Working Breeds
Golden Retriever Puppies: Genetics, Health Care

Golden Retriever Puppies

Golden Retrievers Puppies are one of the most popular dog breeds in the world, renowned for their friendly temperament, intelligence, and loyalty. Originating in Scotland in the mid-19th century, these dogs were initially bred as hunting companions, excelling in retrieving game from both land and water. Today, they are cherished as family pets, therapy animals, and service dogs. This article provides a comprehensive genetic introduction, physical characteristics, lifespan statistics, common diseases, solutions, and resources for further reading.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
https://www.youtube.com/@Dogsreaders
Genetic Introduction

Golden Retrievers are a crossbreed resulting from the mating of the now-extinct Yellow Retriever with the Tweed Water Spaniel, Irish Setter, and Bloodhound. Their genetics have been fine-tuned to emphasize traits such as a double coat for water resistance, strong retrieving instincts, and a calm temperament. They belong to the sporting group and exhibit genetic diversity within their three recognized subtypes:
- British Golden Retrievers: Distinguished by a broader skull and cream-colored coat.
- American Golden Retrievers: Slightly leaner build with a dense, golden coat.
- Canadian Golden Retrievers: Taller and lighter in color compared to the British subtype.
Genetic Traits and Lineage Information

Golden Retrievers owe their distinctive traits to specific genetic markers:
- Coat Genetics:
- The MC1R and TYRP1 genes control the pigmentation of their coat, allowing variations from light cream to deep golden shades. Selective breeding has helped maintain these appealing coat colors over generations.

- Temperament Genes:
- Genetic studies indicate that DRD4 (Dopamine receptor) and OXTR (Oxytocin receptor) play key roles in their calm and friendly disposition, as well as their high trainability and social behavior.

- Health Predispositions:
- Genes such as COL9A2 and COL11A1 have been associated with hip dysplasia, a common ailment in the breed. Additionally, mutations in the ADAMTS10 and BEST1 genes contribute to progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) and cataracts, which are prevalent in Golden Retrievers.

- Lineage Diversity:
- While the breed originated from a deliberate crossbreeding program, genetic testing shows that the three modern subtypes retain subtle variations due to geographic isolation and breeding preferences over time. For example, British Golden Retrievers often carry a higher frequency of genes related to stockier builds and cream-colored coats, while American Golden Retrievers have retained genes for agility and athleticism.

- Cancer Risk Factors:
- Unfortunately, Golden Retrievers have a higher incidence of certain cancers (e.g., hemangiosarcoma and lymphoma) due to hereditary factors. Research is ongoing to identify specific genetic markers associated with these conditions to improve screening and breeding practices.
Genetic Table of Golden Retrievers

| Trait | Gene | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Coat Color | MC1R, TYRP1 | Determines shades of cream to golden. |
| Double Coat | FGF5 | Provides water resistance and insulation. |
| Hip Dysplasia Susceptibility | COL9A2, COL11A1 | Linked to joint and cartilage development. |
| Eye Health | ADAMTS10, BEST1 | Associated with cataracts and progressive retinal atrophy (PRA). |
| Temperament Traits | DRD4, OXTR | Influence on social behavior and trainability. |
| Cancer Risk | TP53, BRCA1/BRCA2 | Linked to high cancer prevalence in the breed. |
Physical Characteristics

Golden Retrievers are medium-to-large-sized dogs, renowned for their athletic build and strikingly beautiful coat. They exhibit balanced proportions, which make them equally adept as working dogs and companions.
Size and Build
- Males typically weigh between 65-75 pounds and stand 23-24 inches tall at the shoulder.
- Females weigh 55-65 pounds and have a height range of 21.5-22.5 inches.
- Puppies grow quickly, weighing around 10-15 pounds at 8 weeks old, with an eventual growth spurt into their full size by 12-18 months.

Coat and Color
Golden Retrievers are characterized by their dense, water-resistant double coat:
- The outer coat is smooth or wavy, offering protection from elements like water and debris.
- The undercoat is soft and insulating, keeping them warm in colder climates.
- Coat colors range from light cream to deep golden, with slight feathering on the legs, chest, and tail adding elegance to their appearance.
Head and Expression

Golden Retrievers have a broad, well-defined skull with a straight muzzle and dark, friendly eyes that convey intelligence and kindness. Their medium-sized, pendant ears sit high and hang close to their cheeks, enhancing their gentle appearance.
Movement
Golden Retrievers are known for their fluid, powerful gait. Their well-angulated shoulders and muscular hindquarters enable them to move with a combination of grace and strength, whether sprinting, swimming, or walking alongside their owners.
Physical Characteristics

Table: Height and Weight
| Subcategory | Weight (lbs) | Height (in) |
| Male (Adult) | 65-75 | 23-24 |
| Female (Adult) | 55-65 | 21.5-22.5 |
| Puppy (8 weeks) | 10-15 | 7-9 |
Geographic and Climate-Based Lifespan Variations:
- Temperate Climates (e.g., USA, UK, Canada):
- Lifespan: 10–12 years.
- Golden Retrievers thrive in temperate regions due to their double coat, which insulates them against cold winters and moderate summers. Regular exercise and a balanced diet ensure longevity.
- Hot Climates (e.g., India, Middle East):
- Lifespan: 9–11 years (slightly shorter).
- Heat stress and dehydration can impact their health. Extra care with hydration, grooming to manage shedding, and controlled outdoor activities are crucial.
- Cold Climates (e.g., Scandinavia, Russia):
- Lifespan: 10–13 years.
- Their water-resistant double coat helps them adapt well to colder weather. Joint care is critical in regions with icy conditions to prevent injuries.
- High Altitudes (e.g., mountainous regions):
- Lifespan: 9–12 years.
- Increased risk of respiratory and cardiovascular strain due to lower oxygen levels. Limited strenuous activities at high altitudes are advised.
Geographic Factors Influencing Health:

- Access to Veterinary Care: Developed countries with advanced veterinary care see healthier Golden Retrievers with longer lifespans.
- Diet and Nutrition: Regions with access to premium dog food tailored to the breed’s needs have a significant positive impact on lifespan.
- Genetic Diversity: Overbreeding in some regions leads to higher genetic predispositions to diseases, reducing lifespan.
Biologically Life Span

