Hepatitis Treated?

A. Infectious Hepatitis (CAV-1)
Supportive care (IV fluids, anti-nausea meds)
Antibiotics (For secondary infections)
Liver protectants (SAMe, milk thistle)
B. Toxic Hepatitis
Detoxification (Activated charcoal if toxin ingestion is recent)
Hospitalization for severe cases
Prognosis:
Mild cases often recover with treatment.
Severe liver damage may be fatal or require lifelong management.
6. Is There a Vaccine for Canine Hepatitis?

✅ Yes! The DA2PP vaccine (which includes CAV-2, cross-protective against CAV-1) is core for puppies and adult dogs.
Vaccine Schedule:
Puppies:
Every 3–4 weeks until 16 weeks old
Adults:
Booster every 1–3 years
Note: CAV-1 itself is rarely used in vaccines due to side effects (e.g., “blue eye” reaction).
7. How Can I Prevent Hepatitis in My Dog?
Vaccinate regularly (DA2PP)
Avoid toxins (Keep xylitol, grapes, antifreeze away)
Limit exposure to infected dogs or contaminated areas
Feed a balanced diet (Avoid fatty table scraps)
8. Can Dogs Recover Fully from Hepatitis?

Mild cases: Often recover with no lasting damage.
Chronic hepatitis: May require lifelong medication (e.g., immunosuppressants, ursodiol).
Severe cirrhosis: Liver failure may be fatal or require euthanasia.
Follow-up: Regular bloodwork monitors liver health post-recovery.
9. Is Canine Hepatitis Contagious to Other Pets or Humans?
Dogs: CAV-1 spreads via bodily fluids (highly contagious in kennels).
Cats/Other Pets: Not affected by CAV-1.
Humans: No risk—CAV-1 is species-specific.
Exception: Leptospirosis (a bacterial cause of hepatitis) can infect humans.
10. What Should I Feed a Dog with Hepatitis?

Vet-Approved Diet Tips:
Low copper (Avoid liver, shellfish)
High-quality protein (Eggs, lean chicken)
Hepatoprotective supplements (Vitamin E, SAMe)
Avoid fatty foods
Prescription diets (Hill’s l/d, Royal Canin Hepatic) are often recommended.
Yellow gums/eyes
Black, tarry stools
Sudden collapse
MEDIUM BREEDS
Common Behavioral Issues in Dogs:Understanding and Addressing

Solutions For Managing Them

Common Behavioral Issues in Dogs: Dogs are intelligent and loving companions, but like humans, they can develop behavioral issues. Recognizing and addressing these problems early can make a significant difference in your dog’s well-being and your relationship with them. This article explores common behavioral issues in dogs and provides practical solutions for managing them.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
1. Aggression
Aggression in dogs can manifest in various ways, such as growling, snapping, or biting. It can stem from fear, dominance, territorial instincts, or frustration.
Causes:
- Fear or anxiety
- Lack of socialization
- Territorial behavior
- Past trauma or abuse
Solutions:
- Gradual socialization with people and other animals
- Positive reinforcement training
- Consulting a professional dog trainer or behaviorist
- Ensuring adequate physical and mental stimulation
2. Excessive Barking

Dogs bark to communicate, but excessive barking can become a nuisance.
Causes:
- Boredom or loneliness
- Attention-seeking behavior
- Alarm or territorial instincts
- Anxiety or fear
Solutions:
- Provide regular exercise and mental stimulation
- Train the “quiet” command using positive reinforcement
- Avoid rewarding unnecessary barking
- Address any underlying anxiety or fear issues
3. Separation Anxiety

