Giant Breeds
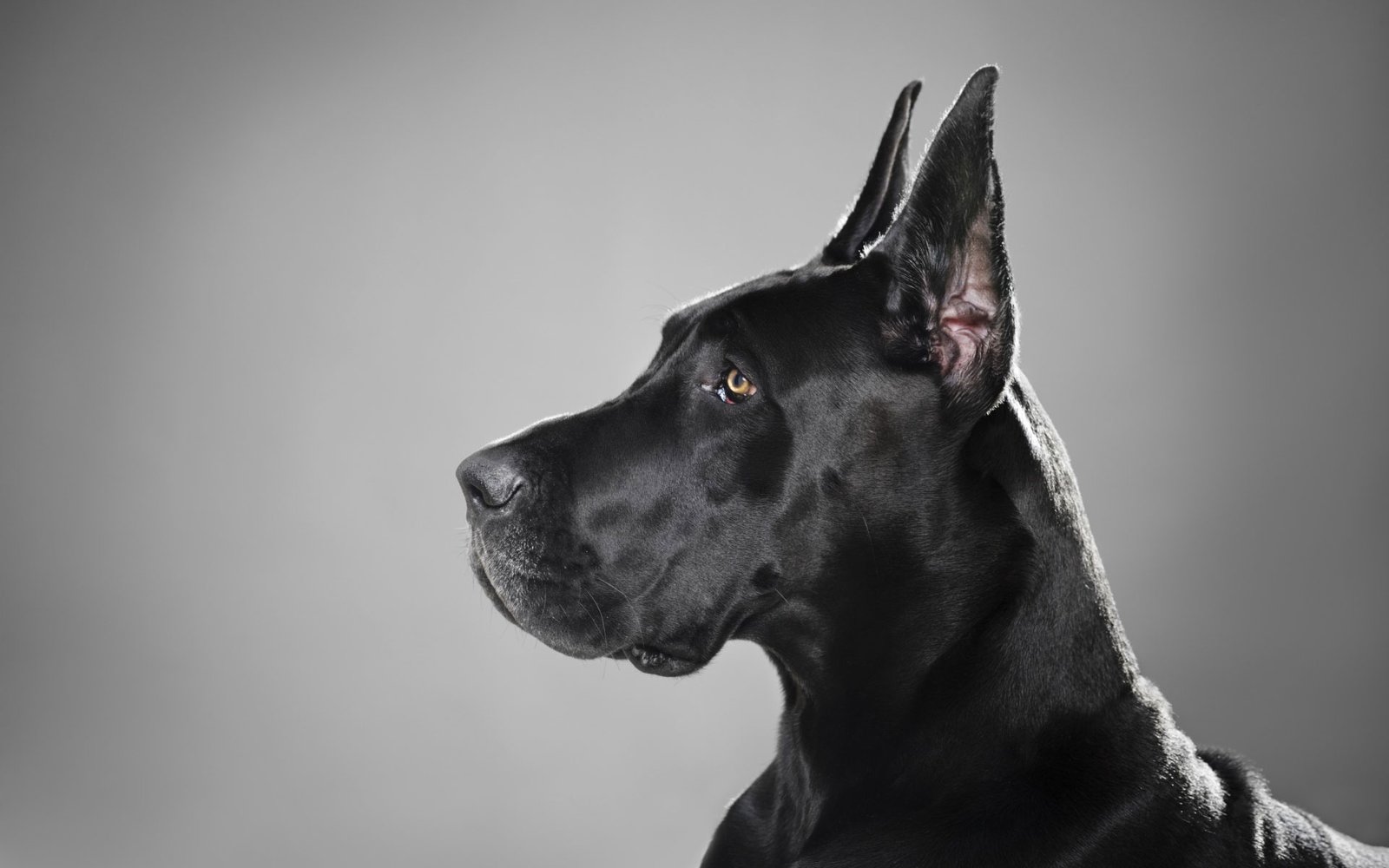
Great Dane:The Gentle Giant Dog

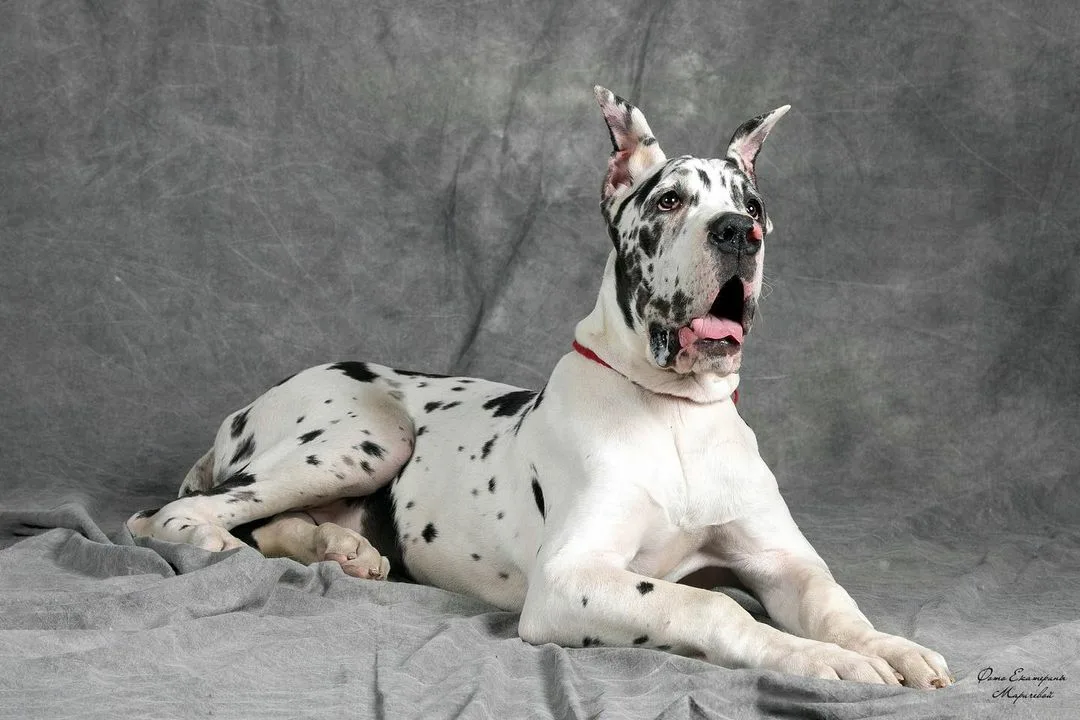
The Great Dane, often referred to as the “gentle giant” of the canine kingdom, is a breed that captivates hearts with its imposing size and refined demeanor. Known for their towering stature, affectionate personalities, and regal appearance, Great Danes have a unique charm that makes them a favorite among dog enthusiasts worldwide.
Whether you’re considering adding a Great Dane to your family or simply want to learn more about this majestic breed, this article will guide you through their history, traits, care needs, and more.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
https://www.youtube.com/@Dogsreaders

A Brief History of the Great Dane
The Great Dane’s origins can be traced back over 400 years to Germany, where they were initially bred as hunting dogs. Known as “boar hounds,” these dogs were tasked with hunting wild boars, a role that requires strength, speed, and courage.