Golden Retrievers typically live 10-12 years. Their lifespan is influenced by factors such as genetics, diet, and exercise.
Table: Life Stages
| Life Stage | Age Range | Description |
| Puppy | 0-1 year | Rapid growth, socialization, and training phase. |
| Adolescent | 1-2 years | Energetic and playful, with maturing behavior. |
| Adult | 2-7 years | Full physical and behavioral maturity. |
| Senior | 8+ years | Reduced activity, potential onset of age-related health issues. |
Golden Retrievers are prone to certain diseases due to their genetics, physiology, and lifestyle. Below is a detailed description of the most common conditions, their causes, preventive measures, and assumptions.
1. Hip Dysplasia

- Description: A genetic condition where the hip joint doesn’t fit properly into the socket, causing pain, arthritis, and reduced mobility.
- Causes:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Rapid growth during the puppy stage.
- Excessive weight or lack of exercise exacerbates symptoms.
- Prevention:
- Controlled exercise during growth stages.
- Feeding a diet designed for large-breed puppies to prevent rapid growth.
- Regular vet checkups for early detection.
- Assumptions: Dogs with balanced diets and proper exercise are less likely to show severe symptoms even if genetically predisposed.
2. Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA)

- Description: A hereditary degenerative condition of the retina that leads to blindness.
- Causes:
- Genetic mutations in the ADAMTS10 or BEST1 genes.
- Lack of genetic screening before breeding.
- Prevention:
- Conducting genetic testing for breeding dogs.
- Routine eye exams for early diagnosis.
- Assumptions: PRA cannot be cured, but its progression can be managed with supportive care.
3. Cancer (Hemangiosarcoma, Lymphoma, Mast Cell Tumors)

- Description: Golden Retrievers have one of the highest incidences of cancer among all breeds.
- Causes:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins.
- Aging increases the likelihood of mutations leading to cancer.
- Prevention:
- Regular veterinary screenings (e.g., blood tests, ultrasounds).
- Avoiding exposure to known carcinogens (e.g., pesticides).
- Assumptions: Early detection improves treatment outcomes but does not guarantee a cure.
4. Ear Infections

- Description: Floppy ears trap moisture, creating an ideal environment for bacterial or fungal infections.
- Causes:
- Swimming or bathing without proper ear drying.
- Allergies leading to inflammation.
- Poor ear hygiene.
- Prevention:
- Regularly clean ears with vet-recommended solutions.
- Dry ears thoroughly after swimming or bathing.
- Assumptions: Dogs living in humid climates are more susceptible.
5. Obesity

- Description: Excessive weight gain leads to joint issues, diabetes, and heart conditions.
- Causes:
- Overfeeding or free feeding.
- Lack of adequate exercise.
- High-calorie treats and table scraps.
- Prevention:
- Portion-controlled feeding using measured meals.
- Daily physical activities (e.g., walks, playtime).
- Weight monitoring at vet visits.
- Assumptions: Owners who are proactive with diet and exercise can significantly reduce obesity-related health risks.
6. Subaortic Stenosis (SAS)

- Description: A hereditary heart condition where blood flow is obstructed due to narrowing below the aortic valve.
- Causes:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Faulty development of the heart during gestation.
- Prevention:
- Screening breeding dogs for SAS.
- Routine cardiac checkups.
- Assumptions: Dogs diagnosed early can lead a relatively normal life with medication and lifestyle adjustments.
7. Hypothyroidism

- Description: A condition where the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones, leading to weight gain, lethargy, and coat issues.
- Causes:
- Autoimmune destruction of the thyroid gland.
- Genetic susceptibility.
- Prevention:
- Regular blood tests to monitor thyroid levels.
- Ensuring a well-balanced diet.
- Assumptions: Hypothyroidism is easily managed with daily medication.
Summary Table: Common Diseases

| Disease | Description | Prevention/Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Hip Dysplasia | Malformation of the hip joint causing pain and lameness. | Regular exercise, weight control, surgery in severe cases. |
| Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA) | Degenerative eye disease leading to blindness. | Genetic testing before breeding. |
| Cancer (e.g., Hemangiosarcoma, Lymphoma) | High cancer prevalence in this breed. | Routine vet checkups, early detection. |
| Ear Infections | Due to floppy ears and moisture retention. | Regular cleaning, keeping ears dry. |
| Obesity | Prone to overeating and weight gain. | Portion control, regular exercise. |
| Subaortic Stenosis (SAS) | Narrowing of the aorta causing heart issues. | Cardiac screening, medication as needed. |
| Hypothyroidism | Underactive thyroid leading to lethargy and coat issues. | Daily medication, routine thyroid testing. |
Recommendations for Prevention:

- Genetic Screening: Ensure breeders test for hereditary diseases like PRA, SAS, and hip dysplasia.
- Routine Vet Visits: Regular health checkups help catch diseases early.
- Diet and Exercise: Balanced nutrition and regular physical activity are essential for overall health.
- Owner Education: Understanding the breed’s health needs ensures a proactive approach to care.
Solutions and Resources

- Genetic Testing: Identify and mitigate hereditary health risks.
- Diet: Provide a high-quality, balanced diet tailored to life stage.
- Exercise: Ensure daily walks and activities to maintain physical and mental health.
- Regular Vet Visits: Early detection of diseases is crucial.
Helpful URLs

Golden Retriever Puppies: Genetics, Health Care
- American Kennel Club (AKC) Golden Retriever Page
- Golden Retriever Health Foundation
- PetMD Golden Retriever Guide
Recommended Books

- “The Art of Raising a Puppy” by The Monks of New Skete
- “Golden Retrievers for Dummies” by Nona Kilgore Bauer
- “Your Golden Retriever Puppy Month by Month” by Terry Albert
FAQs

Q1: How often should I groom my Golden Retriever puppy?
Golden Retrievers should be brushed 3-4 times a week to minimize shedding and maintain a healthy coat.
Q2: At what age should Golden Retriever puppies be spayed or neutered?
Consult your veterinarian, but typically between 12-18 months for optimal health benefits.
Q3: Are Golden Retrievers good with children?
Yes, they are known for their friendly and gentle demeanor, making them excellent family dogs.
Latest Research Summary on Golden Retrievers