Separation anxiety occurs when a dog becomes overly distressed when left alone, leading to destructive behaviors such as chewing, howling, and house soiling.
Causes:
- Over-attachment to the owner
- Sudden changes in routine
- Past traumatic experiences
Solutions:
- Gradually increasing alone time to build independence
- Providing interactive toys or treat-dispensing puzzles
- Using calming techniques such as soothing music
- Seeking professional help if symptoms persist
4. Chewing and Destructive Behavior
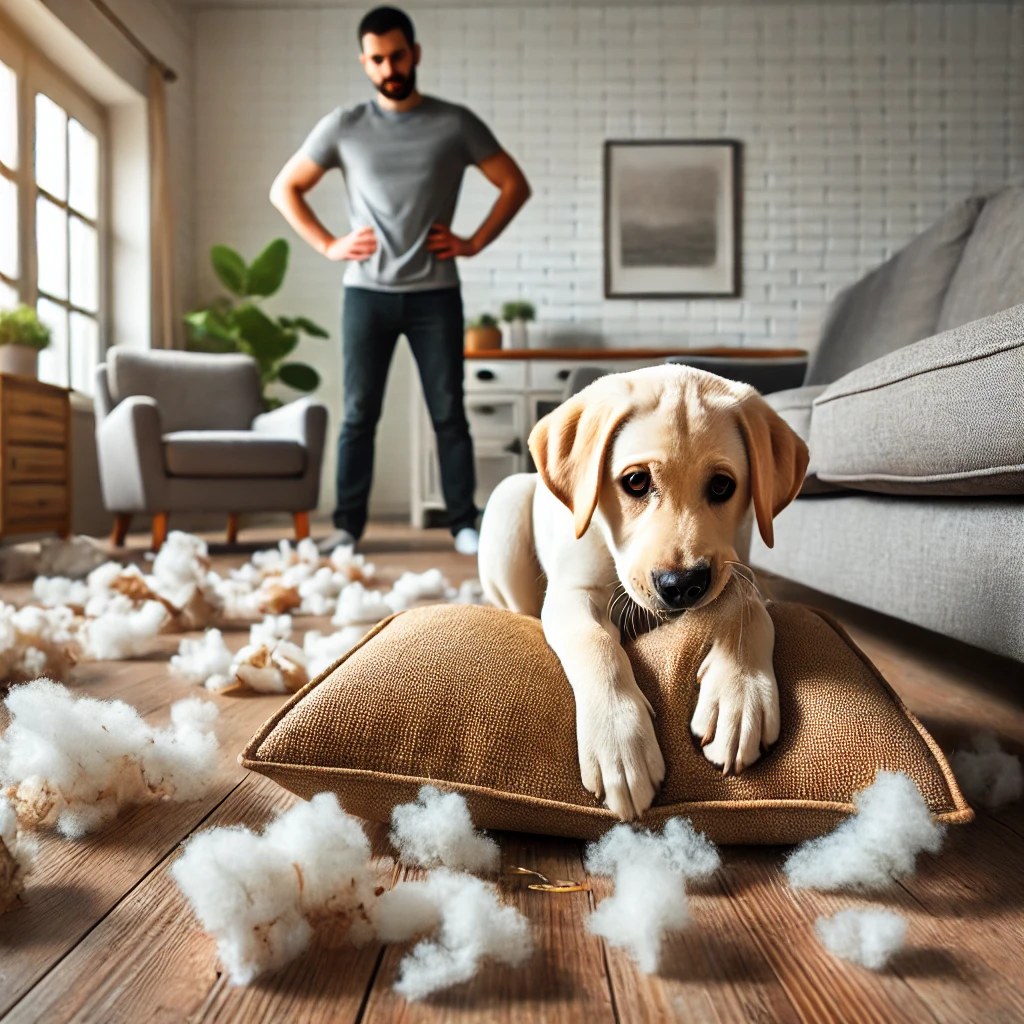

Dogs explore the world with their mouths, but destructive chewing can be frustrating.
Causes:
- Teething (in puppies)
- Boredom or lack of exercise
- Anxiety or stress
Solutions:
- Provide appropriate chew toys
- Increase daily physical activity
- Use deterrent sprays on forbidden objects
- Avoid punishing, and redirect to appropriate behavior
5. Jumping on People
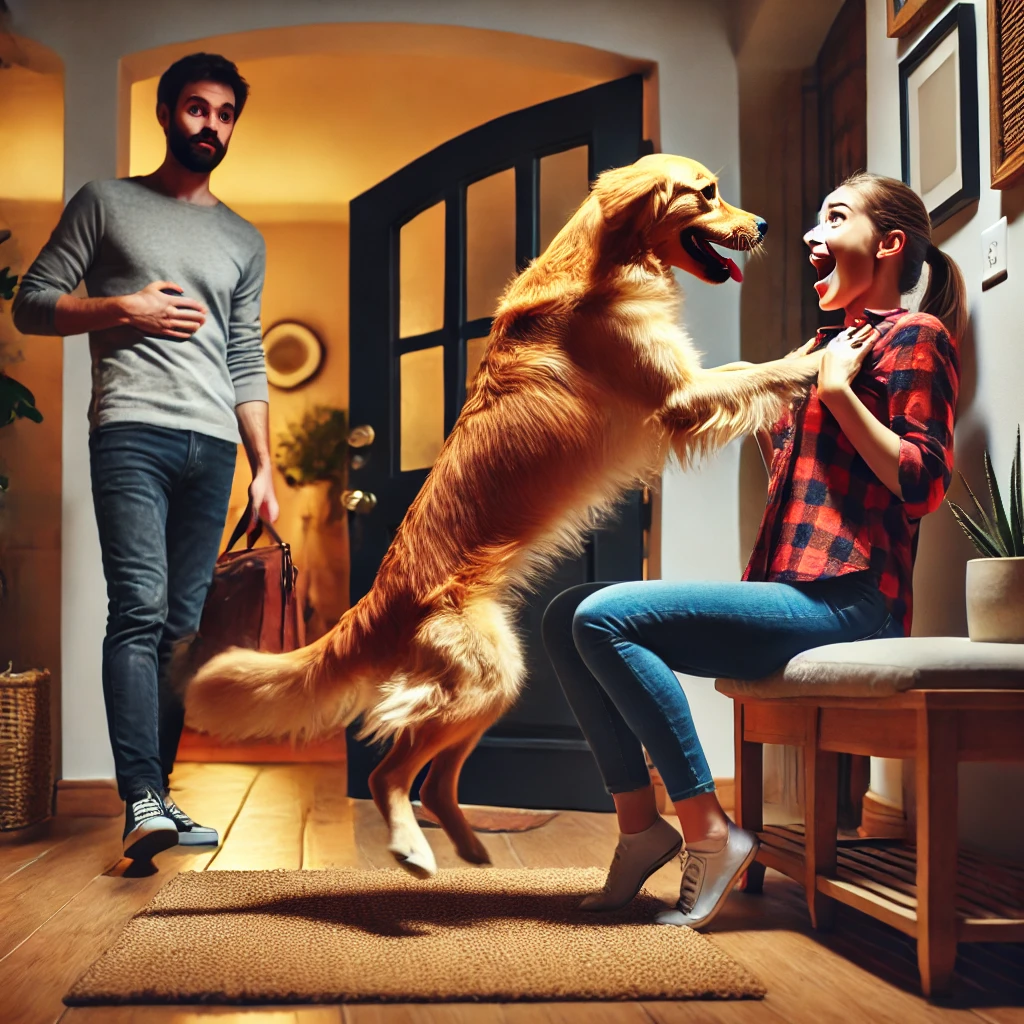