Over time, as hunting became less common, the breed evolved into a companion animal, admired for its noble looks and friendly disposition. Despite its name, the Great Dane is not Danish, but owes its moniker to French naturalist Georges-Louis Leclerc, who mistakenly associated the breed with Denmark.

Physical Characteristics
When you think of a Great Dane, their remarkable size likely comes to mind first. These dogs are one of the tallest breeds in the world, with males standing between 30-34 inches at the shoulder and females slightly smaller at 28-32 inches. Weighing between 100-200 pounds, their size is undeniably impressive, without being bulky or clumsy.
Their coats are short, sleek, and smooth, making grooming a breeze. Great Danes come in various colors and patterns, including fawn, brindle, black, blue, harlequin (white with irregular black patches), and mantle. Each color variation adds to their distinguished appearance.

Temperament and Personality
Beneath their towering frame lies a heart full of affection and loyalty. Great Danes are renowned for their gentle and friendly nature, earning them the nickname “gentle giant.” They are excellent family dogs, known to be great with children and other pets. Despite their size, they are surprisingly calm and well-mannered indoors, making them suitable for homes of all sizes.
Great Danes are intelligent and eager to please, which makes training relatively straightforward. However, their sheer size means early training and socialization are essential to ensure they grow up to be well-behaved companions.
While they are generally not aggressive, their protective nature makes them excellent watchdogs. They will bark to alert their owners when something seems amiss, but they are not prone to unnecessary barking.

Caring for a Great Dane
Owning a Great Dane is rewarding, but it comes with responsibilities that potential owners should consider.
1. Diet and Exercise
Great Danes require a balanced diet tailored to their size and activity level. High-quality dog food that supports large-breed growth is crucial, especially during their puppy years, to prevent joint and bone issues. Portions should be carefully monitored, as overeating can lead to obesity and associated health problems.
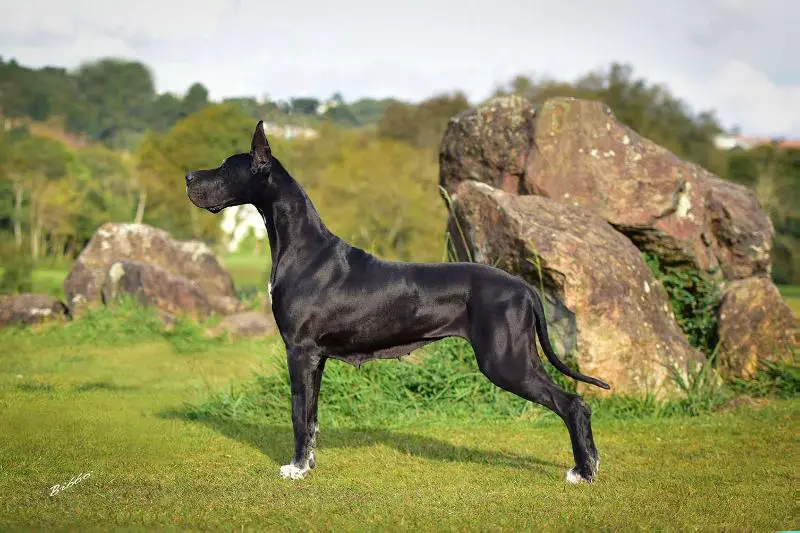

While they don’t need as much exercise as other large breeds, regular walks and playtime are necessary to keep them healthy and happy. Avoid strenuous activities or jumping, especially during their growing phase, as this can strain their developing joints.
2. Health Considerations
Great Danes are generally healthy, but are prone to certain breed-specific health issues, including:
- Bloat (Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus): A potentially life-threatening condition that affects large, deep-chested breeds. It’s crucial to monitor mealtimes and avoid vigorous activities after eating.
- Hip Dysplasia: A genetic condition where the hip joint doesn’t fit properly into the socket.
- Heart Disease: Dilated cardiomyopathy is a concern among Great Danes.
Routine veterinary check-ups and a proactive approach to preventive care can help ensure your Great Dane leads a healthy life.

3. Grooming and Maintenance
Great Danes are low-maintenance when it comes to grooming. Weekly brushing will keep their coat smooth and shiny, and baths can be given as needed. Their nails should be trimmed regularly, as overly long nails can cause discomfort or walking issues.
4. Space and Comfort
Despite their size, Great Danes are often described as “lap dogs” at heart. They love to be close to their humans and often forget how large they are! Providing a comfortable space with a large dog bed and room to stretch out is important.

Is a Great Dane Right for You?
Great Danes are loving, loyal, and majestic companions, but they aren’t the right fit for everyone. Their size alone can be a challenge, from finding space in your home to managing costs for food, veterinary care, and larger accessories like crates and beds. They also have a shorter lifespan compared to smaller breeds, typically living 7-10 years, which can be a consideration for some pet owners.
However, for those who have the space, time, and love to give, a Great Dane can bring immeasurable joy and companionship. Their loyal, gentle nature makes them wonderful family pets and formidable protectors.

Seasonal Foods Table
Below is a table summarizing popular seasonal foods and their availability throughout the year:
|
Season |
Foods |
|---|---|
|
Spring |
Asparagus, Artichokes, Strawberries, Peas, Radishes, Spinach |
|
Summer |
Watermelon, Corn, Zucchini, Tomatoes, Peaches, Cucumbers |
|
Fall |
Pumpkins, Apples, Sweet Potatoes, Pears, Squash, Brussels sprouts |
|
Winter |
Oranges, Kale, Pomegranates, Beets, Turnips, Carrots |
Eating seasonally not only ensures produce is fresh and flavorful, but also supports local farming and sustainability.

Recommended Books on Great Danes
If you’re looking to learn more about Great Danes, whether you’re a current owner or considering bringing one into your life, there are several excellent books available that provide valuable insights. Here are a few recommendations:
- “The Great Dane Handbook” by Linda Whitwam
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about raising, training, and caring for a Great Dane. It includes tips for first-time owners, health advice, and insights into the breed’s unique characteristics.
- “Great Danes (Complete Pet Owner’s Manual)” by Joe Stahlkuppe
A handy guide for new and experienced owners alike, this book provides detailed information about the breed, from grooming and feeding to training and health considerations.