Golden Retrievers have been the subject of significant research in recent years due to their popularity and unique genetic predispositions. Below is an overview of the latest findings:
1. Increased Cancer Prevalence

- Research Highlights:
- A 2023 study by the Golden Retriever Lifetime Study (GRLS), involving over 3,000 dogs, confirmed that cancer remains the leading cause of death among Golden Retrievers, with nearly 60% of the breed developing the condition.
- The most common types include hemangiosarcoma, lymphoma, and mast cell tumors.
- Researchers have identified specific genetic mutations, such as in the TP53 (tumor suppressor) gene, which may contribute to the breed’s susceptibility.
- Significance:
- Early detection strategies, such as regular ultrasounds and bloodwork, are being encouraged.
- Research is ongoing to develop gene-editing techniques and tailored treatments, such as immunotherapy, to combat these cancers.
2. Genetics of Hip Dysplasia

- Research Highlights:
- A 2022 genetic study conducted by Cornell University identified new markers linked to hip dysplasia, including mutations in the COL9A2 and COL11A1 genes.
- The study confirmed that environmental factors like weight gain and improper exercise during a puppy’s growth phase exacerbate symptoms.
- Significance:
- Breeding programs are now incorporating advanced genetic screening tools to reduce the prevalence of hip dysplasia in Golden Retrievers.
- Owners are advised to manage weight and exercise carefully, particularly during the first 18 months of life.
3. Eye Health and Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA)

- Research Highlights:
- A 2021 study from the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine identified two novel mutations in the BEST1 gene that are linked to PRA.
- PRA was found to progress faster in dogs living in regions with higher UV exposure, suggesting a potential environmental component to disease development.
- Significance:
- Advances in genetic testing now allow breeders to screen for PRA-related mutations, significantly reducing the number of affected puppies.
- Protective measures, such as UV-blocking dog goggles for outdoor activities, have been recommended in high-UV regions.
4. Obesity and Its Impact on Lifespan

- Research Highlights:
- A long-term study by Purdue University (published in 2022) revealed that obesity shortens a Golden Retriever’s lifespan by an average of 2 years.
- The study also found that nearly 40% of pet Golden Retrievers are overweight due to improper portion sizes and lack of exercise.
- Significance:
- Veterinarians are advocating for the use of body condition scoring (BCS) systems and portion-controlled feeding to maintain optimal weight.
- Nutritional research is focusing on formulating diets tailored to Golden Retrievers’ unique needs, especially those prone to obesity.
5. Advancements in Genetic Testing

- Research Highlights:
- The Canine Health Foundation (CHF) published a breakthrough in 2023, creating a comprehensive genetic panel specifically for Golden Retrievers.
- This panel screens for over 20 conditions, including cancer markers, PRA, and hip dysplasia susceptibility genes.
- Significance:
- This tool allows breeders and owners to make informed decisions about health management and breeding practices.
- Early identification of genetic risks is improving treatment outcomes for diseases like heart conditions and eye disorders.
References

- Golden Retriever Lifetime Study: www.morrisanimalfoundation.org
- Cornell University Hip Dysplasia Study: www.vet.cornell.edu
- University of Pennsylvania PRA Research: www.vet.upenn.edu
- Canine Health Foundation Research: www.akcchf.org
- Purdue University Obesity Study: www.purdue.edu
If you’d like more detail on any specific research study or want me to expand on emerging therapies and technologies, let me know!

Working Breeds
German Shepherd Exercise Blueprint: Age-Wise Workouts for Peak Performance

📢 This is Part 16 of the German Shepherd Series on DogsReader

Explore all articles in the series to master the care, training, and development of the world’s most intelligent dog breed.
🐶 Visit: www.dogsreader.com
📩 Ask our 24/7 Dog Chatbot anything – trained with official AKC knowledge!
📧 Contact: dogsreaders@gmail.com
📱 Follow us on Facebook & Instagram
▶️ [Subscribe to us on YouTube | Facebook | Instagram |
🐾 Introduction: A German Shepherd’s Body is Built for Action

Introduction: The Power of Movement
German Shepherd Exercise Blueprint: The German Shepherd is not just a loyal family companion—it’s an athlete, protector, and thinker. Exercise is the fuel that powers their mental sharpness, physical strength, and emotional balance. However, not all German Shepherds need the same workout. Puppies, adults, and senior dogs have different exercise requirements, especially across varying weather conditions and global climates.
In this award-worthy article, we’ll break down optimal workouts by age and climate, and follow it with the ultimate post-exercise nutrition and supplement guide by country and season.
🐾 German Shepherd Puppy Exercise (0–12 Months)

🧠 Key Focus:
- Growth-safe play
- Joint protection
- Controlled environments
🏋️♀️ Recommended Activities:
- 5 minutes per month of age (e.g., 3-month-old = 15 mins)
- Leash walks (short, sniffing allowed)
- Puzzle toys and hide-n-seek
- Shallow water play
- Light incline climbing (grass hills)
🌍 Country/Climate Tips:
- Cold Winters (USA, Canada, Germany): Limit outdoor time. Use boots and coats. Try indoor games.
- Hot Summers (India, UAE, Mexico): Exercise early morning or post-sunset. Avoid pavement.
- Mild Climates (UK, Australia, Japan): Year-round outdoor walking/play. Monitor for growth spurts.
🐕 German Shepherd Adult Exercise (1–6 Years)

🧠 Key Focus:
- Peak physical condition
- Endurance + agility
- Daily consistency
Goal: Peak physical performance, mental resilience, and breed-appropriate challenge.
Daily Exercise Time:
90 to 120 minutes/day, divided between morning and evening
Recommended Activities:
-
Jogging & Running beside a bike (gradual start)
-
Tug Games with Resistance
-
Advanced Fetch & Ball-Launchers
-
Agility Training (A-frames, weave poles, tunnels)
-
Tracking & Scent Work
-
Swim Training (great joint protection)
-
Protection Training / Schutzhund-style Drills (with professionals)
-
Weighted Backpack Hikes (only after 18 months)
🎯 Mix 50% physical exercise + 50% mental stimulation for balance.
Country & Climate Adaptations:

🌞 Hot Countries:
-
Schedule workouts early (before 9am) or post-sunset.
-
Prioritize shade and water.
-
Swimming is ideal!
❄️ Cold Regions:
-
Use padded gear for long treks.
-
Snow fetch is fun—but watch for ice cuts.
-
Indoor treadmill sessions for heavy snow days.
🌧 Rainy Zones:
-
Indoor agility and stair workouts.
-
Rotate with treat puzzles, hide-and-seek games, and obedience drills.
German Shepherd Senior Exercise (7+ Years)

🧠 Key Focus:
- Joint health
- Low-impact movement
- Mental stimulation
Goal: Preserve muscle tone, joint health, and cognitive sharpness.
Daily Exercise Time:
30 to 45 minutes, broken into low-impact sessions
Best Activities:
-
Leisure Walks with Scent Exploration
-
Hydrotherapy (underwater treadmills, pool swims)
-
Stretching & Balance Exercises
-
Slow Obstacle Walks
-
Basic Training Refresher Commands
-
Massage & Range-of-Motion Routines
💡 Keep it low-impact. Avoid stairs, jumping, or heavy pulling. Joint supplements like glucosamine are strongly recommended.
Climate Considerations:

-
Cold weather: Use orthopedic beds, warm coats, and paw balm.
-
Hot weather: Walk during coolest times of the day, ensure constant hydration.
-
Rainy zones: Soft indoor mats for traction; mental games for enrichment.
🗺️ Country-Wise Lifestyle Customization

| Country | Climate Type | Best Exercise Options |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Varies (state-wise) | Hiking, park fetch, seasonal agility |
| Canada | Cold | Snow play, indoor scent games, treadmill work |
| India | Hot/Humid | Early walks, indoor games, short leash runs |
| Germany | Moderate | Urban trekking, forest walks, Schutzhund |
| Australia | Hot & Dry | Beach runs, evening jogs, obstacle play |
| UK | Rainy/Cool | Indoor obstacle courses, ball play, park walks |
| UAE | Desert Heat | Pool swims, climate-controlled training centers |
⚠️ Common Mistakes to Avoid

-
Overexercising puppies or seniors
-
Ignoring climate risks (heatstroke, hypothermia)
-
Not varying routines—boredom = behavior problems
-
Exercising immediately after meals
-
Skipping warm-ups and cool-downs
🎖 Pro Tip: Weekly Rotation Chart (Sample)

| Day | Activity Mix |
|---|---|
| Monday | Obedience + Scent work |
| Tuesday | Jog + Agility + Fetch |
| Wednesday | Off-leash Trail Hike |
| Thursday | Rest day + Puzzle Games |
| Friday | Tracking Game + Basic Commands Review |
| Saturday | Long Walk + Park Socialization |
| Sunday | Tug Game + Brain Toy Challenge |
🧠 Exercise is a Lifetime Contract
From puppy play to senior strolls, exercise isn’t just about energy release—it’s about mental health, bonding, and unlocking the legendary potential of the German Shepherd. Adapt to their age, adjust to your country, and stay consistent.
A tired German Shepherd is a happy, well-behaved one.
🥩 Post-Exercise Nutrition & Supplements by Age, Season, and Region

📊 Country-Wise + Seasonal Nutrition Table
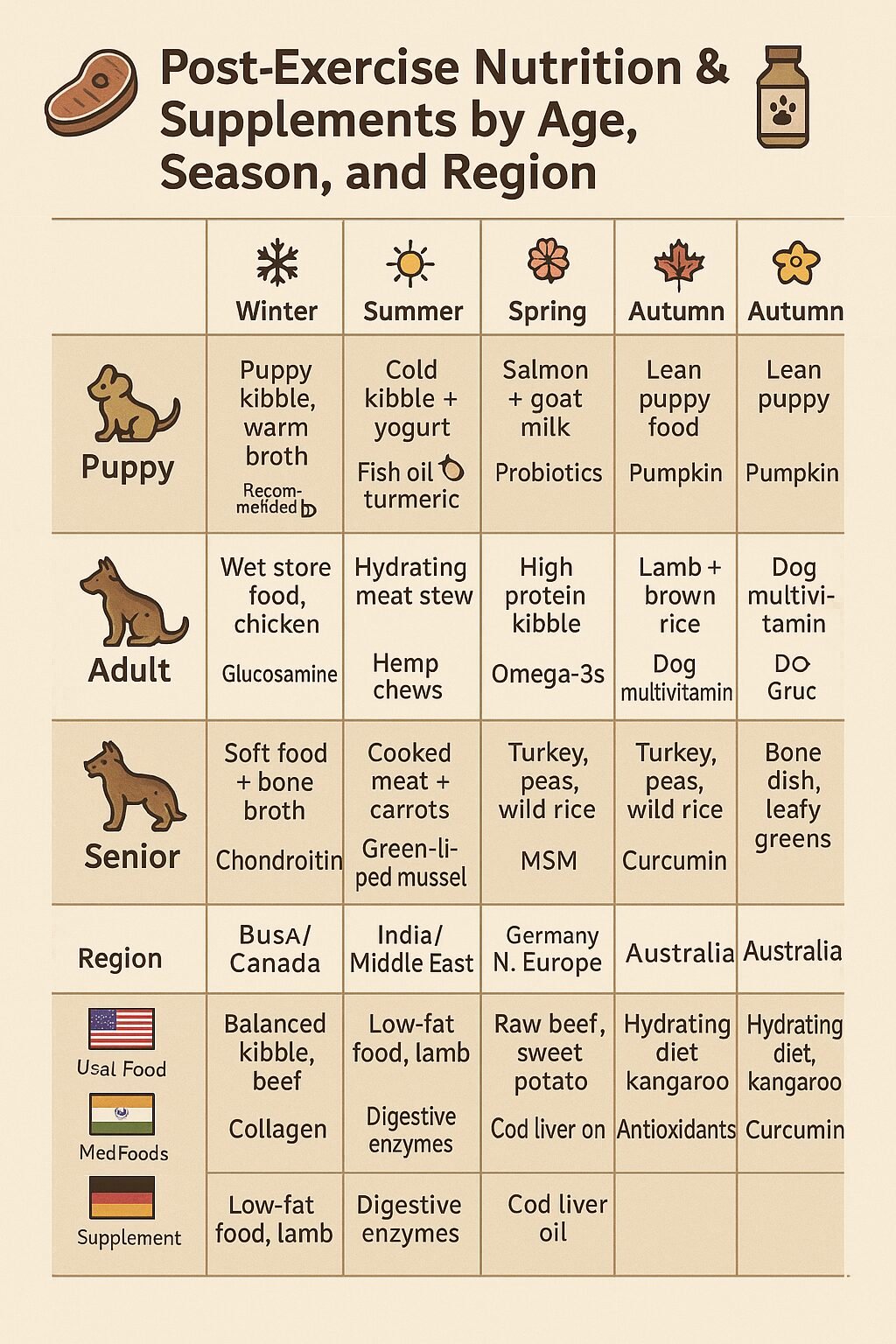
Click Any Picture To Buy From Amazon
| Life Stage | Season | Countries | Ideal Foods Post Exercise | Recommended Supplements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Puppy | Winter | USA, Germany, Canada | Warm broth over high-protein kibble | Fish oil,
|
| Summer | India, UAE, Mexico | Cold goat milk, puppy biscuits, chicken & rice | Probiotics,
|
|
| Spring | UK, Japan, France | Raw-fed mix or soft meat blend | DHA,
|
|
| Autumn | USA, Australia, Europe | High-calorie puppy mash | Digestive enzymes,
|
|
| Adult | Winter | Russia, Canada, USA | Lamb, brown rice, steamed veggies | Glucosamine, Omega-3s, Multivitamin |
| Summer | Brazil, India, UAE | Lean fish, quinoa, pumpkin | Electrolytes, Joint support
|
|
| Spring | USA, UK, Australia | Chicken, oats, carrots | Liver tonic,Taurine
|
|
| Autumn | Germany, France, Japan | Beef stew, boiled egg | Vitamin B complex,
|
|
| Senior | Winter | Canada, Poland, Norway | Soft turkey or salmon, mashed sweet potato | Joint formula, Turmeric
|
| Summer | India, UAE, Mexico | Cold cottage cheese, papaya cubes | Probiotics,
|
|
| Spring | UK, Japan, USA | Chicken broth soup with rice | Ginseng, Eye health blend, Anti-inflammatory herbs | |
| Autumn | France, Germany, Spain | Softened kibble, sardines | Bone density mix,
|
💡 Always offer fresh water post-exercise and wait 30–45 minutes before feeding to prevent bloating in deep-chested breeds like the German Shepherd.
Closing Statement: The Body Fuels the Mind
Your German Shepherd’s physical routine should evolve with time, age, climate, and geography. By tuning into their changing needs and pairing exercise with proper nutrition, you not only extend their life—you enhance their spirit. Whether bounding through snow or strolling in spring rain, your GSD thrives when the body and mind move in harmony.
📌 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