Jumping is often a sign of excitement, but it can be problematic, especially with large dogs.
Causes:
- Seeking attention
- Excitement and lack of impulse control
- Reinforcement of the behavior (owners encouraging jumping)
Solutions:
- Ignore the behavior and reward calm greetings
- Teach an alternative behavior such as “sit”
- Use consistent training with all family members
6. Leash Pulling

Dogs that pull on the leash make walks challenging and unpleasant.
Causes:
- Overexcitement
- Lack of leash training
- Desire to explore surroundings quickly
Solutions:
- Use a front-clip harness to discourage pulling
- Train using the “heel” command
- Stop walking when pulling occurs and resume only when calm
- Reinforce good behavior with treats and praise
7. Digging
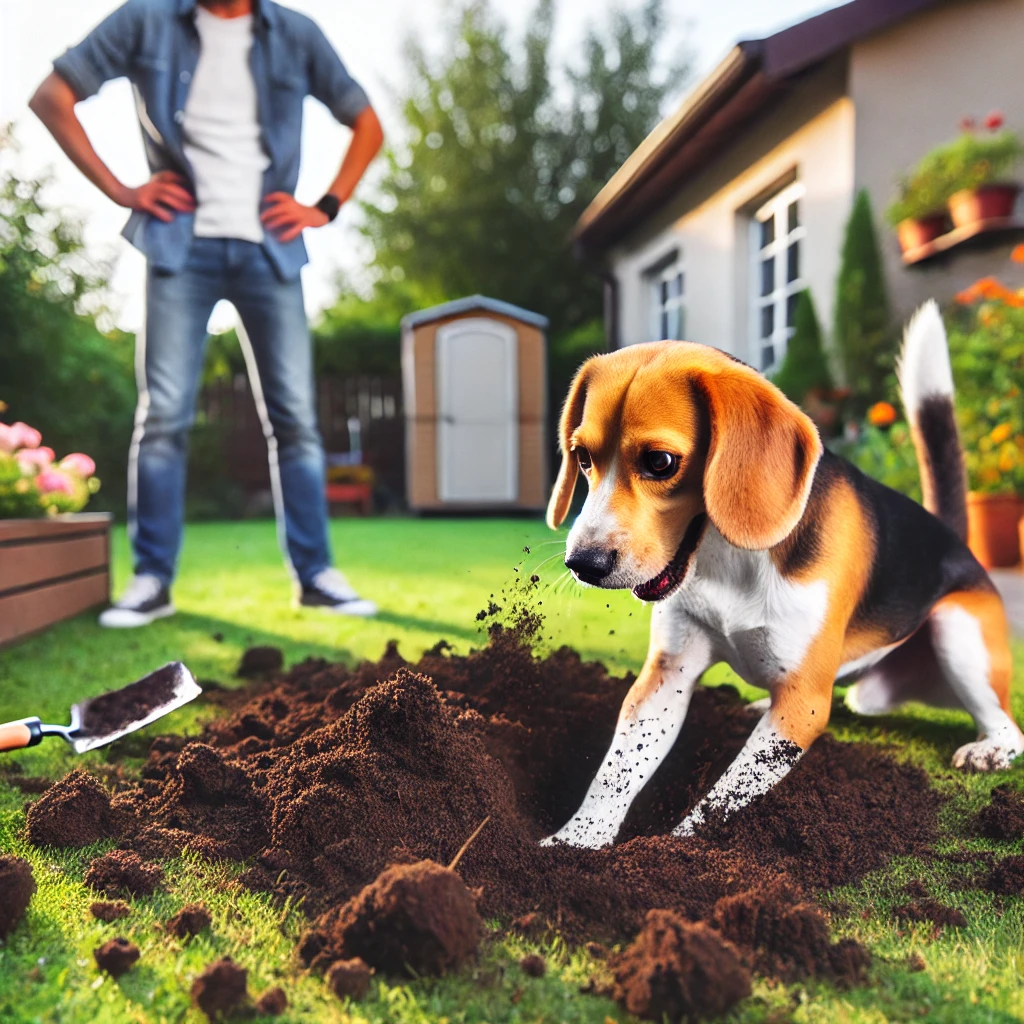