- “Great Dane Training Guide” by Cesar Troy
Focused on training, this book illustrates effective, breed-specific techniques for obedience, socialization, and house training. It’s particularly helpful for first-time dog owners.
- “The Great Dane Care Guide” by Adam Campbell
This book emphasizes responsible ownership, including advice on nutrition, exercise, and creating a comfortable environment tailored to a Great Dane’s needs.
- “Great Dane Chronicles: Tales, Tips, and Care” by Grace Harper
A mix of personal anecdotes, practical advice, and breed-specific tips, this book is a delightful and informative read for Great Dane enthusiasts.
These books can serve as essential resources to help you understand the majestic nature of Great Danes and ensure your pet leads a happy and healthy life.

Latest Health Research on Great Danes
Ongoing research continues to provide critical insights into the health and well-being of Great Danes. Recent studies have focused on genetic predispositions and lifestyle factors that can impact their longevity and quality of life.
For example, advancements in understanding dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) have identified specific nutritional and genetic links that breeders and owners should be aware of. Feeding a balanced diet with optimal taurine levels has been suggested as a preventative measure, though more research is ongoing in this area (FDA’s Update on DCM and Grain-Free Food).
Recent developments in managing hip dysplasia have also been promising, with innovative therapies like stem cell treatments showing potential to improve mobility and reduce pain in affected dogs. To learn more about hip dysplasia and available treatments, visit the official American Kennel Club Canine Health Foundation (AKC Canine Health Foundation).

For addressing bloat (Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus), veterinarians now often recommend prophylactic gastropexy for at-risk breeds, including Great Danes, especially during spaying or neutering. This procedure significantly reduces the risk of this life-threatening condition. For further guidance, consult resources from the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA on Canine Bloat).
Stay informed about the latest health research, and maintaining close communication with your veterinarian are critical steps in ensuring your Great Dane leads a healthy and fulfilling life.
FAQs
1. How much space does a Great Dane need?
While Great Danes can adapt to living in smaller spaces like apartments, they thrive in homes with enough room to move around comfortably. It’s essential to provide them with a large bed or designated resting area, and regular outdoor exercise to keep them healthy and happy.
2. Are Great Danes good with children and other pets?
Yes, Great Danes are known for their gentle and loving nature, making them great companions for children. They are usually friendly with other pets, but early socialization and proper introductions are important to ensure positive relationships.
3. What is the average cost of owning a Great Dane?
The cost of owning a Great Dane includes food, veterinary care, grooming, accessories, and possible training. Due to their size, these costs can be significant. On average, expect to spend several thousand dollars per year, with higher initial costs for adoption or purchasing from a breeder.

4. How much exercise does a Great Dane need?
Great Danes require moderate exercise. Daily walks and some playtime are sufficient to meet their energy needs. However, avoid overly strenuous activities, especially when they are still growing, to prevent stress on their joints and bones.
5. Do Great Danes shed a lot?
Great Danes shed moderately throughout the year, with heavier shedding during seasonal changes. Regular brushing can help manage shedding and keep their coat healthy.
6. What are common health issues in Great Danes?
Some common health issues in Great Danes include hip dysplasia, dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), and bloat (Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus). Regular veterinary checkups and preventive care are crucial for managing these risks and maintaining their health.

7. How long do Great Danes typically live?
Great Danes have a shorter lifespan than many other dog breeds, typically ranging from 7 to 10 years. Proper care, a balanced diet, and regular vet visits can help extend their lifespan and improve their quality of life.
8. Are Great Danes difficult to train?
Great Danes are intelligent and typically eager to please, which makes them relatively easy to train. Positive reinforcement methods work best, and consistent training from a young age helps them become well-mannered adults.

9. Do Great Danes bark a lot?
Great Danes are not known to be excessive barkers. They are generally calm and reserved, but will alert their owners to strangers or unusual activity, making them good watchdogs.
10. Can Great Danes be left alone for long periods?
While Great Danes are independent, they are also social dogs that form strong bonds with their families. Leaving them alone for extended periods can lead to separation anxiety and destructive behaviors. Regular companionship and interaction are important for their well-being.
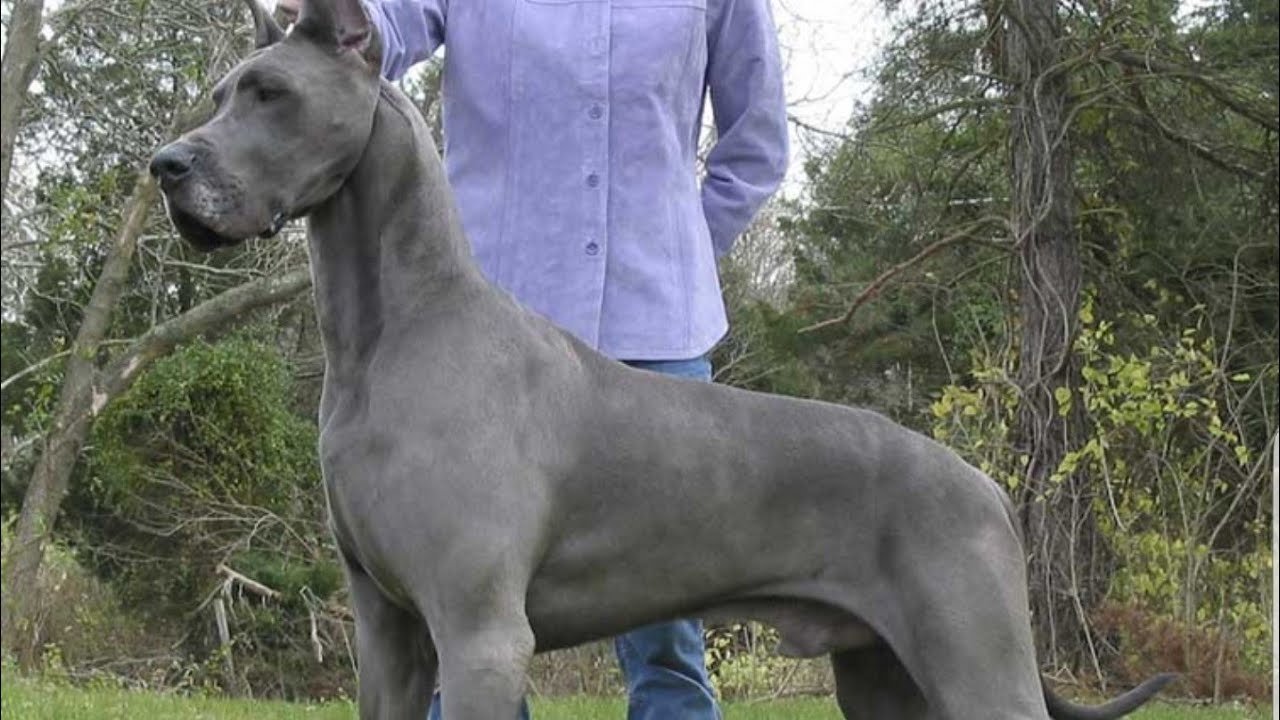


Giant Breeds
Leptospirosis in Dogs: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention

What is Leptospirosis?