❓ How much exercise does a German Shepherd puppy need?
A German Shepherd puppy should follow the “5-minute rule” — 5 minutes of exercise per month of age, up to twice a day. For example, a 4-month-old puppy should get 20 minutes of light, controlled activity twice daily.
❓ Can I over-exercise my German Shepherd?
Yes, over-exercising can harm joints, especially in puppies and senior dogs. Always tailor workouts based on your dog’s age, health, and weather conditions.
❓ What are the best exercises for a senior German Shepherd?

Low-impact activities like walking on soft ground, swimming, and mental enrichment games (e.g., treat puzzles or nose work) are ideal for seniors to maintain health without stressing joints.
❓ Are there different exercises for German Shepherds in hot vs. cold climates?
Absolutely. In hot climates, focus on swimming, early morning walks, and shaded play. In cold climates, use coats and booties and try indoor games or snow walks if safe.
❓ What’s the ideal post-exercise diet for a German Shepherd?
Post-exercise meals should be given 30–45 minutes later to avoid bloat. Focus on lean protein, moderate carbs, and supplements based on age and season—like joint support for seniors or probiotics in summer.
❓ Do German Shepherds need different exercises based on country or region?
Yes. Factors like humidity, temperature, and terrain impact your dog’s energy needs. For instance, sled pulling works in snowy Canada, while shaded trail hikes suit tropical regions like India or Brazil.

Working Breeds
German Shepherd Training Unleashed: Full Command Control for Real-World Brilliance

📢 This is Part 15 of the German Shepherd Series on DogsReader

Explore the full series and gain expert insights into one of the world’s most intelligent breeds.
🐶 Visit: www.dogsreader.com
📩 Ask our 24/7 Dog Chatbot anything – trained with official AKC knowledge!
📧 Contact: dogsreaders@gmail.com
📱 Follow us on Facebook & Instagram
▶️ [Subscribe to us on YouTube | Facebook | Instagram |
Introduction: Beyond Sit and Stay

German Shepherd Training Unleashed: German Shepherds aren’t just dogs – they’re highly capable partners in action. With their sharp minds, drive to learn, and desire to please, these dogs are engineered for excellence. Whether you’re training for obedience, protection, or working roles, mastering the right commands can transform your German Shepherd into a true champion.
In this article, we guide you through the essential, intermediate, and advanced command stages to unlock your German Shepherd’s full working potential.
1. Understanding Command Training Philosophy

Before diving into the actual commands, it’s important to grasp the mindset of the German Shepherd:
- They thrive on structure.
- They bond deeply with their trainer.
- They excel with consistency and challenge.
Whether it’s a family environment or a police academy, the foundational training principle remains the same: clear leadership, positive reinforcement, and purposeful progression.
2. Basic Obedience Commands (Foundation Stage)

These form the groundwork for all future training:
- Sit
- Stay
- Come
- Down
- Heel
- Leave it
- No
These commands should be taught with:
- Short daily sessions
- Positive reward systems (treats, praise, or toy)
- Clear voice tones and consistent gestures
🧠 Pro Tip: Teach hand signals with each verbal cue to reinforce long-distance control.
3. Intermediate Working Commands (Real-World Integration)

Once your dog masters the basics, they’re ready for more complex and practical training:
- Wait (Useful for doors, vehicles, food bowls)
- Watch me (For focus in high-distraction areas)
- Place (Go to a specific location and stay)
- Back up (Create space on command)
- Take it / Drop it (Retrieve or release items)
- Speak / Quiet (Controlled barking – excellent for alert or protection dogs)
These commands increase control and mental stimulation while preparing your dog for either professional duties or elevated home discipline.
4. Advanced Commands (Working & Professional Environments)