Digging is a natural instinct but can become destructive when it affects gardens and yards.
Causes:
- Boredom or excess energy
- Hunting instinct
- Seeking comfort in hot or cold weather
Solutions:
- Provide ample exercise and mental engagement
- Designate a specific digging area with loose soil or sand
- Distract with toys and activities
- Address any rodent or pest issues in the yard
8. Begging for Food

While it may seem harmless, feeding dogs from the table can reinforce bad habits.
Causes:
- Past reinforcement of begging behavior
- Hunger or interest in human food
- Lack of discipline during meal times
Solutions:
- Avoid giving food from the table
- Establish a designated feeding schedule
- Train with the “leave it” command
- Provide healthy dog treats as alternatives
9. Fearfulness and Phobias

Some dogs may display excessive fear or phobias toward certain objects, noises, or situations.
Causes:
- Traumatic past experiences
- Lack of early socialization
- Genetic predisposition
Solutions:
- Gradual desensitization and counterconditioning
- Avoid forcing the dog into fearful situations
- Provide reassurance and positive reinforcement
- Consult a behaviorist for severe phobias
10. Resource Guarding

Resource guarding occurs when a dog aggressively protects food, toys, or other valued items.
Causes:
- Instinctual survival behavior
- Fear of losing valued possessions
- Inconsistent training
Solutions:
- Teach “drop it” and “leave it” commands
- Trade valued items for treats to build trust
- Avoid punishing guarding behavior, as it can escalate aggression
- Seek professional help for severe cases
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can I tell if my dog’s behavior is normal or a problem?
If your dog’s behavior is excessive, destructive, or causing distress to you or them, it is likely a problem. Monitoring patterns and frequency can help determine whether intervention is needed.
2. Can all behavioral issues be fixed?
Most behavioral problems can be managed or corrected with patience, training, and consistency. However, some cases may require professional help from trainers or veterinarians.
3. When should I seek professional help for my dog’s behavior?
If your dog’s behavior poses a risk to themselves or others, persists despite training efforts, or worsens over time, consulting a veterinarian or behaviorist is advisable.
4. How long does it take to correct behavioral issues?
The duration varies depending on the severity of the issue, consistency in training, and the individual dog. Some problems improve within weeks, while others may take months of reinforcement.
5. Are certain breeds more prone to behavioral issues?
Some breeds have tendencies toward specific behaviors due to genetics, but environment, training, and socialization play significant roles in shaping a dog’s behavior.
Closing Statement
Understanding and addressing behavioral issues in dogs requires patience, consistency, and a positive approach. Whether through training, socialization, or professional guidance, dog owners can help their pets become well-adjusted and happy companions.
For more expert dog care tips, training guides, and breed-specific information, visit DogsReader at www.dogsreaders.com and follow us on Facebook and Instagram!
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months agoMerle Chihuahua: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months agoMaltese: A Beloved Companion
-

 Large Breeds4 months ago
Large Breeds4 months agoSamoyeds Hypoallergenic: Closer Look at the Breed
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months agoMerle Pomeranian: A Adorable Companion
-

 Large Breeds4 months ago
Large Breeds4 months agoStandard Poodle Weight: Country Wise
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS4 months agoYorkshire Terrier: a Big Personality
-

 Terrier Breeds3 months ago
Terrier Breeds3 months agoDog Breeds: by Country & Category
-

 Experts Nutritions3 months ago
Experts Nutritions3 months agoBest Dog Food: Large Breeds