Leptospirosis in Dogs: is a bacterial infection caused by Leptospira bacteria, which can affect both dogs and humans. It is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can spread between animals and humans. The bacteria thrive in warm, moist environments, particularly in stagnant water, making it a common concern in tropical and subtropical regions.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
Causes of Leptospirosis in Dogs

Dogs contract leptospirosis through direct or indirect contact with infected urine, water, or soil. The most common ways dogs get infected include:
- Drinking or swimming in contaminated water (lakes, rivers, puddles)
- Contact with infected wildlife such as rats, raccoons, or farm animals
- Exposure to infected dogs or livestock
- Ingestion of contaminated food
- Open wounds or cuts that come into contact with infected surfaces
Symptoms of Leptospirosis in Dogs

Symptoms of leptospirosis vary depending on the severity of the infection. Some dogs may show mild signs, while others develop severe complications. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Muscle pain and stiffness
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Bleeding disorders (bloody vomit, urine, or stool)
- Respiratory distress
- Kidney or liver failure (in severe cases)
If left untreated, leptospirosis can be fatal, leading to severe organ damage and death.
Diagnosis of Leptospirosis in Dogs

To diagnose leptospirosis, veterinarians perform:
- Blood tests:
- To detect organ damage and infections.
- Urine tests:
- To identify bacterial presence.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) tests:
- To detect Leptospira DNA in blood or urine.
- Serology tests:
- To measure the presence of antibodies against Leptospira.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and preventing complications.
Treatment for Leptospirosis in Dogs

Treatment depends on the severity of the infection. Common approaches include:
- Antibiotics (Doxycycline or Penicillin):
- To kill the bacteria and prevent further spread.
- Intravenous (IV) fluids:
- To prevent dehydration and support kidney function.
- Pain relief and anti-nausea medications:
- To manage symptoms.
- Hospitalization:
- Required in severe cases where dogs develop kidney or liver damage.
With prompt medical intervention, many dogs recover fully from leptospirosis.
Preventing Leptospirosis in Dogs

Preventing leptospirosis is crucial for your dog’s health. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Vaccination:
- Leptospirosis vaccines are available and recommended for at-risk dogs.
- Annual booster shots are necessary for continued protection.
- Avoid Stagnant Water:
- Prevent your dog from drinking, swimming, or playing in unknown water sources.
- Rodent Control:
- Keep your environment free of rodents, which are primary carriers of leptospirosis.
- Proper Hygiene:
- Clean up urine and feces in the home or kennel promptly.
- Avoid contact with wildlife urine.
- Limit Exposure to Infected Animals:
- Keep your dog away from unknown or sick animals.
Leptospirosis Vaccination by Country

| Country | Vaccine Name | Frequency | Recommended Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Nobivac Lepto 4 | Annually | 8-12 weeks, booster after 3-4 weeks |
| Canada | Vanguard L4 | Annually | 8-12 weeks, booster after 3-4 weeks |
| UK | Nobivac L4 | Annually | 8-12 weeks, booster after 4 weeks |
| Australia | Protech Lepto | Annually | 6-12 weeks, booster after 4 weeks |
| Germany | Eurican Lmulti | Annually | 8-12 weeks, booster after 3-4 weeks |
| France | Canigen L4 | Annually | 8-12 weeks, booster after 3-4 weeks |
| India | Biocan L | Annually | 6-8 weeks, booster after 3-4 weeks |
| Japan | Duramune Lepto | Annually | 8-12 weeks, booster after 3-4 weeks |
| Brazil | Recombitek 4 Lepto | Annually | 8-12 weeks, booster after 3-4 weeks |
| South Africa | Leptoferm C | Annually | 8-12 weeks, booster after 3-4 weeks |
Breeds More Susceptible to Leptospirosis

Some dog breeds are at a higher risk of contracting leptospirosis due to their environment, size, and lifestyle. The following table highlights these breeds and the reasons they are more vulnerable:
| Breed | Reason for Higher Risk |
| Labrador Retriever | Frequent exposure to water and outdoor activities |
| Golden Retriever | Often found in wet, wooded, or rural areas |
| German Shepherd | Active lifestyle, exposure to farms and working environments |
| Rottweiler | High outdoor activity, strong prey drive leading to interaction with wildlife |
| Beagle | Hunting instincts increase contact with contaminated areas |
| Boxer | Prone to outdoor play, especially in damp environments |
| Doberman Pinscher | Active dogs that may frequently roam outside |
| Cocker Spaniel | Enjoys water-based activities, increasing exposure risk |
| Dachshund | Low body height makes them more likely to ingest contaminated water |
| Siberian Husky | Outdoor and working lifestyle increases exposure |
Veterinarian–Recommended Supplements by Breed

| Breed | Recommended Supplements |
| Labrador Retriever | Omega-3,
|
| German Shepherd | Hip & Joint Supplements, Probiotics,
|
| Golden Retriever | Omega-3,Joint Care
|
| Rottweiler | Calcium,Hip & Joint Support
|
| Beagle | Probiotics,
|
| Boxer | Taurine (for heart health),
|
| Doberman Pinscher | Coenzyme Q10,
|
| Cocker Spaniel | Skin & Coat Supplements,
|
| Dachshund | Joint Supplements, Calcium, Omega-3 |
| Siberian Husky | Fish Oil,
|
Can Humans Get Leptospirosis from Dogs?

Yes, leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can spread from dogs to humans. People can contract the infection through:
- Direct contact with infected dog urine
- Contaminated water or soil exposure
- Open wounds or mucous membrane contact with the bacteria
In humans, leptospirosis causes flu-like symptoms, kidney or liver damage, and, in severe cases, meningitis. Proper hygiene, vaccination, and timely treatment can reduce risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can leptospirosis be transmitted to humans?
Yes, leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease, meaning humans can contract it from infected animals, particularly through urine or contaminated water.
2. Is leptospirosis common in urban areas?
While more common in rural and tropical regions, urban dogs are still at risk due to exposure to rodents and contaminated water.
3. How effective is the leptospirosis vaccine?
The vaccine significantly reduces the risk of infection but does not provide 100% immunity. Annual boosters are essential for maintaining protection.
4. Can a dog recover from leptospirosis?
Yes, with early diagnosis and treatment, many dogs recover. However, severe cases may result in permanent organ damage or death.
5. What should I do if my dog has been exposed to leptospirosis?
Contact your vet immediately. Early treatment with antibiotics can prevent severe illness.
6. How can I protect my dog from leptospirosis if I live in a high-risk area?
Ensure your dog is vaccinated, avoid stagnant water, and maintain good hygiene. Controlling rodent populations also helps.
7. Can puppies get leptospirosis?
Yes, puppies can contract leptospirosis, especially if not vaccinated. It’s crucial to follow the recommended vaccination schedule.
8. How long does leptospirosis survive in the environment?
Leptospira bacteria can survive in moist conditions for weeks to months, making proper prevention essential.
Closing Statement
Leptospirosis is a serious bacterial infection that can affect dogs and humans. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for keeping your dog safe. Vaccination, proper hygiene, and avoiding contaminated environments are key preventive measures. If you suspect your dog has leptospirosis, seek immediate veterinary care to ensure a swift and successful recovery.
For more expert pet care tips, visit DogsReader and follow us on our social media channels!
📩 Contact us at www.dogsreader.com
📢 Follow us on Facebook, youtube & Instagram @dogsreader for the latest updates!
Giant Breeds
Cancer in Dogs: Causes, Symptoms, and Latest Research