These are tailored for dogs being trained as K9 units, military dogs, service dogs, or high-discipline family companions:
- Search (Find a person or item)
- Track (Follow scent)
- Guard (Take protective stance)
- Bite / Release (Used in police or protection training only under professional guidance)
- Escort / Block (Walk beside or prevent others from approaching)
- Silent Commands (Training via signals alone)
📌 Important: Advanced commands must be taught with precision and care. In protection work, always consult a professional trainer to avoid behavioral risks.
5. Command Drills: Keeping Your German Shepherd Sharp

Repetition keeps your GSD engaged and responsive. Here are suggested drills:
- Command Chain Training (Link 3-5 commands in succession)
- Distraction Drills (Train in parks, busy areas, or with other dogs around)
- Distance Recall Challenges (Test “Come” command from long distances)
- Obstacle Work (Combine physical tasks with commands: sit on platform, jump, stay)
💡 Weekly refreshers keep even senior German Shepherds mentally young.
6. Common Training Mistakes to Avoid

- Mixing up commands
- Changing tone inconsistently
- Training while distracted or frustrated
- Over-rewarding or confusing the reward timing
- Using punishment instead of correction
📣 Consistency + Patience = Success
7. Creating Your Own Custom Command List

You can personalize your GSD’s command set to suit your lifestyle:
- “Go get the leash”
- “Turn off the light”
- “Find [name]”
- “Get the keys”
The key is to connect action with reward and keep commands short and clear.
Closing Statement : A Dog That Thinks Before Acting

When trained well, a German Shepherd doesn’t just follow commands – they anticipate them. You’re not just raising a pet; you’re raising a partner. Through discipline, consistency, and love, your German Shepherd can achieve a level of intelligence and control few breeds can match.
Stay tuned for Part 16 in the German Shepherd Series, only on DogsReader.
🐾 Frequently Asked Questions – Mastering Commands: German Shepherd Training

1. What are the most important commands every German Shepherd should know?
Basic commands such as Sit, Stay, Come, Heel, Down, and No are essential for obedience. Intermediate and advanced commands like Search, Guard, Track, and Silent Commands help unlock their full working potential.
2. At what age should I start command training for my German Shepherd?
You can begin basic command training as early as 8 weeks old using positive reinforcement. More advanced training should wait until the dog is physically and mentally ready, around 6 months and older.
3. How long does it take to train a German Shepherd in commands?
Most German Shepherds grasp basic commands in 2–4 weeks with consistent training. Advanced command mastery for working purposes may take several months to a year, depending on the dog and trainer’s experience.
4. Can German Shepherds learn commands in multiple languages?

Yes, German Shepherds can learn commands in any language, including German, English, or hand signals. Many working dogs are trained in German to avoid confusion in public environments.
5. What’s the difference between obedience and working dog commands?

Obedience commands are for home behavior and safety (like Sit or Stay). Working dog commands include advanced instructions like Track, Guard, Search, and Bite/Release used in police, military, or service dog roles.
6. Should I use hand signals or verbal cues when training?
Ideally, you should use both hand signals and verbal cues during training. This ensures your German Shepherd understands commands visually and audibly, which is especially helpful in loud or distracting environments.
7. Can an older German Shepherd still learn new commands?

Absolutely. German Shepherds are highly intelligent at any age. While puppies learn faster, adult and senior dogs can still be trained effectively with the right approach and consistency.
8. Are German Shepherds good at remembering commands long-term?
Yes, German Shepherds have exceptional memory retention when trained properly. They can remember commands for months or even years with periodic refreshers.

Working Breeds
German Shepherd Intelligence: Uncovered Mind, Memory, and Mental Mastery
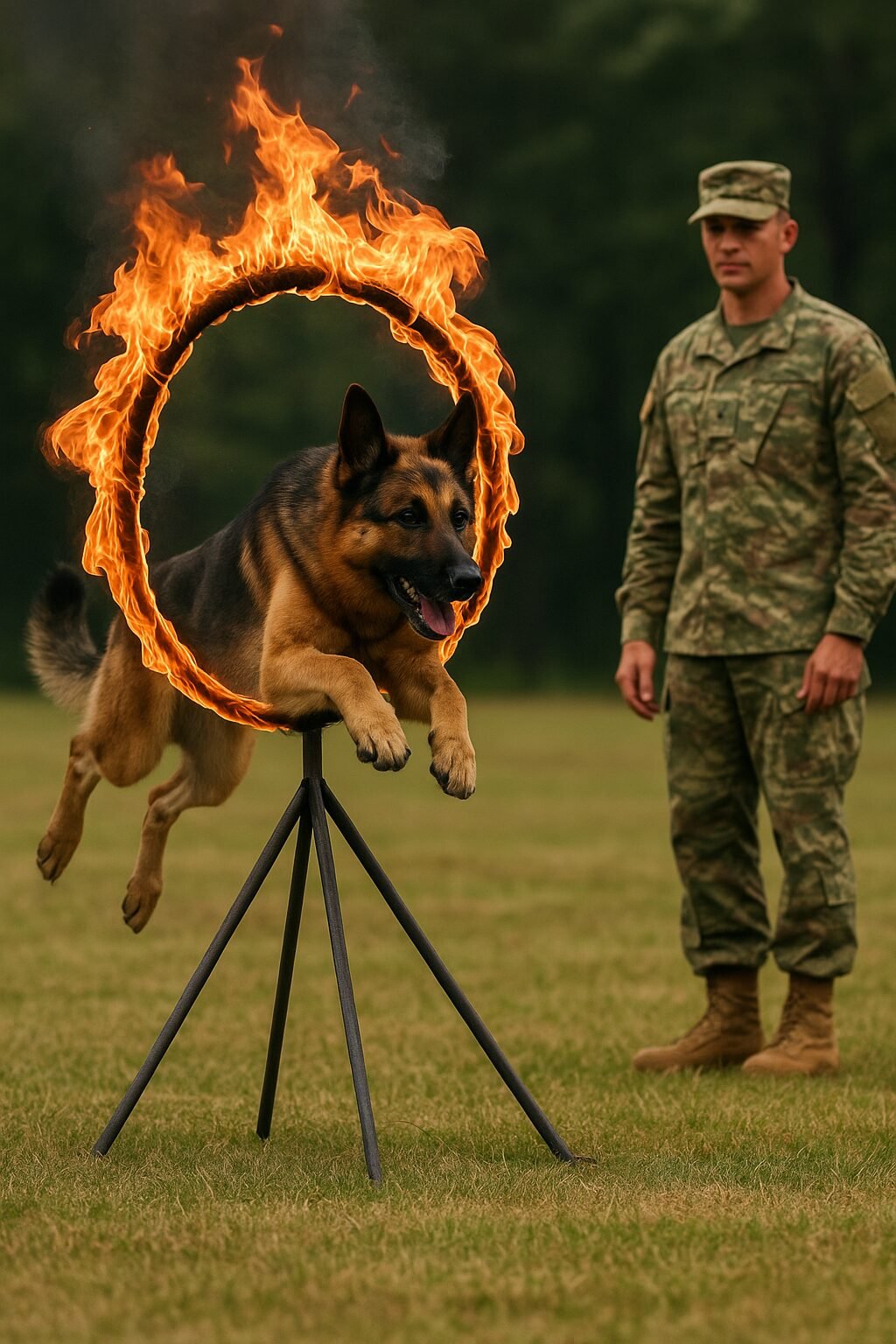