A Guide for Puppies, Adults, and Senior Dogs
Cancer in dogs: is one of the leading causes of death in dogs, affecting pets of all ages, though it is more common in older dogs. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for cancer is essential for early detection and effective management. This comprehensive guide covers cancer in dogs across all life stages, including puppies, adult dogs, and senior dogs, and explores the latest research to help you protect your furry friend.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
What is Cancer in Dogs?

Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. It can affect any organ or tissue and may spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Common types of cancer in dogs include:
- Lymphoma: Affects the lymph nodes and immune system.
- Mast Cell Tumors: Skin cancer often found in older dogs.
- Osteosarcoma: Bone cancer, common in large breeds.
- Hemangiosarcoma: Cancer of the blood vessels, often affecting the spleen or heart.
- Mammary Gland Tumors: Common in unspayed female dogs.
Most Common Types of Cancer in Dogs

- Lymphoma:
- Affects the lymphatic system.
- Symptoms: Swollen lymph nodes, lethargy, weight loss.
- Common in breeds like Golden Retrievers and Boxers.
-
Mast Cell Tumors:
- A type of skin cancer.
- Symptoms: Lumps or bumps on the skin, redness, itching.
- Common in breeds like Boxers, Bulldogs, and Boston Terriers.
-
Osteosarcoma:
- Bone cancer, often affecting the legs.
- Symptoms: Lameness, swelling, pain.
- Common in large breeds like Great Danes and Rottweilers.
-
Hemangiosarcoma:
- Cancer of the blood vessels, often affecting the spleen or heart.
- Symptoms: Weakness, collapse, pale gums.
- Common in breeds like German Shepherds and Golden Retrievers.
-
Mammary Gland Tumors:
- Affects unspayed female dogs.
- Symptoms: Lumps in the mammary area, swelling, discharge.
- Common in breeds like Poodles and Dachshunds.
Causes of Cancer in Dogs

The exact cause of cancer is often unknown, but several factors can increase the risk:
- Genetics: Certain breeds are more prone to specific cancers.
- Age: Older dogs are at higher risk.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins, pesticides, or secondhand smoke.
- Diet and Obesity: Poor nutrition and excess weight can contribute to cancer risk.
- Hormonal Factors: Unspayed females have a higher risk of mammary tumors.
Cancer in Different Age Groups

1. Puppies
- Rare but Possible: Cancer in puppies is uncommon but can occur, often due to genetic factors.
- Common Types: Lymphoma, bone cancer (osteosarcoma).
- Symptoms: Lumps, swelling, lethargy, or unexplained pain.
2. Adult Dogs
- Moderate Risk: Adult dogs (ages 4-7) can develop cancer, especially if predisposed by breed or genetics.
- Common Types: Mast cell tumors, lymphoma, and skin cancers.
- Symptoms: Lumps, changes in appetite, weight loss, or persistent sores.
3. Senior Dogs
- Highest Risk: Dogs over 10 years old are most susceptible to cancer.
- Common Types: Hemangiosarcoma, mammary tumors, and osteosarcoma.
- Symptoms: Lethargy, difficulty breathing, lameness, or sudden collapse.
Symptoms of Cancer in Dogs

- Lumps or Bumps: Unusual growths on the skin or under the surface.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained or rapid weight loss.
- Lethargy: Lack of energy or enthusiasm.
- Changes in Appetite: Refusal to eat or increased hunger.
- Persistent Sores: Wounds that do not heal.
- Difficulty Breathing: Coughing or labored breathing.
- Lameness or Swelling: Especially in the legs or joints.
Latest Research on Canine Cancer

Genetic Studies:
-
- Research has identified genetic markers for certain cancers in breeds like Golden Retrievers and Boxers.
- Reference: Journal of Veterinary Oncology, 2022.
Immunotherapy:
-
- New treatments like cancer vaccines and immune checkpoint inhibitors are showing promise in treating lymphoma and melanoma.
- Reference: Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 2023.
Early Detection Tools:
-
- Liquid biopsies (blood tests) are being developed to detect cancer earlier and monitor treatment progress.
- Reference: Veterinary Cancer Society, 2023.
Diet and Cancer Prevention:
-
- Studies suggest that diets rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids may reduce cancer risk.
- Reference: American Journal of Veterinary Research, 2022.
Treatment Options for Canine Cancer

- Surgery: Removal of tumors when possible.
- Chemotherapy: Used to shrink or slow the growth of cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Targets specific areas to destroy cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
- Palliative Care: Focuses on improving quality of life for dogs with advanced cancer.
Table 1: Supplements to Prevent Cancer in Dogs

This table outlines supplements that can help reduce the risk of cancer in dogs, categorized by age group and specific needs. Always consult your veterinarian before introducing new supplements.
Table 2: How to Use Supplements for Dogs

This table provides detailed instructions on how to administer supplements to dogs based on their age and specific needs.
| Supplement | How to Use | Age Group |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Add fish oil or flaxseed oil to food. Use dosage based on weight (consult your vet). | Puppies, Adults, Seniors |
| Antioxidants (Vitamin C, E) | Give chewable tablets or liquid form. Follow dosage instructions on the label. | Puppies, Adults, Seniors |
| Probiotics | Mix powder or liquid form into food daily. Follow dosage instructions on the label. | Puppies, Adults, Seniors |
| Turmeric (Curcumin) | Mix turmeric powder into food. Use dosage based on weight (consult your vet). | Adults, Seniors |
| Mushroom Extracts (Reishi, Shiitake) | Use capsules or powder. Mix into food or water. Follow vet-recommended dosage. | Adults, Seniors |
| Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) | Give chewable tablets or capsules. Follow dosage instructions on the label. | Seniors |
| Vitamin E for Dogs, Promote Cardiovascular Health, | Use liquid drops or capsules. Mix into food or water. Follow vet-recommended dosage. | Adults, Seniors |
| Colostrum | Add powder to food daily. Use dosage based on weight (consult your vet). | Puppies, Adults |
| Glucosamine and Chondroitin | Give chewable tablets or capsules. Follow dosage instructions on the label. | Seniors |
| Milk Thistle | Use liquid drops or capsules. Mix into food or water. Follow vet-recommended dosage. | Adults, Seniors |
Key Notes for Using Supplements

- Consult Your Vet:
Always check with your veterinarian before starting any supplements, especially for puppies and senior dogs.
-
Dosage:
Follow the recommended dosage based on your dog’s weight and age. Over-supplementation can be harmful.
-
Monitor for Reactions:
Watch for any adverse reactions like vomiting, diarrhea, or lethargy.
-
Combine with a Healthy Lifestyle:
Supplements should complement a balanced diet, regular exercise, and routine vet check-ups.
Prevention of Cancer in Dogs

- Regular Vet Check-Ups: Early detection is key.
- Healthy Diet: Feed a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3s.
- Spaying/Neutering: Reduces the risk of mammary and testicular cancers.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit exposure to pesticides, herbicides, and secondhand smoke.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is linked to increased cancer risk.
How Dangerous is Cancer in Dogs?

Cancer can be life-threatening, especially if not detected early. However, many types of cancer are treatable, and early intervention can significantly improve outcomes. Senior dogs are at the highest risk, with cancer being a leading cause of death in older pets.
Closing Statement

Cancer is a serious but manageable condition in dogs. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to protect your puppy, adult dog, or senior pup. Regular vet visits, a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed about the latest research are key to ensuring your dog’s long-term health and well-being.
(FAQs) About Cancer in Dogs

Below are detailed answers to common questions about cancer in dogs, including causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options.
1. What is cancer in dogs?
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. It can affect any organ or tissue and may spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Common types include lymphoma, mast cell tumors, and osteosarcoma.
2. What are the most common types of cancer in dogs?
- Lymphoma: Affects the lymph nodes and immune system.
- Mast Cell Tumors: Skin cancer often found in older dogs.
- Osteosarcoma: Bone cancer, common in large breeds.
- Hemangiosarcoma: Cancer of the blood vessels, often affecting the spleen or heart.
- Mammary Gland Tumors: Common in unspayed female dogs.
3. What causes cancer in dogs?
The exact cause is often unknown, but risk factors include:
- Genetics (certain breeds are more prone).
- Age (older dogs are at higher risk).
- Environmental factors (exposure to toxins, pesticides, or secondhand smoke).
- Diet and obesity.
- Hormonal factors (e.g., unspayed females have a higher risk of mammary tumors).
4. What are the symptoms of cancer in dogs?
- Lumps or bumps on the skin or under the surface.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Lethargy or lack of energy.
- Changes in appetite.
- Persistent sores or wounds that do not heal.
- Difficulty breathing or coughing.
- Lameness or swelling in the legs or joints.
5. Are certain breeds more prone to cancer?
Yes, some breeds are more susceptible:
- Golden Retrievers: Lymphoma and hemangiosarcoma.
- Boxers: Mast cell tumors.
- Great Danes: Osteosarcoma.
- German Shepherds: Hemangiosarcoma.
6. How is cancer diagnosed in dogs?
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical examination.
- Blood tests.
- Imaging (X-rays, ultrasounds).
- Biopsy of the affected tissue.
7. Can cancer in dogs be cured?
Some types of cancer can be cured if detected early and treated aggressively. Others can be managed to improve quality of life and extend survival time.
8. What are the treatment options for cancer in dogs?
- Surgery: Removal of tumors.
- Chemotherapy: To shrink or slow the growth of cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Targets specific areas to destroy cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
- Palliative Care: Focuses on improving quality of life for dogs with advanced cancer.
9. How can I prevent cancer in my dog?
- Regular vet check-ups for early detection.
- Feed a balanced, high-quality diet.
- Spay or neuter your dog to reduce the risk of mammary and testicular cancers.
- Avoid exposure to toxins (e.g., pesticides, secondhand smoke).
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
10. Are there supplements to help prevent cancer in dogs?
Yes, supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric (curcumin), mushroom extracts, and antioxidants (vitamin C, E) may help reduce cancer risk. Always consult your vet before starting supplements.
11. Can puppies get cancer?
Yes, though rare, puppies can develop cancer, often due to genetic factors. Common types include lymphoma and osteosarcoma.
12. Is cancer more common in senior dogs?
Yes, cancer is more common in dogs over 10 years old. Senior dogs are at higher risk due to weakened immune systems and age-related changes.
13. What are the signs of advanced cancer in dogs?
- Severe weight loss.
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- Persistent pain or discomfort.
- Lethargy and refusal to eat.
- Visible tumors or swelling.
14. Can diet play a role in preventing cancer in dogs?
Yes, a diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and low in processed foods may help reduce cancer risk. Avoid feeding raw or undercooked meat, which can carry harmful bacteria.
15. Are there natural remedies for cancer in dogs?
Some natural remedies, like turmeric, mushroom extracts, and CBD oil, may help manage symptoms or support treatment. However, they should not replace veterinary care. Always consult your vet before using natural remedies.
16. How long can a dog live with cancer?
Survival time depends on the type of cancer, stage, and treatment. Some dogs live for years with proper treatment, while others may only survive a few months.
17. Is cancer painful for dogs?
Cancer can be painful, especially if it affects bones or internal organs. Pain management is an important part of treatment.
18. Can I use human cancer treatments for my dog?
No, human treatments are not safe for dogs. Always use treatments prescribed by your veterinarian.
19. What is the cost of cancer treatment for dogs?
Costs vary widely depending on the type of cancer and treatment. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation can range from 1,000to10,000 or more.
20. When should I consider euthanasia for my dog with cancer?
Consider euthanasia if your dog:
- Is in unmanageable pain.
- Has a poor quality of life (e.g., unable to eat, drink, or move).
- No longer responds to treatment.
Discuss this difficult decision with your veterinarian.

Giant Breeds
Bordetella in Dogs: Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment

Understand the Topic

Bordetella in Dogs, commonly referred to as “kennel cough,” is a highly contagious respiratory disease that affects dogs of all ages and breeds. Caused by the bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica, this condition is a significant concern for dog owners, especially those who frequently board their pets, visit dog parks, or engage in activities where dogs interact closely. While Bordetella is rarely life-threatening, it can lead to discomfort and secondary infections if left untreated. This article explores the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of Bordetella in dogs.
Types of Bordetella Bacteria
| Bordetella Species | Primary Host | Disease Caused | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bordetella bronchiseptica | Dogs, cats, rabbits, pigs, and other mammals | Kennel cough (Canine Infectious Tracheobronchitis) | Coughing, sneezing, nasal discharge, difficulty breathing |
| Bordetella pertussis | Humans | Whooping cough | Severe coughing fits, vomiting after coughing, difficulty breathing |
| Bordetella parapertussis | Humans, sheep | Milder form of whooping cough | Persistent cough, mild respiratory symptoms |
| Bordetella avium | Birds (especially turkeys) | Avian bordetellosis (Turkey Coryza) | Sneezing, nasal discharge, swollen sinuses, respiratory distress |
Key Facts About Bordetella in Dogs:
-
Bordetella bronchiseptica is the most common type affecting dogs.
-
It spreads through airborne droplets, contaminated surfaces, and direct contact with infected animals.
-
Vaccination is the best preventive measure, along with good hygiene and immune-boosting supplements.
Annual Dog Vaccination Guide (Including Bordetella in Dogs)
| Age Group | Core Vaccines | Non-Core Vaccines (Based on Risk) |
| Puppies (Under 1 Year) |
Distemper, Parvovirus, Adenovirus, Rabies |
Bordetella, Lyme, Leptospirosis, Canine Influenza |
| Adult Dogs (1-7 Years) |
Rabies (as required by law), Distemper, Parvovirus, Adenovirus |
Bordetella (yearly booster), Lyme (if at risk), Leptospirosis, Canine Influenza |
| Senior Dogs (7+ Years) | Rabies (as required by law),
Distemper, Parvovirus |
Bordetella (booster if social), Lyme (booster based on exposure), Leptospirosis, Canine Influenza |
Preventive Supplements for Bordetella Click Any Picture to Buy from Amazon