📍 Part 14 of the German Shepherd Series on DogsReader
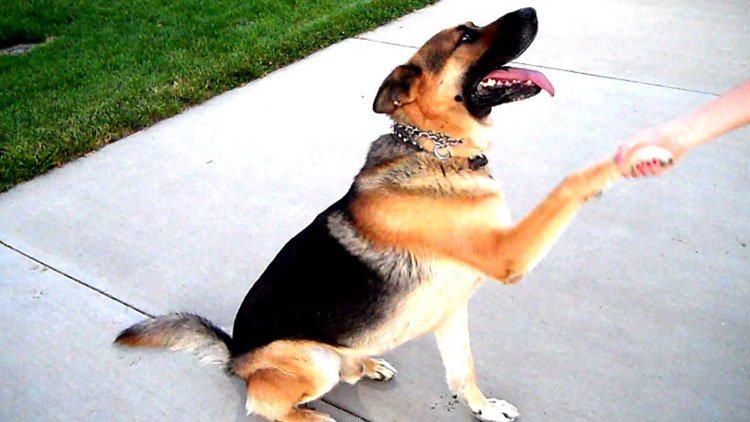

Introduction: Why German Shepherds Are Considered Canine Geniuses
German Shepherd Intelligence : German Shepherds aren’t just working dogs — they’re intellectual powerhouses. From police forces to therapy roles, their brainpower is what sets them apart. In this 15th installment of the DogsReader German Shepherd Series, we uncover the layers of intelligence that make the breed one of the most trainable and dependable dogs in the world.
Mental Capacity: Ranking the German Shepherd’s Intelligence
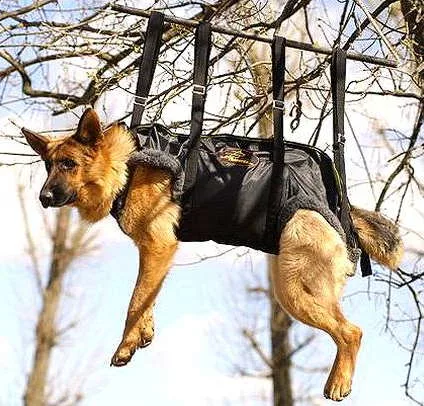

According to renowned canine psychologist Stanley Coren, German Shepherds rank 3rd among the most intelligent dog breeds, right after the Border Collie and Poodle. But their intelligence is not just about performing tricks — it includes:
-
Working Intelligence: Quick command response time
-
Adaptive Intelligence: Problem-solving based on real-life experiences
-
Instinctive Intelligence: Natural ability to guard, herd, and protect
Short-Term Memory vs. Long-Term Memory in GSDs
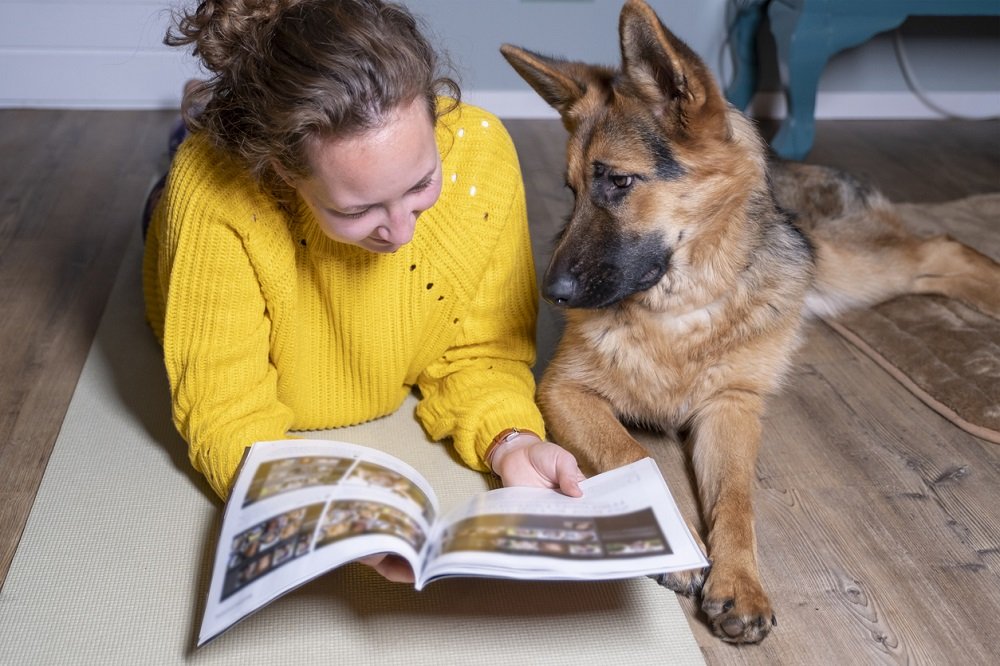

German Shepherds are capable of retaining both short-term and long-term memories.
-
Short-Term Memory: Allows them to react and learn commands within seconds
-
Long-Term Memory: Enables them to remember people, places, and training even after months or years
➡️ This is why military and police units invest in them – their memory retention is unmatched.
Mind Mapping & Cognitive Training