| Age Group | Recommended Supplements | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Puppies
(8 weeks) ( 1- year) |
Probiotics( Purina FortiFlora),
|
Boosts immune system, supports gut health, and enhances resistance to infections | Puppies should also receive Bordetella vaccination as a primary prevention |
| Adult Dogs (1 – 7 years) |
Elderberry extract (dog-safe),
|
Strengthens respiratory health, reduces inflammation, and supports immunity | Regular vet check-ups and vaccinations are crucial for preventing Bordetella |
| Senior Dogs (7+ years) |
Glucosamine with immune boosters,
|
Enhances immune function, supports lung health, and helps with age-related immunity decline | Older dogs may require extra respiratory care and routine vet monitoring |
Additional Preventive Measures:
-
Vaccination: Bordetella vaccine (oral, nasal, or injectable) is the best prevention.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced, nutrient-rich diet enhances natural immunity.
-
Clean Environment: Avoid exposure to crowded dog areas if the dog is not vaccinated.
-
Hydration: Adequate water intake prevents dry throat irritation.
How to Use Preventive Supplements for Bordetella in Dogs

| Age Group | Supplement | Dosage & Usage | Frequency | Administration Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Puppies (8 weeks – 1 year) | Probiotics (e.g., Purina FortiFlora) | 1 sachet or as per brand guidelines | Daily | Mix with food |
| Colostrum supplements | ¼ – ½ tsp powder or per vet recommendation | Daily | Sprinkle over food or mix with water | |
| Vitamin C | 50 – 100 mg | Once daily | Mix with food or use a chewable tablet | |
| Echinacea (Dog-safe) | 5 – 10 mg per lb of body weight | Once daily | Liquid drops in food/water or capsule | |
| Adult Dogs (1 – 7 years) | Omega-3 (Fish Oil) | 250 – 500 mg | Daily | Mix oil with food or use capsules |
| Elderberry extract (Dog-safe) | 5 – 10 mg per lb of body weight | Once daily | Liquid drops in food | |
| Vitamin C & E | 100 – 250 mg Vitamin C, 10-20 IU Vitamin E | Daily | Given with meals | |
| Probiotics | 1 capsule or as per brand | Daily | Mix with food | |
| L-lysine | 250 – 500 mg | Daily | Crush tablets into food | |
| Senior Dogs (7+ years) | Glucosamine with immune boosters | 500 – 1000 mg | Daily | Chewable tablets or powder in food |
| Spirulina | 100 – 200 mg | Daily | Powder mixed into food | |
| Mushroom blend supplements | Per brand recommendation | Daily | Powder or capsule with food | |
| Zinc & Vitamin E | 10 – 20 mg Zinc, 20 IU Vitamin E | Daily | Given with food |
Additional Tips for Supplement Usage:
Always consult your vet before adding supplements to your dog’s diet.
Start with a low dose and gradually increase if needed.
Use high-quality, dog-safe supplements.
Avoid over-supplementation, as excess vitamins/minerals can cause health issues.
For more information regarding 4 seasonal cxcercieses of all dog breeds recommended by the doctors and experts,you can visit our youtube channel:
What Causes Bordetella in Dogs?

Bordetella is primarily caused by the bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica, but it often occurs in conjunction with other pathogens, such as canine parainfluenza virus or canine adenovirus. The disease spreads through airborne droplets when an infected dog coughs or sneezes, as well as through direct contact with contaminated surfaces like food bowls, toys, or bedding.
Dogs are most at risk in environments where they are in close proximity to other dogs, such as:
- Boarding kennels
- Doggy daycares
- Grooming salons
- Dog parks
- Shelters
Puppies, senior dogs, and those with weakened immune systems are particularly susceptible to infection.
Symptoms of Bordetella in Dogs

The most recognizable symptom of Bordetella is a persistent, dry, hacking cough, often described as a “honking” sound. Other symptoms may include:
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Watery eyes
- Mild fever
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
In severe cases, Bordetella can progress to pneumonia, especially in young puppies or immunocompromised dogs. If your dog exhibits difficulty breathing, a high fever, or a lack of energy, seek veterinary care immediately.
Preventing Bordetella in Dogs
Prevention is key to protecting your dog from Bordetella. Here are some effective strategies:
- Vaccination:
- The Bordetella vaccine is available in injectable, nasal, and oral forms. While it doesn’t guarantee complete immunity, it significantly reduces the severity of symptoms if your dog contracts the disease. Dogs that frequently interact with other dogs should be vaccinated every 6 to 12 months.
- Limit Exposure:
- Avoid exposing your dog to crowded or unsanitary environments, especially if they are unvaccinated or have a weakened immune system.
- Hygiene Practices:
- Regularly clean and disinfect your dog’s food and water bowls, toys, and bedding. If your dog has been in contact with other dogs, wash their paws and coat to reduce the risk of contamination.
- Isolate Infected Dogs:
- If your dog shows symptoms of Bordetella, keep them away from other dogs to prevent the spread of the disease.
- Treating Bordetella in Dogs
Most cases of Bordetella are mild and resolve on their own within 1 to 2 weeks. However, veterinary intervention may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment options include:
- Antibiotics:
- If a bacterial infection is present, your vet may prescribe antibiotics to target Bordetella bronchiseptica.
- Cough Suppressants:
- To ease your dog’s discomfort, cough suppressants may be recommended, but only under veterinary supervision.
- Supportive Care:
- Ensure your dog stays hydrated and well-rested. A humidifier or steam from a hot shower can help soothe irritated airways.
- Isolation and Rest:
- Keep your dog isolated from other pets and provide a calm, stress-free environment to aid recovery.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be required, particularly if pneumonia develops.
Closing Statement
Bordetella is a common but manageable condition in dogs. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, dog owners can take proactive steps to protect their furry companions. Vaccination, good hygiene, and minimizing exposure to high-risk environments are the best ways to reduce the likelihood of infection. If your dog shows signs of Bordetella, consult your veterinarian promptly to ensure a swift and full recovery. With proper care and attention, your dog can bounce back from this pesky respiratory infection and return to their happy, healthy self.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Bordetella in Dogs
Bordetella, or kennel cough, is a common but often misunderstood condition in dogs. To help dog owners better understand this respiratory infection, we’ve compiled a detailed list of frequently asked questions and answers.
1. What is Bordetella?
Bordetella is a highly contagious respiratory infection in dogs caused by the bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica. It is often associated with kennel cough, a term used to describe a range of infectious respiratory diseases in dogs.
2. How is Bordetella transmitted?
Bordetella spreads through:
- Airborne droplets: When an infected dog coughs or sneezes, the bacteria can become airborne and infect nearby dogs.
- Direct contact: Sharing toys, food bowls, or bedding with an infected dog.
- Contaminated surfaces: The bacteria can survive on surfaces for a short period, increasing the risk of transmission.
3. What are the symptoms of Bordetella in dogs?
The most common symptom is a persistent, dry, hacking cough that may sound like a “honk.” Other symptoms include:
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Watery eyes
- Mild fever
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
In severe cases, Bordetella can lead to pneumonia, especially in puppies or dogs with weakened immune systems.
4. Is Bordetella contagious to other animals or humans?
- Other dogs: Yes, Bordetella is highly contagious among dogs.
- Cats: In rare cases, Bordetella bronchiseptica can infect cats, particularly those with compromised immune systems.
- Humans: While extremely rare, there have been isolated cases of immunocompromised individuals contracting the bacteria. However, the risk to humans is minimal.
5. How is Bordetella diagnosed?
A veterinarian will typically diagnose Bordetella based on:
- Clinical signs (e.g., persistent cough)
- History of exposure (e.g., recent boarding or contact with other dogs)
- Physical examination
In some cases, additional tests, such as blood work, X-rays, or bacterial cultures, may be needed to rule out other conditions like pneumonia.
6. How is Bordetella treated?
Treatment depends on the severity of the infection:
- Mild cases: Often resolve on their own within 1-2 weeks. Rest and hydration are key.
- Moderate to severe cases: Antibiotics may be prescribed to target the bacteria, and cough suppressants can help ease discomfort.
- Supportive care: Using a humidifier or steam can soothe irritated airways.
Severe cases, especially those involving pneumonia, may require hospitalization.
7. Can Bordetella be prevented?
Yes, prevention is possible through:
- Vaccination: The Bordetella vaccine is available in injectable, nasal, and oral forms. It is recommended for dogs that frequently interact with other dogs.
- Good hygiene: Regularly clean and disinfect your dog’s belongings and avoid sharing items with other dogs.
- Limiting exposure: Avoid crowded or unsanitary environments, especially for unvaccinated or immunocompromised dogs.
8. How effective is the Bordetella vaccine?
The Bordetella vaccine is effective in reducing the severity and duration of symptoms but does not provide complete immunity. Dogs that are vaccinated may still contract the disease, but their symptoms are typically milder.
9. How often should my dog be vaccinated for Bordetella?
The frequency of vaccination depends on your dog’s lifestyle:
- High-risk dogs: Those frequently boarded, groomed, or visiting dog parks should be vaccinated every 6-12 months.
- Low-risk dogs: Dogs with minimal exposure to other dogs may not require frequent vaccination. Consult your veterinarian for a tailored recommendation.
10. Can my dog get Bordetella more than once?
Yes, dogs can contract Bordetella multiple times, as immunity from infection or vaccination is not lifelong. However, subsequent infections are often less severe.
11. Is Bordetella life-threatening?
In most cases, Bordetella is not life-threatening and resolves with proper care. However, complications like pneumonia can arise, particularly in puppies, senior dogs, or those with weakened immune systems. Prompt veterinary care is essential in such cases.
12. Can I board my dog if they have had Bordetella?
Most boarding facilities require dogs to be symptom-free and cleared by a veterinarian before returning. Even if your dog has recovered, they may still carry the bacteria for a short period, so it’s important to follow your vet’s advice.
13. How long does it take for Bordetella to go away?
Mild cases of Bordetella typically resolve within 1-2 weeks. With treatment, symptoms may improve within a few days. Severe cases, especially those involving pneumonia, may take longer to heal.
14. Can I walk my dog if they have Bordetella?
It’s best to limit your dog’s activity and avoid public areas until they have fully recovered. Rest is important for healing, and walking your dog could expose other dogs to the infection.
15. What should I do if my dog shows symptoms of Bordetella?
- Isolate your dog: Keep them away from other pets to prevent spreading the infection.
- Consult your veterinarian: They can confirm the diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment.
- Provide supportive care: Ensure your dog stays hydrated, rested, and comfortable.
16. Are certain dogs more at risk for Bordetella?
Yes, the following dogs are at higher risk:
- Puppies and senior dogs
- Dogs with weakened immune systems
- Unvaccinated dogs
- Dogs in crowded or stressful environments (e.g., shelters, kennels)
17. Can Bordetella lead to other health problems?
If left untreated, Bordetella can progress to pneumonia or exacerbate existing respiratory conditions. Early treatment is crucial to prevent complications.
18. Is there a natural remedy for Bordetella?
While natural remedies like honey (in small amounts) can soothe a dog’s throat, they should not replace veterinary care. Always consult your vet before trying home remedies.
19. Can I get my dog vaccinated if they already have Bordetella?
Vaccination is not recommended for dogs currently infected with Bordetella. Wait until your dog has fully recovered before discussing vaccination with your vet.
20. How can I clean my home after my dog has had Bordetella?
Thoroughly clean and disinfect your dog’s belongings, including toys, bedding, and food bowls. Use a pet-safe disinfectant and wash any fabrics your dog has come into contact with.
By understanding Bordetella and taking preventive measures, you can help keep your dog healthy and reduce the risk of infection. If you have further questions or concerns, consult your veterinarian for personalized advice.
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months agoMerle Chihuahua: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months agoMaltese: A Beloved Companion
-

 Large Breeds4 months ago
Large Breeds4 months agoSamoyeds Hypoallergenic: Closer Look at the Breed
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months agoMerle Pomeranian: A Adorable Companion
-

 Large Breeds4 months ago
Large Breeds4 months agoStandard Poodle Weight: Country Wise
-

 MEDIUM BREEDS4 months ago
MEDIUM BREEDS4 months agoAmerican Water Spaniel Colors Chocolate In Crcols:
-

 SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months ago
SMALL DOG BREEDS5 months agoYorkshire Terrier: a Big Personality
-

 Terrier Breeds3 months ago
Terrier Breeds3 months agoDog Breeds: by Country & Category