GSDs have the ability to mentally “map” their environment. With consistent training, they learn:
-
Names of toys and family members
-
Task sequences in protection or obedience routines
🧠 Mental stimulation is just as important as physical exercise. Neglecting either can lead to behavioral issues.
Examples of Mental Mastery in Real Life

Here are true-to-life demonstrations of the breed’s cognitive excellence:
-
A retired K9 officer named Max once tracked a missing child 2 miles away using only a blanket as a scent source.
-
Luna, a therapy German Shepherd, learned to recognize anxiety attacks in her owner before visible symptoms occurred.
-
In competitive obedience, German Shepherds consistently outperform other breeds in multi-step routines.
Best Brain Games to Unlock Full Potential

-
Find the Treat: Enhances scent memory and reward-driven focus
-
Puzzle Toys: Keeps their problem-solving skills sharp
-
Name That Toy: Teach them toy names for vocabulary expansion
-
Hide and Seek: Stimulates hunting instincts and recall memory
-
Command Chains: Train your dog to follow multi-step commands
💡 DogsReader Tip: Change up the difficulty level every week to avoid cognitive stagnation.
How to Identify Cognitive Decline Early

Even the smartest dogs age. Watch for signs such as:
-
Hesitation in routine tasks
-
Forgetting commands
-
Disorientation in familiar environments
-
Increased anxiety or restlessness
📌 Early diagnosis leads to better mental wellness treatment — explore our upcoming article on “Senior Care for German Shepherds.”
Closing Statement : The Mental Marvel That Is the German Shepherd

Their intelligence is not just in obedience — it’s in their emotional depth, decision-making ability, and working dedication. From pup to elite performer, a German Shepherd’s brain deserves to be nurtured just as much as their body.
📢 This is Part 14 of the German Shepherd Series on DogsReader
Discover all parts of the series and exclusive dog care knowledge on our website.
🐶 Visit: www.dogsreader.com
📩 Ask our 24/7 Dog Chatbot anything – trained with official AKC knowledge!
📧 Contact: dogsreaders@gmail.com
📱 Follow us on Facebook & Instagram [Subscribe to us on YouTube | Facebook | Instagram | www.dogsreader.com]
▶️ Subscribe to us on YouTube!
FAQs
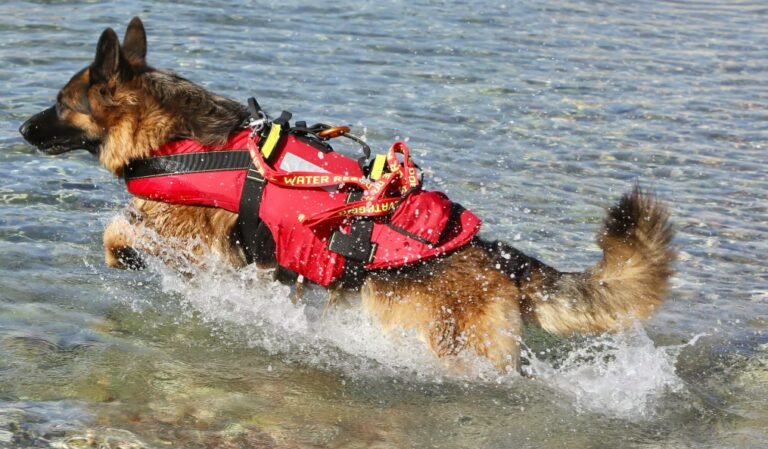

“German Shepherd Intelligence Uncovered: Mind, Memory, and Mental Mastery”
1. Are German Shepherds really smarter than other dog breeds?
Yes, German Shepherds are ranked as the third most intelligent dog breed in the world. Their quick learning, emotional intelligence, and memory retention make them top performers in obedience, protection, and service roles.
2. How intelligent is a German Shepherd compared to a human?
A well-trained adult German Shepherd has cognitive skills comparable to a 2.5 to 3-year-old human child. They understand hundreds of words, can follow multi-step commands, and even interpret emotions.
3. Can German Shepherds remember their owners after years?

Absolutely. Thanks to their strong long-term memory, German Shepherds can remember their owners, voices, and environments even after being separated for several years.
4. What kind of mental games do German Shepherds like?
German Shepherds enjoy puzzle toys, scent games, name-learning challenges, and hide-and-seek. These games stimulate their brain, reduce anxiety, and prevent boredom-related behaviors.
5. Do German Shepherds have better memory than other breeds?
Yes. Their working memory and adaptive intelligence are superior to many other breeds, which is why they excel in military, police, and therapy roles.
6. How can I test my German Shepherd’s intelligence at home?
Simple games like “which hand has the treat,” toy name recognition, or obstacle challenges can help test your German Shepherd’s problem-solving ability and memory recall at home.
7. How much mental stimulation does a German Shepherd need daily?

A German Shepherd needs at least 30–45 minutes of mental enrichment daily in addition to physical exercise. Without it, they can become restless, destructive, or depressed.
8. Can German Shepherds suffer from memory loss or dementia?
Yes, senior German Shepherds can develop Canine Cognitive Dysfunction (CCD), similar to dementia in humans. Early signs include confusion, changes in sleep, and forgetting commands.
9. What is the best age to start brain training for a German Shepherd puppy?
You can begin simple mental games and memory exercises as early as 8 weeks old. Start with basic commands and short tasks, then gradually increase difficulty.
10. How do police German Shepherds train their memory so well?
They undergo repetition-based and scenario-driven training that conditions them to remember commands, scents, routines, and locations even under stress or distraction.

-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months agoMerle Chihuahua: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months agoMaltese: A Beloved Companion
-

 Large Breeds4 months ago
Large Breeds4 months agoSamoyeds Hypoallergenic: Closer Look at the Breed
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months agoMerle Pomeranian: A Adorable Companion
-

 Large Breeds4 months ago
Large Breeds4 months agoStandard Poodle Weight: Country Wise
-

 MEDIUM BREEDS4 months ago
MEDIUM BREEDS4 months agoAmerican Water Spaniel Colors Chocolate In Crcols:
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months agoYorkshire Terrier: a Big Personality
-

 Terrier Breeds3 months ago
Terrier Breeds3 months agoDog Breeds: by Country & Category